Abstract
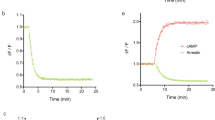
We have extended a melanophore–based bioassay for G–protein coupled receptors to include the functional expression of the murine platelet–derived growth factor (PDGF) β–receptor. The homodimeric ligand PDGF–BB induced activation of the transiently expressed receptor in melanophore cells. This led to dose dependent pigment dispersion whereas it did not induce pigment dispersion in wild type cells. The effective concentration of PDGF–BB giving half–maximal pigment dispersion (EC50) was 1 nM after 30 minutes exposure. PDGF–AA had no abiltity to induce pigment dispersion in melanophore cells transiently expressing the β–PDGF receptor. PDGF–BB–induced pigment dispersion could be blocked by the bisindolylmaleimide Ro 31–8220 which is an inhibitor of protein kinase C isoenzymes. Functional expression of the PDGF β–receptor extends the use of the pigment translocation assay to include transmembrane signaling receptor tyrosine kinases. It opens the opportunity for the discovery of potent agonists and antagonists through massive drug screening and investigations of functional ligand–receptor interactions for single transmembrane domain receptors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Graminski, G.F., Jayawickreme, C.K., Potenza, M.N. and Lerner, M.R. 1993. Pigment dispersion in frog melanophores can be induced by a phorbolester or stimulation of a recombinant receptor that activates phospholipase C. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 5957–5964.
Lerner, M.R. 1994. Tools for investigating functional interactions between ligands and G-protein-coupled receptors. Trends Neurosci. 17: 142–146.
McClintock, T.S., Graminski, G.F., Potenza, M.N., Jayawickreme, C.K., Roby-Shemkovitz, A. and Lerner, M.R. 1993. Functional expression of recombinant G-protein-coupled receptors monitored by video imaging of pigment movement in melanophores. Anal. Biochem. 209: 298–305.
Potenza, M.N. and Lerner, M.R. 1992. A rapid quantitative bioassay for evaluating the effects of ligands upon receptors that modulate cAMP levels in a melanophore Cell line. Pigment Cell Res. 5: 372–378.
Potenza, M.N., Graminski, G.F. and Lerner, M.R. 1992. A method for evaluating the effects of ligands upon Gs protein coupled receptors using a recombinant melanophore-based bioassay. Anal. Biochem. 206: 315–322.
Jayawickreme, C.K., Graminski, G.F., Quillan, J.M. and Lerner, M.R. 1994. Creation and functional screening of a multi-use peptide library. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 1614–1618.
Potenza, M.N., Graminski, G.F., Schmauss, C. and Lerner, M.R. 1994. Functional expression and characterization of human D2 and D3 dopamine receptors. J. Neurosci. 14: 1463–1476.
Daniolos, A., Lerner, A.B. and Lerner, M.R. 1990. Action of light on frog pigment cells in culture. Pigment Cell Res. 3: 38–43.
Sugden, D. and Rowe, S.J. 1992. Protein kinase C activation antagonizes melatonin-induced pigment aggregation in Xenopus laevis melanophores. J. Cell Biol. 119: 1515–1521.
Goldschmidt-Clermont, P.J., Kim, J.W., Machesky, L.M., Rhee, S.G. and Pollard, T.D. 1991. Regulation of phospholipase C-γ1 by profilin and tyrosine phosphorylation. Science 251: 1231–1233.
Margolis, B., Rhee, S. G., Felder, S., Mervic, M., Lyall, R., Levitzki, A., Ullrich, A., Zilberstein, A. and Schlessinger, J. 1989. EGF induces phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II: a potential mechanism for EGF receptor signaling. Cell 57: 1101–1107.
Meisenhelder, J., Suh, P.-G., Rhee, S.G. and Hunter, T. 1989. Phospholipase C-γ is a substrate for the PDGF and EGF receptor protein tyrosine kinases in vivo and in vitro. Cell 57: 1109–1122.
Wahl, M.I., Daniel, T.D. and Carpenter, G. 1988. Antiphosphotyrosine recovery of phospholipase C activity after EGF treatment of A431 cells. Science 241: 968–970.
Wahl, M., Nishibe, S., Suh, P.-G. and Carpenter, G. 1989. Epidermal growth factor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of phospholipase C-II independently of receptor internalization and extracellular calcium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 1568–1572.
Burgess, W.H., Dionne, C.A., Kaplow, J., Mudd, R., Friesel, R., Zilberstein, A., Schlessinger, J. and Jaye, M. 1990. Characterization and cDNA cloning of phospholipase C-γ, a major substrate for heparin binding growth factor 1 (acidic fibroblast growth factor) activated tyrosine kinase. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 4770–4777.
