Abstract
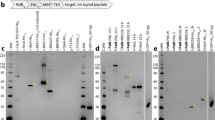
The surface antigen, P69 of Bordetella pertussis, an N-terminal fragment of the precursor protein, P93, is likely to be an important component of future subunit vaccines against whooping cough. We have expressed several defined N-terminal fragments of P93 in E. coli and compared their electrophoretic mobilities with that of purified P69 from B. pertussis. These experiments show that P69 is considerably smaller than the 69 kD originally estimated from its gel mobility and is probably 60.4 kD in size. Our initial plasmids expressed only very low levels of this antigen. We diagnosed the limiting factor to be a poor ribosome binding site (RBS) by demonstrating a large stimulation of expression on a two-cistron plasmid. The limitation of expression could be completely overcome by only two base changes close to the initiation codon, resulting in a further increase in expression of P69 at levels to 30–40% total cell protein. Although the protein accumulated as insoluble inclusion bodies, it could be solubilized by guanidinium chloride.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zeulzer, W.W. and Wheeler, W.E. 1946. Parapertussis pneumonia: report of two fatal cases. J. Pediatr. 9: 493–497.
Linneman, C. and Perry, E.B. 1977. Bordetella parapertussis: clinical and serological observations. J. Pediatr. 19: 229–240.
Pittman, M. 1984. Genus Bordetella, p. 388–393. In: Bergey's Manual of Systematic Bacteriology, Vol. 1. Krieg, N.R. and Holt, J.G. (Eds.) The Williams and Wilkins Co., Baltimore.
Arico, B., Miller, J.F., Roy, C., Stibitz, S., Monack, D., Falkow, S., Gross, R. and Rappuoli, R. 1989. Sequences required for expression of Bordetella pertussis virulence factors share homology with prokaryotic signal transduction proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86: 6671?6675.
Montaraz, J.A., Novotny, P. and Ivanyi, J. 1985. Identification of a 68-kilodalton protective protein antigen from Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect. Immun. 47: 744–751.
Kobisch, M. and Novotny, P. 1990. Identification of a 68-kilodalton outer membrane protein as the major protective antigen of Bordetella bronchiseptica by using specific-pathogen-free piglets. Infect. Immun. 58: 352–357.
Shahin, R.D., Brennan, M.J., Li, Z.M., Meade, B.D. and Manclark, C.R. 1990. Characterization of the protective capacity and immuno-genicity of the 69 kDa outer membrane protein of Bordetella pertussis. J. Exp. Med. 171: 63–73.
Charles, I.G., Dougan, G., Pickard, D., Chatfield, S., Smith, M., Novotny, P., Morrissey, P. and Fairweather, N.F. 1989. Molecular cloning and characterization of protective outer membrane protein P.69 from Bordetella pertussis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 86: 3554–3558.
Klapper, M.H. 1977. The independent distribution of amino acid near neighbor pairs into polypeptides. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 78: 1018–1024.
See, Y.S. and Jackowsky, G. 1989. SDS gel electrophoresis, p. 1–21. In: Protein Structure: A Practical Approach. Creighton, T. E. (Ed.) IRL Press, Oxford.
Thole, J.E.R., Stabel, L.F.E.M., Suykerbuyk, M.E.G., de Wit, P.R.K., Kolk, A.H.J. and Hartskeerl, R.A. 1990. A major immunogenic 36,000-molecular-weight antigen from Mycobacterium leprae contains an immunoreactive region of proline-rich repeats. Infect. Immun. 58: 80–87.
Docherty, K. and Steiner, D.F. 1982. Post-translational proteolysis in polypeptide hormone biosynthesis. Ann. Rev. Physiol. 44: 625–638.
Thomas, G., Thorne, B.A., Thomas, L., Allen, R.G., Hruby, D.E., Fuller, R. and Thorner, J. 1988. Yeast KEX2 endopeptidase correctly cleaves a neuroendocrine prohormone in mammalian cells. Science 241: 226–230.
Makoff, A.J. and Smallwood, A.E. 1990. The use of two-cistron constructions in improving the expression of a heterologous gene in E. coli. Nucl. Acids Res. 18: 1711–1718.
Schoner, B.E., Hsuing, H.N., Belagaje, R.M., Mayne, N.G. and Schoner, R.G. 1984. Role of mRNA translational efficiency in bovine growth hormone expression in Escherichia coli. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81: 5403–5407.
Spanjaard, R.A. and van Duin, J. 1989. Translational reinitiation in the presence and absence of a Shine and Dalgarno sequence. Nucl. Acids Res. 17: 5501–5507.
Makoff, A.J., Oxer, M.D., Romanos, M.A., Fairweather, N.F. and Ballantine, S.P. 1989. Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in E. coli: high level expression by removing rare codons. Nucl. Acids Res. 17: 10191–10202.
Cooper, A. and Bussey, H. 1989. Characterization of the yeast KEX1 gene product: a carboxypeptidase involved in processing secreted precursor proteins. Mol. Cell Biol. 9: 2706–2714.
Gold, L.M., Pribnow, D., Schneider, T., Shinedling, S., Singer, B.S. and Stormo, G. 1981. Translation initiation in prokaryotes. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 35: 365–403.
Hall, M.N., Gabay, J., Debarbouille, M. and Schwartz, M. 1982. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature 295: 616–618.
Iserentant, D. and Fiers, W. 1980. Secondary structure of mRNA and efficiency of translation initiation. Gene 9: 1–12.
Sor, F., Bolotin-Fukuhara, M. and Nomura, M. 1987. Mutational alterations of translational coupling in the L11 ribosomal protein operon of Escherichia coli. J. Bacteriol. 169: 3495–3507.
Ivey-Hoyle, M. and Steege, D.A. 1989. Translation of phage f1 gene VII occurs from an inherently defective initiation site made functional by coupling. J. Mol. Biol. 208: 233–244.
Makoff, A.J., Parry, N and Dicken, L.P. 1989. Translational fusions with fragments of the trpE gene improve the expression of a poorly expressed gene in Escherichia coli. J. Gen. Microbiol. 135: 11–24.
Makoff, A.J., Ballantine, S.P., Smallwood, A.E. and Fairweather, N.F. 1989. Expression of tetanus toxin fragment C in E. coli: its purification and potential use as a vaccine. Bio/Technology 7: 1043–1046.
Meselson, M. and Yuan, R. 1968. DNA restriction enzyme from E. coli. Nature 217: 1110–1114.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Makoff, A., Oxer, M., Ballantine, S. et al. Protective Surface Antigen P69 of Bordetella pertussis: Its Characterization and Very High Level Expression in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 8, 1030–1033 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1190-1030
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1190-1030