Abstract
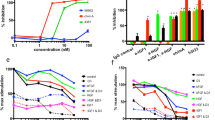
We have designed a molecule, GFB-111, that binds to platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), prevents it from binding to its receptor tyrosine kinase, and blocks PDGF-induced receptor autophosphorylation, activation of Erk1 and Erk2 kinases, and DNA synthesis. GFB-111 is highly potent (IC50 = 250 nM) and selective for PDGF over EGF, IGF-1, aFGF, bFGF, and HRGβ (IC50 values > 100 μM), but inhibits VEGF-induced Flk-1 tyrosine phosphorylation and Erk1/Erk2 activation with an IC50 of 10 μM. GFB-111 treatment of nude mice bearing human tumors resulted in significant inhibition of tumor growth and angiogenesis. The results demonstrate the feasibility of designing novel growth factor–binding molecules with potent anticancer and antiangiogenic activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Heldin, C.H., Ostman, A. & Ronnstrand, L. Signal transduction via platelet-derived growth factor receptors. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1378, F79–F113 (1998).
Heldin, C.H. & Westermark, B. In The molecular and cellular biology of wound repair. Edn. 2 (Plenum Press, New York; 1996).
Raines, E.W., Bowen-Pope, D.F. & Ross, R. Platelet-derived growth factor. In Handbook of experimental pharmacology. Peptide growth factors and their receptors. (Springer, Heidelberg; 1990).
Forsberg, K., Valyi-Nagy, I., Heldin, C.H., Herlyn, M. & Westermark, B. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) in oncogenesis: development of vascular connective tissue stroma in xenotransplanted human melanoma producing PDGF-BB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 90, 393–397 (1993).
Battegay, E.J., Rupp, J., Iruela-Arispe, L., Sage, E.H. & Pech, M. PDGF-BB modulates endothelial proliferation and angiogenesis in vitro via PDGF beta-receptors. J. Cell. Biol. 125, 917–928 (1994).
Thommen, R. et al. PDGF-BB increases endothelial migration on cord movements during angiogenesis in vitro. J. Cell. Biochem. 64, 403–413 (1997).
Kumar, R., Yoneda, J., Bucana, C.D. & Fidler, I.J. Regulation of distinct steps of angiogenesis by different angiogenic molecules. Int. J. Oncol. 12, 749–757 (1998).
Wang, D., Huang, H.J., Kazlauskas, A. & Cavenee, W.K. Induction of vascular endothelial growth factor expression in endothelial cells by platelet-derived growth factor through the activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Cancer Res. 59, 1464–1472 (1999).
Leveen, P. et al. Mice deficient for PDGF-B show renal, cardiovascular and hematological abnormalities. Genes Dev. 8, 1875–1887 (1994).
Soriano, P. Abnormal kidney development and hematological disorders in PDGF beta-receptor mutant mice. Genes Dev. 8, 1888–1896 (1994).
Kazlauskas, A. & Cooper, J.A. Autophosphorylation of the PDGF receptor in the kinase insert region regulates interactions with cell proteins. Cell 58, 1121–1133 (1989).
Lowenstein, E.J. et al. The SH2 and SH3 domain-containing protein GRB2 links receptor tyrosine kinases to ras signaling. Cell 70, 431–442 (1992).
Ramakrishnan, V. et al. A novel monoclonal antibody dependent on domain 5 of the platelet-derived growth factor beta receptor inhibits ligand binding and receptor activation. Growth Factors 8, 253–265 (1993).
Engstrom, U., Engstrom, A., Ernlund, A., Westermark, B. & Heldin, C.H. Identification of a peptide antagonist for platelet-derived growth factor. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 16581–16587 (1992).
Brennand, D.M. et al. Identification of a cyclic peptide inhibitor of platelet-derived growth factor-BB receptor-binding and mitogen-induced DNA synthesis in human fibroblasts. FEBS Lett. 413, 70–74 (1997).
Shulman, T., Sauer, F.G., Jackman, R.M., Chang, C.N. & Landolfi, N.F. An antibody reactive with domain 4 of the platelet-derived growth factor β receptor allows BB binding while inhibiting proliferation by impairing receptor dimerization. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 17400–17404 (1997).
Klohs, W.D., Fry, D.W. & Kraker, A.J. Inhibitors of tyrosine kinase. Curr. Opin. Oncol. 9, 562–568 (1997).