Johnson, D.E. and Williams, L.T. 1993. Structural and functional diversity in the FGF receptor multigene family. Adv. Cancer Res. 60: 1–41.
Mohammadi, M., Honegger, A.M., Rotin, D., Fischer, R., Bellot, F., Li, W., Dionne, C.A., Jaye, M., Rubinstein, M. and Schlessinger, J. 1991. A tyrosine-phosphorylated carboxy-terminal peptide of the fibroblast growth factor receptor (Flg) is a binding site for the SH2 domain of phospholipase C-γ1. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11: 5068–5078.
Kim, H.K., Kim, J.W., Zilberstein, A., Margolis, B., Kim, J.G., Schlessinger, J. and Rhee, S.G. 1991. PDGF stimulation of inositol phospholipid hydrolysis requires PLC-γ1 phosphorylation on tyrosine residues 783 and 1254. Cell 65: 435–441.
Kumjian, D.A., Wahl, M.I., Rhee, S.G. and Daniel, T.O. 1989. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) binding promotes physical association of PDGF receptor with phospholipase C. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86: 8232–8236.
Margolis, B., Zilberstein, A., Franks, C., Felder, S., Kremer, S., Ullrich, A., Rhee, S.G., Skorecki, K. and Schlessinger, J. 1990. Effect of Phospholipase C-γ overexpression on PDGF-induced second messengers and mitogenesis. Science 248: 607–610.
Morrison, D.K., Kaplan, D.R., Rhee, S.G. and Williams, L.T. 1990. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)-dependent association of phospholipase C-γ with the PDGF receptor signaling complex. Mol. Cell. Biol. 10: 2359–2366.
Valius, M. and Kazlauskas, A. 1993. Phospholipase C-γ and Phosphatidylinositol 3 kinase are the downstream mediators of the PDGF receptor's mitogenic signal. Cell 73: 321–334.
Wahl, M.I., Olashaw, N.E., Nishibe, S., Rhee, S. G., Pledger, W.J. and Carpenter, G. 1989. Platelet-derived growth factor induces rapid and sustained tyrosine phosphorylation of PLC-γ in quiescent BALB/C3T3 cells. Mol. Cell. Biol. 9: 2934–2943.
Koch, C.A., Anderson, D., Moran, M.F., Ellis, C. and Pawson, T. 1991. SH2 and SH3 domains: elements that control interactions of cytoplasmic signaling proteins. Science 252: 668–674.
Barres, B.A., Hart, I.K., Coles, H.S.R., Burne, J.F., Voyvodic, J.T., Richardson, W.D. and Raff, M.C. 1992. Cell death and control of Cell survival in the oligodendrocyte lineage. Cell 70: 31–46.
Mercola, M., Melton, D.A. and Stiles, C.D. 1988. Platelet-derived growth factor A chain is maternally encoded in Xenopus embryos. Science 241: 1223–1225.
Morrison-Graham, K., Schatteman, G.C., Bork, T., Bowen-Pope, D.F. and Weston, J.A. 1992. A PDGF receptor mutation in the mouse (Patch) perturbs the development of a non-neuronal subset of neural crest-derived cells. Development 115: 133–143.
Pierce, G.F., Mustoe, T.A., Lingelbach, J., Masakowski, V.R., Griffin, G.L., Senior, R.M. and Deuel, T.F. 1989. Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β enhance tissue repair activities by unique mechanisms. J. Cell Biol. 109: 429–440.
Sprugel, K.H., McPherson, J.M., Clowes, A.W. and Ross, R. 1987. Effects of growth factors in vivo: I. Cell ingrowth into porous subcutaneous chambers. Am. J. Pathol. 129: 601–613.
Stephenson, D.A., Mercola, M., Anderson, E., Wang, C., Stiles, C.D., Bowen-Pope, D.F. and Chapman, V.M. 1991. Platelet-derived growth factor receptor α-subunit gene (Pdgfra) is deleted in the mouse patch (Ph) mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88: 6–10.
Ferns, G.A.A., Raines, E.W., Sprugel, K.H., Motani, A.S., Reidy, M.A. and Ross, R. 1991. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science 253: 1129–1132.
Gazit, A., Igarashi, H., Chiu, I.-M., Srinivasan, A., Yaniv, A., Tronick, S.R., Robbins, K.C. and Aaronson, S.A. 1984. Expression of the normal human sis/ PDGF-2 coding sequence induces cellular transformation. Cell 39: 89–97.
