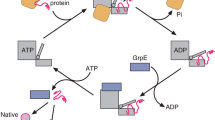
Abstract
The gene encoding the stress-inducible member of human heat shock protein hsp70, was expressed in E. coli using the bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase-based gene expression system. Recombinant hsp70 (R-hsp70) was purified from inclusion bodies after solubilization and refolding, using a combination of ATP-agarose affinity chromatography and ion-exchange chromatography. R-hsp70 was shown to be monomeric and free of its structurally similar E. coli counterpart, DnaK. In addition, R-hsp70 is functional as demonstrated by its ability to bind to peptides and to ATP. The availability of pure, correctly folded R-hsp70 in sufficient quantity will assist in the structural and functional characterization of hsp70. Furthermore, an understanding of the cytoprotective function of hsp70 and its role in immune responses during infections will be facilitated by the availablity of pure R-hsp70.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Morimoto, R.I., Tissieres, A. and Georgopoulos, C. 1994. The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY.
Frydman, J. and Hartl, F.-U. 1994. Molecular chaperone functions of hsp70 and hsp60 in protein folding, p. 251–283. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY.
Bardwell, J.C.A. and Craig, E.A. 1984. Major heat shock genes of Drosophilla and Eischerschia coli heat inducible dnaK gene are homologous. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81: 848–852.
Garcia, R.J., Hellqvist, L., Booth, R.J., Radford, A.J., Britton, W.J., Astbury, L., Trent, R.J. and Basten, A. 1989. Homology of the 70-kD antigens from Mycobacterium leprae and Mycobacterium bovis with the Mycobacterium tuberculosis 71 kD antigen and with the conserved heat shock protein 70 of eukaryotes. Infet. Immun. 57: 204–212.
McKay, D.B., Wilbanks, S.M., Flaherty, K.M., Ha, J.H., O'Brien, M.C. and Shirvanee, L.L. 1994. Stress-70 proteins and their interactions with nucleotides, p. 153–177. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY
Gething, M.-J. and Sambrook, J. 1992. Protein folding in the cell. Nature 355: 33–45.
Hightower, L.E., Sadis, S.E. and Tanaka, I.M. 1994. Interaction of vertebrate hsc 70 and hsp70 with unfolded proteins and peptides, p. 179–208. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY.
Flynn, G.C, Pohl, J., Folocco, M.T. and Rothman, J.E. 1991. Peptide-binding specificity of the molecular chaperone, BiP. Nature 353: 726–730.
Glick, B.S. 1995. Can hsp70 proteins act as force generating motors? Cell 80: 11–14.
Flaherty, K.M., DeLuca-Flaherty, C. and McKay, D.B. 1994. Three dimensional structure of ATP-ase fragment of a 70-kD heat shock cognate protein. Nature 346: 623–628.
Kabsch, W., Manhertz, H.G., Suck, D., Pai, E.F. and Holmes, K.C. 1990. Atomic structure of the actin: DNAase 1 complex. Nature 347: 37–44.
Flaherty, K.M., McKay, D.B., Kabsch, W. and Holmes, K.C. 1991. Similarity of the three dimensional structures of the actin and the ATP-ase fragment of a 70 kD heat shock cognate protein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 5041–5045.
Young, R.A. 1990. Stress proteins and immunology. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 8: 401–420.
Kaufmann, S.H.E. and Schoel, B. 1994 Heat shock proteins as antigens in immunity against infection and self, p. 495–531. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY.
Nadler, S.G., Tepper, M.A., Schacter, B. and Mazzuco, C.E. 1994. Interaction of immunosuppressant deoxyspergualin with a member of the hsp70 family of heat shock proteins Science 258: 484–486.
Delgiudice, G., Gervaix, A., Constntino, P., Wyler, C., Tougne, C., Del Graeff-Meeder, E.R., van Embden, J., Van der Zee, R., Nencioni, R., Rappuoli, R., Suter, S. and Lambert, P.H. 1993. Priming to heat shock proteins in infante vaccinated against pertussis. J. Immunol. 150: 2025–2032.
Barrios, C., Georgopoulos, G., Lambert, P.H. and Del-Giudice, G. 1994. Heat shock proteins as carrier molecules: in vivo helper effect mediated by E. coli Gro EL and DnaK proteins requires crosslinking with antigen. Clin. Expt. Immunol. 98: 229–233.
Benjamin, I.J. and Williams, S.R. 1994. Expression and functions of stress proteins in the ischemic heart, p. 533–552. In: The Biology of Heat Shock Proteins and Molecular Chaperones. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring, New York, NY.
Hunt, C. and Morimoto, R.I. 1985. Conserved features of eukaryotic hsp70 genes revealed by comparison with the nucleotide sequence of human hsp70. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82: 6455–6459.
Studier, F.W. and Moffatt, B.A. 1986. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA poly-merase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes J. Mol. Biol. 189: 113–118.
Welch, W.J. and Fermisco, J.R. 1985. Rapid purification of mammalian 70,000-Dalton stress proteins: affinity of the protyeins for nucleotides. Mol. Cell Biol. 5: 1229–1237.
Fourie, A.M., Sambrook, J.F. and Gething, M.-J. 1994. Common and divergent peptide binding specificities of hsp70 molecular chaperones. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 30470–30478.
Gragerov, A., Zeng, Li, Zhao, X., Burkholder, W. and Gottesman, M.E., Specificity of the DnaK-peptide binding. J. Mol. Biol. 235: 848–854.
Blond-Elguindi, S., Cwirla, S.E., Dower, S.E., Lipshutz, R.J., Sprang, S.R., Sambrook, J.F. and Gething, M.J.H. 1993. Affinity panning of a library of peptides displayed on bacteriophages reveals the binding specificities of Bip. Cell 75: 717–729.
Tytell, M., Barbe, M.F. and Brown, I.R. 1994. Induction of heat shock (stress protein) 70 and its mRNA in the normal and light damaged rat retina after whole body hyperthermia. J. Neurosci. Res. 38: 19–31.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jindal, S., Murray, P., Rosenberg, S. et al. Human Stress Protein hsp70: Overexpression in E. coli, Purification and Characterization. Nat Biotechnol 13, 1105–1109 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1095-1105
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1095-1105