Levitzki, A. & Gazit, A. Tyrosine kinase inhibition: an approach to drug development. Science 267, 1782–1788 (1995).
Ferns, G.A. et al. Inhibition of neointimal smooth muscle accumulation after angioplasty by an antibody to PDGF. Science 253, 1129–1132 (1991).
Duan, D.S., Pazin, M.J., Fretto, L.J. & Williams, L.T. A functional soluble extracellular region of the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) β receptor antagonizes PDGF-stimulated responses. J. Biol. Chem. 266, 413–418 (1991).
Green, L.S. et al. Inhibitory DNA ligands to platelet-derived growth factor B-chain. Biochemistry 35, 14413–14424 (1996).
Park, H.D., Lin, Q. & Hamilton, A.D. Protein surface recognition by synthetic receptors: a route to novel sub-micromolar inhibitors for chymotrypsin. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 121, 8–13 (1999).
Hamuro, Y., Calama, M.C., Park, H.S. & Hamilton, A.D. A calixarene with four peptide loops: an antibody mimic for recognition of protein surfaces. Angew. Chem. Int. Edn. Engl. 36, 2680–2683 (1997).
Oefner, C., Arey, A.D., Winkler, F.K., Eggimann, B. & Hosang, M. Crystal structure of human platelet derived growth factor, EMBO J. 11, 3921–3926 (1996).
Anderson, M. et al. Involvement of loop 2 of platelet derived growth factor-AA and -BB in receptor binding. Growth Factors 12, 159–164 (1995).
Muller, Y.A. et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor: crystal structure and functional mapping of the kinase domain receptor binding site. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 7192–7197, 1997.
Campion, S.R. & Niyogi, S.K. Interaction of the epidermal growth factor with its receptor. Prog. Nucleic Acid Res. Mol. Biol. 49, 353–383 (1994).
Stauber, D.J., DiGabriele, A.D. & Hendrickson, W.A. Structural interactions of fibroblast growth factor receptor with its ligands. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97, 49–54 (2000).
McInnes, C. & Sykes, B.D. Growth factor receptors: structure, mechanism and drug discovery. Biopolymers 43, 339–366 (1997).
Jones, J.T. et al. Binding interaction of the heregulinβ egf domain with ErbB3 and ErbB4 receptors assessed by alanine scanning mutagenesis. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 11667–11674 (1998).
McGuire, T., Qian, Y., Hamilton, A.D. & Sebti, S.M. Platelet derived growth factor receptor tyrosine phosphorylation requires protein geranylgeranylation and not farnesylation. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 27402–27407 (1996).
Sun, J. et al. Antitumor efficacy of a novel class of non-thiol-containing peptidomimetic inhibitors of farnesyltransferase and geranylgeranyltransferase I: combination therapy with the cytotoxic agents cisplatin, taxol and gemcitabine. Cancer Res. 59, 4919–4926 (1999).
Weidner, N., Semple, J.P., Welch, W.R. & Folkman, J. Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis—correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 324, 1–8 (1991).
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH PO1 CA78038-01A1 and United States Army grant DAMD17-99-1-9458. We would also like to thank Dr. Axel Ullrich (Max-Planck-Institute for Biochemistry) and Dr. Richard Jove (Moffitt Cancer Center and USF) for NIH3T3 cells overexpressing the VEGF/flk-1 receptor and EGFR, respectively.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blaskovich, M., Lin, Q., Delarue, F. et al. Design of GFB-111, a platelet-derived growth factor binding molecule with antiangiogenic and anticancer activity against human tumors in mice. Nat Biotechnol 18, 1065–1070 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/80257
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/80257
This article is cited by
-
Syntheses, structures, and biological activities of two supramolecules consisting of resorcinolcalix[4]arene and amino-pyridine moieties
Journal of Inclusion Phenomena and Macrocyclic Chemistry (2024)
-
Calix[4]API-s: fully functionalized calix[4]arene-based facial active pharmaceutical ingredients
Molecular Diversity (2021)
-
Calixdrugs: calixarene-based clusters of established therapeutic drug agents
Molecular Diversity (2016)
-
Extracellular assembly and activation principles of oncogenic class III receptor tyrosine kinases
Nature Reviews Cancer (2012)
-
Binding and Fluorescence Resonance Energy Transfer (FRET) of Ruthenium(II)-Bipyridine-Calixarene System with Proteins—Experimental and Docking Studies
Journal of Fluorescence (2012)