Abstract
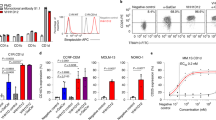
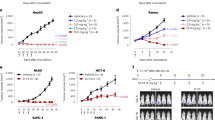
The Human Combinatorial Antibody Library (HuCAL) was screened for antibodies specific to human leukocyte antigen-DR (HLA-DR) that induce programmed death of lymphoma/leukemia cells expressing the target antigen. The active Fab fragments were affinity-matured, and engineered to IgG4 antibodies of sub-nanomolar affinity. The antibodies exhibited potent in vitro tumoricidal activity on several lymphoma and leukemia cell lines and on chronic lymphocytic leukemia patient samples. They were also active in vivo in xenograft models of non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell death occurred rapidly, without the need for exogenous immunological effector mechanisms, and was selective to activated/tumor-transformed cells. Although the expression of HLA-DR on normal hematopoietic cells is a potential safety concern, the antibodies caused no long-lasting hematological toxicity in primates, in vivo. Such monoclonal antibodies offer the potential for a novel therapeutic approach to lymphoid malignancies.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vose, J.M. et al. Phase II study of Rituximab in combination with CHOP chemotherapy in patients with previously untreated, aggressive non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 19, 389–397 (2001).
Dyer, M.J.S., Hale, G., Hayhoe, F.G.J. & Waldmann, H. Effects of CAMPATH-1 antibodies in vivo in patients with lymphoid malignancies: influence of antibody isotype. Blood 73, 1431–1439 (1989).
Tedder, T.F., Streuli, M., Schlossman, S.F. & Saito, H. Isolation and structure of a cDNA encoding the B1 (CD20) cell-surface antigen of human B lymphocytes. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. USA 85, 208–212 (1988).
Peiper, S.C., Ashmun, R.A. & Look, A.T. Molecular cloning, expression, and chromosomal localization of a human gene encoding the CD33 myeloid differentiation antigen. Blood 72, 314–321, (1988).
Kaufman, J.F., Auffray, C., Korman, A.J., Shackelford, D.A. & Strominger, J. The class II molecules of the human and murine major histocompatibility complex. Cell 36, 1–13 (1984).
Vaickus, L., Jones, V.E., Morton, C.L., Whitford, K. & Bacon, R.N. Antiproliferative mechanism of anti-class II monoclonal antibodies. Cell Immunol. 119, 445–458 (1989).
Kabelitz, D. & Janssen, O. Growth inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus transformed B cells by anti-HLA-DR antibody L243: Possible relationship to L243-induced down-regulation of CD23 antigen expression. Cell. Immunol. 120, 21–30 (1989).
Newell, M.K., VanderWall, J., Beard, K.S. & Freed, J.H. Ligation of major histocompatiblity complex class II molecules mediates apoptotic cell death in resting B lymphocytes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 10459–10463 (1993).
Truman, J.-P., Ericson, M.L., Choqueux-Seebold, J.M., Charron, D.J. & Mooney, N.A. Lymphocyte programmed cell death is mediated via HLA class II DR. Intl. Immunol. 6, 887–896 (1994).
Vidovic', D. & Toral, J. Selective apoptosis of neoplastic cells by the HLA-DR-specific monoclonal antibody. Cancer Lett. 128, 127–135 (1998).
Bridges, S.H., Kruisbeek, A.M. & Longo, D.L. Selective in vivo antitumor effects of monoclonal anti-I-A antibody on B cell lymphoma. J. Immunol. 139, 4242–4249 (1987).
Epstein, A.L. et al. Two new monoclonal antibodies, Lym-1 and Lym-2, reactive with human B-lymphocytes and derived tumors, with immunodiagnostic and immunotherapeutic potential. Cancer Res. 47, 830–840 (1987).
Gingrich, R.D., Dahle, C.E., Hoskins, K.F. & Senneff, M.J. Identification and characterization of a new surface membrane antigen found predominantly on malignant B lymphocytes. Blood 75, 2375–2387 (1990).
Yoshino, T. et al. Ligation of HLA class II molecules promotes sensitivity to CD95 (Fas antigen, APO-1)-mediated apoptosis. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 2190–2194 (1995).
Altomonte, M., Pucillo, C., Damante, G. & Maio, M. Cross-linking of HLA class II antigens modulates the release of tumor necrosis factor-α by the EBV-B lymphoblastoid cell line JY. J. Immunol. 151, 5115–5122 (1993).
Drenou, B. et al. A caspase-independent pathway of MHC class II antigen-mediated apoptosis of human B lymphocytes. J. Immunol. 163, 4115–4124 (1999).
Knappik, A. et al. Fully synthetic human combinatorial antibody libraries (HuCAL) based on modular consensus frameworks and CDRs randomized with trinucleotides. J. Mol. Biol. 296, 57–86 (2000).
Billing, R. & Chatterjee, S. Prolongation of skin allograft survival in monkeys treated with anti-Ia and anti-blast/monocyte monoclonal antibodies. Transplant. Proc. 15, 649–650 (1983).
Jonker, M., Nooij, F.J.M., den Butter, G., van Lambalgen, R. & Fuccello, A.J. Side effects and immunogenicity of murine lymphocyte-specific monoclonal antibodies in subhuman primates. Transplantation 45, 677–682 (1988).
