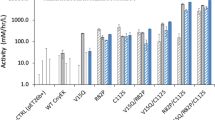
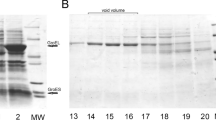
Abstract
We describe a novel approach to the production in E. coli of a peptide fragment derived from the human parathyroid hormone (hPTH). The first 38 amino acids of hPTH were fused at the amino terminus to a derivative of the bacteriophage T4–encoded gp55 protein, and were expressed in the E. coli cytoplasm in inclusion bodies at levels exceeding 50% of the total cell protein. Solubilization and subsequent incubation of the inclusion bodies in dilute hydrochloric acid facilitated the cleavage of an acid–labile aspartyl–prolyl peptide bond engineered into the fusion protein, thus releasing the hormone fragment directly from the inclusion body preparation. The ammo–terminal prolyl–prolyl dipeptide–extension was subsequently removed by treatment with Lactococcus lactis dipeptidyl peptidase IV which was overexpressed in E. coli and purified to near homogeneity from the cytosol of the recombinant bacteria. In pilot–scale fermentations, more than 80 mg of pure hPTH(1–38) were isolated per liter of bacterial culture, with an overall yield of 35%. This process is suitable for scale–up, is cost effective, and by employing recombinant dipeptidyl peptidase IV, should be widely and directly applicable to the manufacturing of peptides of pharmaceutical interest.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gottesmann, S. 1989. Genetics of proteolysis in Escherichia coli. Annu. Rev. Genet. 23: 163–198.
Ray, M.V.L., Duyne, P.V., Bertelsen, A.H., Jackson-Matthews, D.E., Sturmer, A.M., Merkler, D.J., Consalvo, A.P., Young, S.D., Gilligan, J.P. and Shields, P.P. 1993. Production of recombinant salmon calcitonin by in vitro amidation of an Escherichia coli produced precursor peptide. Bio/Technology 11: 64–70.
Moks, T., Abrahmsen, L., Oesterlöf, B., Josephson, S., Oesterling, M., Enfors, S., Persson, I., Nilsson, B. and Uhlen, M. 1987. Large-scale affinity purification of human insulin-like growth factor I from culture medium of Escherichia coli. Bio/Technology 5: 379–382.
Forsberg, G., Brobjer, M., Holmgren, E., Bergdahl, K., Persson, P., Gautvik, K. and Hartmanis, M. 1991. Thrombin and H64A subtilisin cleavage of fusion proteins for preparation of human recombinant parathyroid hormone. J. Protein Chemistry. 10: 517–526.
King, R., Wells, J.R.E., Krieg, P., Snoswell, M., Brazier, J., Bagley, C.J., Wallace, J.C., Ballard, F.J., Ross, M. and Francis, G.L. 1992. Production and characterization of recombinant insulin-like growth factor I (IGF-I) and potent analogues of IGF-I, with Gly or Arg substituted for Glu3, following their expression in Escherichia coli as fusion proteins. J. Mol. Endocrinology 8: 29–41.
Gardella, T.J., Rubin, D., Abou-Samra, A.B., Keutmann, H.T., Potts, J.T., Kronenberg, H.M. and Nussbaum, S. 1990. Expression of human parathyroid hormone (1–84) in Escherichia coli as a factor X-cleavable fusion protein. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 15854–15859.
Wingender, E., Bercz, G., Blöcker, H., Frank, R. and Meyer, H. 1989. Expression of human parathyroid hormone in Escherichia coli. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 4367–4373.
Gross, E. and Witkop, B. 1962. Nonenzymatic cleavage of peptide bonds: The methionine residues in bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. J. Biol. Chem. 237: 1856–1862.
Forsberg, G., Baastrup, B., Brobjer, M., Lake, M., Jörnvall, H. and Hartmanis, M. 1989. Comparison of two chemical cleavage methods for preparation of a truncated form of recombinant human insulin-like growth factor I from a secreted fusion protein. BioFactors 2: 105–112.
Landon, M.J. 1977. Cleavage at aspartyl-proline bonds. Methods in Enzymol. 47: 45–149.
Hock, J.M., Gera, I., Fonseca, J. and Raisz, L.G. 1988. Human parathyroid hormone (1–34) increases bone mass in ovariectomized and orchidectomized rats. Endocrinology 122: 2899–2904.
Hesch, R.D., Busch, U., Prokop, M., Delling, G. and Rittinghaus, E.F. 1989. Increase of vertebral density by combination therapy with pulsatile 1–38 hPTH and sequential addition of calcitonin nasal spray in osteoporotic patients. Calc. Tissue Int. 44: 176–180.
Gram, H. and Rüger, W. 1985. Genes 55, α-gt, 47 and 46 of bacteriophage T4: The genomic organization as deduced by sequence analysis. EMBO J. 4: 257–264.
