Abstract
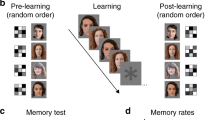
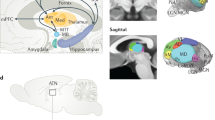
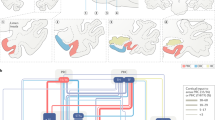
Circuits within the hippocampal formation are active during memory processing. Here we used functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) to examine multiple sites across the long axis of the hippocampal formation while subjects performed different phases of an associative memory task, learning to associate faces with names. Viewing faces and hearing names in isolation resulted in separate hippocampal activation patterns. Pairing faces with names resulted a spatially redistributed activation pattern, rather than a simple summation of the activation patterns resulting from viewing faces and hearing names in isolation. Recalling names when cued with faces reactivated a pattern similar to that found during paired training. Finally, the activation patterns representing faces and names were found to be experience dependent, emerging with repeated exposure. Interpreted in the context of hippocampal anatomy and physiology, these findings reveal hippocampal circuit mechanisms that underlie memory encoding and retrieval.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Squire, L. R. Memory and the hippocampus: a synthesis from findings with rats, monkeys, and humans. Psychol. Rev. 99, 195–231 (1992) [erratum, Psychol. Rev. 99, 582, 1992].
Colombo, M., Fernandez, T., Nakamura, K. & Gross, C. G. Functional differentiation along the anterior-posterior axis of the hippocampus in monkeys. J. Neurophysiol. 80, 1002–1005 (1998).
Moser, M. B. & Moser, E. I. Distributed encoding and retrieval of spatial memory in the hippocampus. J. Neurosci. 18, 7535–7542 (1998).
Amaral, D. G. Emerging principles of intrinsic hippocampal organization. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 3, 225–229 (1993).
Pare, D. & Llinas, R. Non-lamellar propagation of entorhinal influences in the hippocampal formation: multiple electrode recordings in the isolated guinea pig brain in vitro. Hippocampus 4, 403–409 (1994).
Eichenbaum, H., Mathews, P. & Cohen, N. J. Further studies of hippocampal representation during odor discrimination learning. Behav. Neurosci. 103, 1207–1216 (1989).
Vargha-Khadem, F. et al. Differential effects of early hippocampal pathology on episodic and semantic memory. Science 277, 376–380 (1997) [erratum, Science 277, 1117, 1997].
Kim, J. J. & Fanselow, M. S. Modality-specific retrograde amnesia of fear. Science 256, 675–677 (1992).
Rempel-Clower, N. L., Zola, S. M., Squire, L. R. & Amaral, D. G. Three cases of enduring memory impairment after bilateral damage limited to the hippocampal formation. J. Neurosci. 16, 5233–5255 (1996).
Debski, E. A., Cline, H. T. & Constantine-Paton, M. Activity-dependent tuning and the NMDA receptor. J. Neurobiol. 21, 18–32 (1990).
Marr, D. Simple memory: a theory for archicortex. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 262, 23–81 (1971).
Anderson, P., Bliss, T. V. & Skrede, K. K. Lamellar organization of hippocampal pathways. Exp. Brain Res. 13, 222–238 (1971).
Insausti, R., Amaral, D. G. & Cowan, W. M. The entorhinal cortex of the monkey: II. cortical afferents. J. Comp. Neurol. 264, 356–395 (1987).
Suzuki, W. A. & Amaral, D. G. Perirhinal and parahippocampal cortices of the macaque monkey: cortical afferents. J. Comp. Neurol. 350, 497–533 (1994).
Witter, M. P. & Amaral, D. G. Entorhinal cortex of the monkey: V. projections to the dentate gyrus, hippocampus, and subicular complex. J. Comp. Neurol. 307, 437–459 (1991).
Witter, M.P., Groenewegen, H.J. & Lopes da Silva, F.H, Lohman, A.H. Functional organizationof the extrinsic and intrinsic circuitry of the parahippocampal region. Prog. Neurobiol. 33 161–253 (1989)
Gustafsson, B., Wigstrom, H., Abraham, W. C. & Huang, Y. Y. Long-term potentiation in the hippocampus using depolarizing current pulses as the conditioning stimulus to single volley synaptic potentials. J. Neurosci. 7, 774–780 (1987).
Pavlidis, P., Montgomery, J. & Madison, D. V. Presynaptic protein kinase activity supports long-term potentiation at synapses between individual hippocampal neurons. J. Neurosci. 20, 4497–4505 (2000).
Kohonen, T. Associative Memory—A System-Theoretical Approach (Springer, Berlin, 1977).
McClelland, J. L. & Rumelhart, D. E. Distributed memory and the representation of general and specific information. J. Exp. Psychol. Gen. 114, 159–197 (1985).
Henke, K., Buck, A., Weber, B. & Wieser, H. G. Human hippocampus establishes associations in memory. Hippocampus 7, 249–256 (1997).
Schacter, D. L. & Wagner, A. D. Medial temporal lobe activations in fMRI and PET studies of episodic encoding and retrieval. Hippocampus 9, 7–24 (1999).
Lepage, M., Habib, R. & Tulving, E. Hippocampal PET activations of memory encoding and retrieval: the HIPER model. Hippocampus 8, 313–322 (1998).
Stern, C. E. et al. The hippocampal formation participates in novel picture encoding: evidence from functional magnetic resonance imaging. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 8660–8665 (1996).
Gabrieli, J. D. E., Brewer, J. B., Desmond, J. E. & Glover, G. H. Separate neural bases of two fundamental memory processes in the human medial temporal lobe. Science 276, 264–266 (1997).
Saykin, A. J. et al. Functional differentiation of medial temporal and frontal regions involved in processing novel and familiar words: an fMRI study. Brain 122, 1963–1971 (1999).
Kelley, W. M. et al. Hemispheric specialization in human dorsal frontal cortex and medial temporal lobe for verbal and nonverbal memory encoding. Neuron 20, 927–936 (1998).
Kirchhoff, B. A., Wagner, A. D., Maril, A. & Stern, C. E. Prefrontal-temporal circuitry for episodic encoding and subsequent memory. J. Neurosci. 20, 6173–6180 (2000).
Woods, R. P., Grafton, S. T., Watson, J. D., Sicotte, N. L. & Mazziotta, J. C. Automated image registration: II. Intersubject validation of linear and nonlinear models. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 22, 153–165 (1998).
Duvernoy, H. M. The Human Hippocampus; An Atlas of Applied Anatomy (J. F. Bergman, Munich, 1998).
Amaral, D. G. & Insausti, R. in The Human Nervous System (ed. Paxinos, R.) 711–755 (Academic, San Diego, 1990).
Acknowledgements
We thank B. Rakitin for his assistance in data analysis. This work was supported in part by federal grants AG08702 and AG00946, the Beeson Faculty Scholar Award from the American Federation of Aging and the Charles S. Robertson gift from the Banbury Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Small, S., Nava, A., Perera, G. et al. Circuit mechanisms underlying memory encoding and retrieval in the long axis of the hippocampal formation. Nat Neurosci 4, 442–449 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/86115
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/86115
This article is cited by
-
Graphomotor memory in Exner’s area enhances word learning in the blind
Communications Biology (2021)
-
Memory and cognition in schizophrenia
Molecular Psychiatry (2019)
-
Distinct hippocampal functional networks revealed by tractography-based parcellation
Brain Structure and Function (2016)
-
The influence of age and mild cognitive impairment on associative memory performance and underlying brain networks
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2015)
-
Postmortem examination of patient H.M.’s brain based on histological sectioning and digital 3D reconstruction
Nature Communications (2014)