Heldin, C.-H., Wasteson, A. and Westermark, B. 1985. Platelet-derived growth factor. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 39: 169–187.
Ross, R., Raines, E.W. and Bowen-Pope, D.F. 1986. The biology of platelet-derived growth factor. Cell 46: 155–169.
Westermark, B. and Heldin, C.-H. 1991. Platelet-derived growth factor in autocrine transformation. Cancer Res. 51: 5087–5092.
Bilder, G.E., Krawiec, J.A., McVety, K., Gazit, A., Gilon, C., Lyall, R., Zilberstein, A., Levitzki, A., Perrone, M.H. and Schreiber, A.B. 1991. Tyrphostins inhibit PDGF-induced DNA synthesis and associated early events in smooth muscle cells. Am. J. Physiol. 260: C721–C730.
Domin, J., Higgins, T. and Rozengurt, E. 1994. Preferential inhibition of platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated DNA synthesis and protein tyrosine phosphorylation by nordihydroguaiaretic acid. J. Biol. Chem. 269: 8260–8267.
Engstrom, U., Engstrom, A., Ernlund, A., Westermark, B. and Heldin, C.-H. 1992. Identification of a peptide antagonist for platelet-derived growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 16581–16587.
Matsui, T., Heidaran, M., Miki, T., Popescu, N., La Rochelle, W., Kraus, M., Pierce, J. and Aaronson, S. 1989. Isolation of a novel receptor cDNA establishes the existence of two PDGF receptor genes. Science 243: 800–804.
Yarden, Y., Escobedo, J.A., Kuang, W.-J., Yang-Feng, T.L., Daniel, T.O., Tremble, P.M., Chen, E.Y., Ando, M.E., Harkins, R.N., Francke, U., Fried, V.A., Ullrich, A. and Williams, L.T. 1986. Structure of the receptor for platelet-derived growth factor helps define a family of closely related growth factor receptors. Nature 323: 226–232.
Bishayee, S., Majumdar, S., Khire, J. and Das, M. 1989. Ligand-induced dimerization of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 11699–11705.
Frackelton, A.R. Jr., Tremble, P.M. and Williams, L.T. 1984. Evidence for the platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated tyrosine phosphorylation of the platelet-derived growth factor receptor in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 259: 7909–7915.
Heldin, C.-H., Ernlund, A., Rorsman, C. and Ronnstrand, L. 1989. Dimerization of the B-type platelet-derived growth factor receptors occurs after ligand binding and is closely associated with receptor kinase activation. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 8905–8912.
Seifert, R.A., Hart, C.E., Phillips, P.E., Forstrom, J.W., Ross, R., Murray, M.J. and Bowen-Pope, D.F. 1989. Two different subunits associate to create isoform-specific platelet-derived growth factor receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 264: 8771–8778.
Williams, L.T. 1989. Signal transduction by the platelet-derived growth factor receptor. Science 243: 1564–1570.
Cantley, L.C., Auger, K.R., Carpenter, C., Duckworth, B., Graziani, A., Kapeller, R. and Soltoff, S. 1991. Oncogenes and signal transduction. Cell 64: 281–302.
Coughlin, S.R., Escobedo, J.A. and Williams, L.T. 1989. Role of phosphati-dylinositol kinase in PDGF receptor signal transduction. Science 243: 1191–1194.
Kaplan, D.R., Morrison, D.K., Wong, G., McCormick, F. and Williams, L.T. 1990. PDGF β-receptor stimulates tyrosine phosphorylation of GAP and association of GAP with a signaling complex. Cell 61: 125–133.
Kazlauskas, A., Feng, G.-S., Pawson, T. and Valius, M. 1993. The 64-kDa protein that associates with the platelet-derived growth factor receptor β sub-unit via Tyr-1009 is the SH2-containing phosphotyrosine phosphatase Syp. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 6939–6942.
Kypta, R.M., Goldberg, Y., Ulug, E.T. and Courtneidge, S.A. 1990. Association between the PDGF receptor and members of the src family of tyrosine kinases. Cell 62: 481–492.
Li, W., Hu, P., Skolnik, E.Y., Ullrich, A. and Schlessinger, J. 1992. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing Nck protein is oncogenic and a common target for phosphorylation by different surface receptors. Mol. Cell. Biol. 12: 5824–5833.
Lowenstein, E.J., Daly, R.J., Batzer, A.G., Li, W., Margolis, B., Lammers, R., Ullrich, A., Skolnik, E.Y., Bar-Sagi, D. and Schlessinger, J. 1992. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell 70: 431–442.
