Abstract
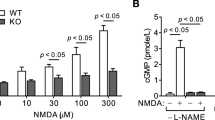
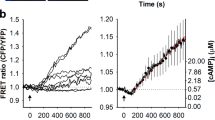
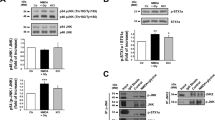
We found that K+/Cl− co-transporter 2 (KCC2) activity, monitored with wide-field fluorescence, was inhibited by intracellular Zn2+, a major component of neuronal injury. Zn2+-mediated KCC2 inhibition produced a depolarizing shift of GABAA reversal potentials in rat cortical neurons. Moreover, oxygen-glucose deprivation attenuated KCC2 activity in a Zn2+-dependent manner. The link between Zn2+ and KCC2 activity provides a previously unknown target for neuroprotection and may be important in activity-dependent regulation of inhibitory synaptic transmission.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Woo, N.S. et al. Hippocampus 12, 258–268 (2002).
Galeffi, F. et al. J. Neurosci. 24, 4478–4488 (2004).
Bonislawski, D.P., Schwarzbach, E.P. & Cohen, A.S. Neurobiol. Dis. 25, 163–169 (2007).
Papp, E. et al. Neuroscience 154, 677–689 (2008).
Weiss, J.H., Sensi, S.L. & Koh, J.Y. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 21, 395–401 (2000).
Lee, H. et al. Eur. J. Neurosci. 21, 2593–2599 (2005).
Galasso, S.L. & Dyck, R.H. Mol. Med. 13, 380–387 (2007).
Aizenman, E. et al. J. Neurochem. 75, 1878–1888 (2000).
Wake, H. et al. J. Neurosci. 27, 1642–1650 (2007).
Rivera, C. et al. J. Neurosci. 24, 4683–4691 (2004).
Blaesse, P. et al. J. Neurosci. 26, 10407–10419 (2006).
Vale, C., Schoorlemmer, J. & Sanes, D.H. J. Neurosci. 23, 7516–7524 (2003).
Buzsàki, G. et al. Exp. Brain Res. 78, 268–278 (1989).
Dietz, R.M., Weiss, J.H. & Shuttleworth, C.W. J. Neurosci. 28, 8014–8024 (2008).
Huang, Y.Z. et al. Neuron 57, 546–558 (2008).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Hartnett and M. Jefferson for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the US-Israel Binational Science Foundation (grant BSF2007121 to M.H. and E.A.) and the US National Institutes of Health (grants NS043277 to E.A. and DC004199 to K.K.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M.H., M.E.K., M.D.-R., M.A.A., C.A.-D. and E.A. performed, analyzed, and designed the experiments. I.S. and K.K. helped with experimental design and analysis. M.H., K.K., I.S. and E.A. wrote and/or edited the paper.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1 and 2 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 199 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hershfinkel, M., Kandler, K., Knoch, M. et al. Intracellular zinc inhibits KCC2 transporter activity. Nat Neurosci 12, 725–727 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2316
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nn.2316
This article is cited by
-
The K+–Cl− Cotransporter KCC2 and Chloride Homeostasis: Potential Therapeutic Target in Acute Central Nervous System Injury
Molecular Neurobiology (2016)
-
K-Cl cotransporter KCC2—a moonlighting protein in excitatory and inhibitory synapse development and function
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2015)
-
A role for intracellular zinc in glioma alteration of neuronal chloride equilibrium
Cell Death & Disease (2014)
-
New therapeutic targets in Alzheimer's disease: brain deregulation of calcium and zinc
Cell Death & Disease (2011)
-
Zinc in the physiology and pathology of the CNS
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2009)