Abstract
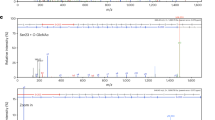
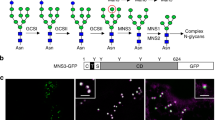
The secreted peptide gene CLAVATA3 (CLV3) regulates stem cell fate in the shoot apical meristem in Arabidopsis thaliana plants, but the molecular structure of the active mature CLV3 peptide is controversial. Here, using nano-LC-MS/MS analysis of apoplastic peptides of A. thaliana plants overexpressing CLV3, we show that CLV3 is a 13-amino-acid arabinosylated glycopeptide. Post-translational arabinosylation of CLV3 is critical for its biological activity and high-affinity binding to its receptor CLV1.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Clark, S.E., Williams, R.W. & Meyerowitz, E.M. Cell 89, 575–585 (1997).
Fletcher, J.C., Brand, U., Running, M.P., Simon, R. & Meyerowitz, E.M. Science 283, 1911–1914 (1999).
Fletcher, J.C. & Meyerowitz, E.M. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 3, 23–30 (2000).
Schoof, H. et al. Cell 100, 635–644 (2000).
Cock, J.M. & McCormick, S. Plant Physiol. 126, 939–942 (2001).
Ni, J. & Clark, S.E. Plant Physiol. 140, 726–733 (2006).
Fiers, M. et al. Plant Physiol. 141, 1284–1292 (2006).
Fiers, M. et al. Plant Cell 17, 2542–2553 (2005).
Kondo, T. et al. Science 313, 845–848 (2006).
Ogawa, M., Shinohara, H., Sakagami, Y. & Matsubayashi, Y. Science 319, 294 (2008).
Ohyama, K., Ogawa, M. & Matsubayashi, Y. Plant J. 55, 152–160 (2008).
Bollig, K. et al. Carbohydr. Res. 342, 2557–2566 (2007).
Ashford, D. et al. Biochem. J. 201, 199–208 (1982).
Akiyama, Y., Mori, M. & Kato, K. Agric. Biol. Chem. 44, 2487–2489 (1980).
Akiyama, Y. & Kato, K. Agric. Biol. Chem. 40, 2343–2348 (1976).
Seitz, O. ChemBioChem 1, 214–246 (2000).
Sassaki, G.L., Gorin, P.A., Souza, L.M., Czelusniak, P.A. & Iacomini, M. Carbohydr. Res. 340, 731–739 (2005).
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research for Priority Areas from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology (MEXT) (No. 19060010), a Grant-in-Aid for Young Scientists from MEXT (No. 18687003), a Grant-in-Aid for Creative Scientific Research from the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (No. 19GS0315) and the Program of Basic Research Activities for Innovative Biosciences from the Bio-oriented Technology Research Advancement Institution (BRAIN). We thank the Radioisotope Research Center of Nagoya University for instrumental support in radioisotope experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
K.O., H.S. and M.O.-O. performed and analyzed experiments. K.O. identified glycopeptides and performed bioassays. H.S. performed sugar linkage analysis and receptor binding assays. M.O.-O. generated transgenic plants. Y.M. designed, performed and analyzed experiments and prepared the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Supplementary information
Supplementary Text and Figures
Supplementary Figures 1–9 and Supplementary Methods (PDF 762 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohyama, K., Shinohara, H., Ogawa-Ohnishi, M. et al. A glycopeptide regulating stem cell fate in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Chem Biol 5, 578–580 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.182
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.182
This article is cited by
-
A Dof-CLE circuit controls phloem organization
Nature Plants (2022)
-
HSL1 and BAM1/2 impact epidermal cell development by sensing distinct signaling peptides
Nature Communications (2022)
-
SISTER OF TM3 activates FRUITFULL1 to regulate inflorescence branching in tomato
Horticulture Research (2021)
-
Predicting and clustering plant CLE genes with a new method developed specifically for short amino acid sequences
BMC Genomics (2020)
-
Production mechanisms, structural features and post-translational modifications of plant peptides
Journal of Plant Biology (2020)