Studier, W.F., Rosenberg, A.H., Dunn, J.J. and Dubendorff, J.W. 1990. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods in Enzymol. 185: 60–89.
Forrest, S.M., Ng, K.W., Findlay, D.M., Michelangeli, V.P., Livesey, S.A., Partridge, N.C., Zajac, J.D. and Martin, T.J. 1985. Characterization of an osteoblast-like cional cell line which responds to both parathyroid hormone and calcitonin. Calcif. Tissue Int. 37: 51–56.
Kikuchi, M., Fukuyama, K. and Epstein, W.L. 1988. Soluble dipeptidyl peptidase IV from terminal differentiated rat epidermal cells: purification and its activity on synthetic and natural peptides. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 266: 369–376.
Bauvois, B. 1988. A collagen-binding glycoprotein on the surface of mouse fibroblasts is identified as dipeptidyl peptidase IV. Biochem. J. 252: 723–731.
Svenson, B., Danielsen, M., Staun, M., Jeppesen, L., Noren, O. and Sjöström, H. 1978. An amphiphilic form of dipeptidyl peptidase IV from pig small-intestinal brush-border membrane. Eur. J. Biochem. 90: 489–498.
Yoshimoto, T. and Walter, R. 1977. Dipeptidyl aminopeptidase IV, a glycoprotein from pig kidney. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 535: 161–166.
Kojima, K., Kama, T., Kato, T. and Nagatsu, T. 1980. Rapid chromatographic purification of dipeptidyl peptidase IV in human submaxillary gland. J. Chromatogr. 189: 233–240.
Khalid, N.M. and Maith, E.H. 1990. Purification and partial characterization of a prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase from Lactobacillus helveticus CNRZ32. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 56: 381–388.
Grenier, D. and McBride, B.C. 1987. Isolation of a membrane-associated Bacteroides gingivalis glycylprolyl protease. Infect. Immun. 55: 3131–3136.
Mayo, B., Kok, J., Venema, K., Bockelmann, W., Teuber, M., Reinke, H. and Venema, G. 1991. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of the X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase gene Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 38–44.
Nardi, M., Chopin, M.C., Chopin, A., Cals, M.M. and Gripon, J.C. 1991. Cloning and DNA sequence analysis of an X-prolyl dipeptidyl aminopeptidase gene from Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis NCDO 763. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 45–50.
Miller, C.G. and McKinnon, S. 1974. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J. Bacteriol. 120: 355–363.
Gribben, J.G., Devereux, S., Thomas, N.S., Keim, M., Lones, H.M., Golstone, A.H. and Linch, D.C. 1990. Development of antibodies to unprotected glycosylation sites on recombinant human GM-CSF. Lancet 335: 434–437.
LaVallie, E.R., DiBlasio, E.A., Kovacic, S., Grant, K.L., Schendel, P.F. and McCoy, J. 1993. A thioredoxin gene fusion expression system that circumvents inclusion body formation in the E. coli cytoplasm. Bio/Technology 11: 187–193.
Daum, J., Donner, P., Geilen, W., Hübner-Kosney, G., Isernhagen, M., Scheidecker, H., Seliger, H., Boidol, W. and Siewert, G. 1989. Production of human adrenocorticotropin by cleavage of alkaline-phosphatase-derived fusion proteins containing repetitive recognition sequences for collagenases. Eur. J. Biochem. 185: 347–354.
Terzaghi, B.E. and Sandine, W.E. 1975. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl. Microbiol. 29: 807–813.
Leenhouts, K.J., Kok, J. and Venema, G. 1988. Campbell-like integration of heterologous plasmid DNA into the chromosome of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 394–400.
Lokker, N.A., Strittmatter, U., Steiner, C., Fagg, B., Graff, P., Kocher, H.P. and Zenke, G. 1991. Mapping the epitopes of neutralizing anti-human 11–3 monoclonal antibodies. Implications for structure-activity relationship. J. Immunology 146: 893–898.
Salomon, Y. 1979. Adenylate cyclase assay, p. 35–55. In: Advances in Cyclic Nucleotide Research, Vol. 10. G. Brooker, P. Greengard, G.A. Robison (Eds. ). Raven Press, New York.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gram, H., Ramage, P., Memmert, K. et al. A Novel Approach for High Level Production of a Recombinant Human Parathyroid Hormone Fragment in Escherichia coli. Nat Biotechnol 12, 1017–1023 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1094-1017
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1094-1017
This article is cited by
-
In vitro refolding with simultaneous purification of recombinant human parathyroid hormone (rhPTH 1–34) from Escherichia coli directed by protein folding size exclusion chromatography (PF-SEC): implication of solution additives and their role on aggregates and renaturation
Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry (2016)