Molloy, C.J., Bottaro, D.P., Fleming, T.P., Marshall, M.S., Gibbs, J.B. and Aaronson, S.A. 1989. PDGF induction of tyrosine phosphorylation of GTPase activating protein. Nature 342: 711–714.
De Lean, A.P., Munson, P.J. and Rodbard, D. 1978. Simultaneous analysis of families of sigmoidal curves: application to bioassay, radioligand assay, and physiological dose-response curves. Am. J. Physiol. 235: E97–E102.
Davis, P.D., Hill, C.H., Keech, E., Lawton, G., Nixon, J.S., Sedgwick, A.D., Wadsworth, J., Westmacott, D. and Wilkinson, S.E. 1989. Potent selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. FEES Lett. 259: 61–63.
Renard, D.C., Bolton, M.M., Rhee, S.G., Margolis, B.L., Zilberstein, A., Schlessinger, J. and Thomas, A.P. 1992. Modified kinetics of platelet-derived growth factor-induced Ca2+ increases in NIH-3T3 Cells overexpressing phospholipase Cγl. Biochem. J. 281: 775–784.
Exton, J.H. 1990. Signaling through phosphatidylcholine breakdown. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 1–4.
Fukami, K. and Takenawa, T. 1992. Phosphatidic acid that accumulates in platelet-derived growth factor-stimulated Balb/c 3T3 cells is a potential mitogenic signal. J. Biol. Chem. 267: 10988–10993.
Ha, K.-S. and Exton, J.H. 1993. Differential translocation of protein kinase C isozymes by thrombin and platelet-derived growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 268: 10534–10539.
Pessin, M.S., Baldassare, J.J. and Raben, D.M. 1990. Molecular species analysis of mitogen-stimulated 1,2-diglycerides in fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 265: 7959–7966.
Hammacher, A., Mellstrom, K., Heldin, C.-H. and Westermark, B. 1989. Isoform-specific induction of actin reorganization by platelet-derived growth factor suggests that the functionally active receptor is a dimer. EMBO J. 8: 2489–2495.
Heidaran, M.A., Pierce, J.H., Yu, J.-C., Lombardi, D., Artrip, J.E., Fleming, T.P., Thomason, A. and Aaronson, S.A. 1991. Role of αβreceptor heterodimer formation in β platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptor activation by PDGF-AB. J. Biol. Chem. 266: 20232–20237.
Kanakaraj, P., Raj, S., Khan, S.A. and Bishayee, S. 1991. Ligand-induced interaction between α-and β-type platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) receptors: Role of receptor heterodimers in kinase activation. Biochemistry 30: 1761–1767.
Wilkinson, S.E., Parker, P.J. and Nixon, J.S. 1993. Isoenzyme specificity of bisindolylmaleimides, selective inhibitors of protein kinase C. Biochem. J. 294: 335–337.
Lammers, R., Gray, A., Schlessinger, J. and Ullrich, A. 1989. Differential signalling potential of insulin-and IGF-1-receptor cytoplasmic domains. EMBO J. 8: 1369–1375.
Lee, J., Dull, T.J., Lax, I., Schlessinger, J. and Ullrich, A. 1989. HER2 cytoplasmic domain generates normal mitogenic and transforming signals in a chimeric receptor. EMBO J. 8: 167–173.
Ohashi, H., Maruyama, K., Liu, Y.-C. and Yoshimura, A. 1994. Ligand-induced activation of chimeric receptors between the ery thropoietin receptor and receptor tyrosine kinases. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 91: 158–162.
Riedel, H., Dull, T.J., Honegger, A.M., Schlessinger, J. and Ullrich, A. 1989. Cytoplasmic domains determine signal specificity, cellular routing characterise tics and influence ligand binding of epidermal growth factor and insulin receptors. EMBO J. 8: 2943–2954.
Rovelli, G., Heller, R.A., Canossa, M. and Shooter, E.M. 1993. Chimeric tumor necrosis factor-TrkA receptors reveal that ligand-dependent activation of the TrlcA tyrosine kinase is sufficient for differentiation and survival of PC 12 cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90: 8717–8721.
Potenza, M.N. and Lerner, M.R. 1991. A recombinant vaccinia virus infects Xenopus melanophores. Pigment Cell Res. 4: 186–192.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Graminski, G., Lerner, M. A Rapid Bioassay for Platelet–Derived Growth Factor β-Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Function. Nat Biotechnol 12, 1008–1011 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1094-1008
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1094-1008