Abstract
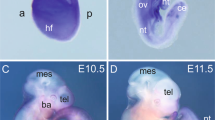
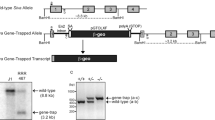
Tyrosine kinase growth factor receptors and Ras/Raf/MEK/MAPK signalling have been implicated in the suppression1–3 as well as augmentation of programmed cell death4. In addition, a Ras-independent role for Raf as a suppressor of programmed cell death has been suggested by the recent finding that Craf1 interacts with members of the Bcl-2 family at mitochondrial membranes5. However, genetic studies of C elegans6 and Drosophila7, as well as the targeted mutagenesis of the murine Araf gene8, have failed to support such a role. Here we show that mice with a targeted disruption in the Braf gene die of vascular defects during mid-gestation. Braf−/− embryos, unlike Araf−/−8 or Craf1−/− embryos (L.W. et al., unpublished), show an increased number of endothelial precursor cells, dramatically enlarged blood vessels and apoptotic death of differentiated endothelial cells. These results establish Braf as a critical signalling factor in the formation of the vascular system and provide the first genetic evidence for an essential role of a Raf gene in the regulation of programmed cell death.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Troppmair, J., Cleveland, J.L., Askew, D.S. & Rapp, U.R. v-Raf/v-Myc synergism in abrogation of IL-3 dependence: v-Raf suppresses apoptosis. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 182, 453–460 (1992).
Arends, M.J., McGregor, A.M., Toft, N.J., Brown, E.J. & Wyllie, A.M. Susceptibility to apoptosis is differentially regulated by c-myc and mutated Ha-ras oncogenes and is associated with endonuclease availability.Br. J. Cancer 68, 1127–1133 (1993).
Wyllie, A.M. et al. Rodent fibroblast tumours expressing human myc and ras genes: growth, metastasis and endogenous oncogene expression. Br. J. Cancer 56, 251–259 (1987).
Tanaka, N. et al. Cellular commitment to oncogene-induced transformation or apoptosis is dependent on the transcription factor IRF-1. Cell 77, 829–839 (1994).
Wang, H.-G., Rapp, U.R. & Reed, J.D. Bcl-2 targets the protein kinase Raf-1 to mitochondria. Cell 87, 629–638 (1996).
Man, M., Golden, A., Man, Y. & Sternberg, P.W. C elegans lin-45 raf gene participates in let-60 ras-stimulated vulval differentiation. Nature 363, 133–140 (1993).
Lu, X., Melnick, M.B., Hsu, J.C. & Perrimon, N. Genetic and molecular analyses of mutations involved in Drosophila raf signal transduction. EMBO J. 13, 2592–2599 (1994).
Pritchard, C.A., Bolin, L., Slattery, R., Murray, R. & McMahon, M. Post-natal lethality and neurological and gastrointestinal defects in mice with targeted disruption of the A-Raf protein kinase gene. Curr. Biol. 6, 614–617 (1996).
Vojtek, A.B., Hollenberg, S.M. & Cooper, J.A., Ras interacts directly with the serine/threonine kinase Raf. Cell 74, 205–214 (1993).
Barnier, J.V., Papin, C., Eychene, A., Lecoq, O. & Calothy, G. The mouse B-raf gene encodes multiple protein isoforms with tissue-specific expression. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 23381–23389 (1995).
Noden, D.M. Origins and assembly of avian embryonic blood vessels. Ann. N.Y. Acad. Sci. 588, 236–249 (1990).
Risau, W. Differentiation of endothelium. FASEB J. 9, 926–933 (1995).
Pardanaud, L., Yassine, F. & Dieterlen-Lievre, F. Relationship between vasculo-genesis, angiogenesis and haemopoiesis during avian ontogeny. Development 105, 473–85 (1989).
Puri, M.C., Rossant, J., Alitalo, K., Bernstein, A. & Partanen, J. The receptor tyrosine kinase TIE is required for integrity and survival of vascular endothelial cells. EMBO J. 14, 5884–5891 (1995).
Modak, S.P. & Bollum, F.J. Detection and measurement of single-strand breaks in nuclear DNA in fixed lens sections. Exp. Cell Res. 75, 307–313 (1972).
Sanders, E.J. & Wride, M.A. Programmed cell death in development. Int. Rev. Cytol. 163, 105–173 (1995).
Donehower, L.A. et al. Mice deficient for p53 are developmentally normal but asusceptible to spontaneous tumours. Nature 356, 215–221 (1992).
Suri, C. et al. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during angiogenesis. Cell 87, 1171–1180 (1996).
Dumont, D.J. et al. Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev. 8, 1897–1909 (1994).
Brooks, P.C. et al. Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79, 1157–1164 (1994).
Pawson, T. Regulation of the Ras signalling pathway by protein-tyrosine kinases. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 22, 455–460 (1994).
Reuter, C.W., Catling, A.D., Jelinek, T. & Weber, M.J. Biochemical analysis of MEK activation in NIH3T3 f ibroblasts. Identification of B-Raf and other activators. J. Biol. Chem. 270, 7644–7655 (1995).
Jaiswal, R.K., Moodie, S.A., Wolfman, A. & Landreth, G.E. The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade is activated by B-Raf in response to nerve growth factor through interaction with p21ras. Mol. Cell. Biol. 14, 6944–6953 (1994).
Pritchard, C.A., Samuels, M.L., Bosch, E. & McMahon, M. Conditionally oncogenic forms of the A-Raf and B-Raf protein kinases display different biological and biochemical properties in NIH 3T3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15, 6430–6442 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wojnowski, L., Zimmer, A., Beck, T. et al. Endothelial apoptosis in Braf-deficient mice. Nat Genet 16, 293–297 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0797-293
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ng0797-293
This article is cited by
-
Know Your Model: A knockout does not always make a null
Lab Animal (2020)
-
The impact of RASopathy-associated mutations on CNS development in mice and humans
Molecular Brain (2019)
-
Regulation of RAF protein kinases in ERK signalling
Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology (2015)
-
C-Raf deficiency leads to hearing loss and increased noise susceptibility
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2015)
-
Opioid Receptor Trafficking and Signaling: What Happens After Opioid Receptor Activation?
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2012)