Vidovic', D. et al. Down-regulation of class II major histocompatibility complex molecules on antigen presenting cells by antibody fragments. Eur. J. Immunol. 25, 3349–3355 (1995).
Ito, K. et al. HLA-DR-IE chimeric class II transgenic, murine class II-deficient mice are susceptible to experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. J. Exp. Med. 183, 2635–2644 (1996).
Krebs, B. et al. High-throughput generation and engineering of recombinant human antibodies. J. Immunol. Meth. 254, 67–84 (2001).
Marget, M. et al. Bypassing hybridoma technology: HLA-C reactive human single-chain antibody fragments (scFv) derived from a synthetic phage display library (HuCAL) and their potential to discriminate HLA class I specificities. Tissue Antigens 56, 1–9 (2000).
Schier, R. et al. Isolation of high-affinity monomeric human anti-c-erbB2 single chain Fv using affinity-driven selection. J. Mol. Biol. 255, 28–43 (1996).
Schier, R. et al. Isolation of picomolar affinity anti-c-erbB-2 single-chain Fv by molecular evolution of the complementarity determining regions in the center of the antibody binding site. J. Mol. Biol. 263, 551–567 (1996).
Ferreira, M.U. & Katzin, A.M. The assessment of antibody affinity distribution by thiocyanate elution: A simple dose-response approach. J. Imm. Meth. 187, 297–305 (1995).
Low, N.M., Holliger, P. & Winter, G. Mimicking somatic hypermutation: Affinity maturation of antibodies displayed on bacteriophage using a bacterial mutator strain. J. Mol. Biol. 260, 359–368 (1996)
Chen, Y. et al. Selection and analysis of an optimized anti-VEGF antibody: Crystal structure of an affinity-matured Fab in complex with antigen. J. Mol. Biol. 293, 865–881 (1999).
Buhmann, R., Nolte, A., Westhaus, D., Emmerich, B. & Hallek, M., CD40-activated B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells for tumor immunotherapy: Stimulation of allogeneic versus autologous T cells generates different types of effector cells. Blood 93, 1992–2002 (1999).
Hong, D.-S., et al. Major histocompatibility complex class II-mediated inhibition of hematopoiesis in long-term marrow cultures involves apoptosis and is prevented by c-kit ligand. Blood 86, 3341–3352 (1995).
Lee, J.W. et al. HLA-DR-triggered inhibition of hematopoiesis involves Fas/Fas ligand interactions and is prevented by c-kit ligand. J. Immunol. 159, 3211–3219 (1977).
DeNardo, S.J. et al. Treatment of B-cell malignancies with 131I Lym-1 monoclonal antibodies Int. J. Cancer Suppl. 3, 96–101 (1988).
Link, B.K. et al. Anti-CD3-based bispecific antibody designed for the therapy of human B-cell malignancy can induce T-cell activation by antigen-dependent and antigen-independent mechanisms. Int. J. Cancer 77, 251–256 (1998).
Gorga, J.C., Foran, J., Burakoff, S.J. & Strominger, J.L. Use of the HLA-DR antigens incorporated into liposomes to generate HLA-DR specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Meth. Enzymol. 108, 607–613 (1984).
Virnekäs, B. et al. E. Trinucleotide phosphoramidites: ideal reagents for the synthesis of mixed oligonucleotides for random mutagenesis. Nucl. Acids Res. 22, 5600–5607 (1994).
Acknowledgements
We thank K. Ito and M. Sandor for cell lines and antibodies; S. Messemer and L. Fontanelle for the xenograft experiments; and the entire team of technicians at MorphoSys AG for technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
It is a policy at GPC that every employee receives a stock option upon employment. All authors affiliated with GPC Biotech AG, or GPC Biotech Inc., namely, Z.A.N., S.L., E.M.S., A.Z., C.B., K.L., B.R., S.A. and M.D. are holders of GPC stock options. To date, these authors, except C.B., are GPC employees. Authors affiliated with Morphosys AG, namely, B.H. C.L., R.R., S.R., E.T.-W., T.K. and M.T. are employees of Morphosys AG and hold stock options of Morphosys. S.Z. was employed at Morphosys AG while engaged in this project.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagy, Z., Hubner, B., Löhning, C. et al. Fully human, HLA-DR-specific monoclonal antibodies efficiently induce programmed death of malignant lymphoid cells. Nat Med 8, 801–807 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1038/nm736
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nm736
This article is cited by
-
Soluble CD4 effectively prevents excessive TLR activation of resident macrophages in the onset of sepsis
Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy (2023)
-
STING: a master regulator in the cancer-immunity cycle
Molecular Cancer (2019)
-
A Review of Obinutuzumab (GA101), a Novel Type II Anti-CD20 Monoclonal Antibody, for the Treatment of Patients with B-Cell Malignancies
Advances in Therapy (2017)
-
Fibroblast Growth Factor Receptor-2 IIIc as a Novel Molecular Target in Colorectal Cancer
Current Colorectal Cancer Reports (2014)
-
Clinical safety and pharmacological profile of the HLA-DR antibody 1D09C3 in patients with B cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia and lymphoma: results from a phase I study
Cancer Immunology, Immunotherapy (2012)