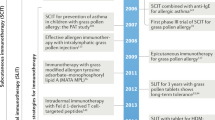
Abstract
Human hybridoma cell lines secreting IgG specific for the major allergen in the pollen of short ragweed, Amb a I, were established from patients who had been receiving antigen injections for immunotherapy. Recombinant Ig genes were then constructed by cloning the heavy and light chain variable region genes of the human hybridoma cell line and joining them to the human α or κ constant region genes in mammalian expression vectors. Amb a I-specific IgA was expressed in two mouse myeloma cell lines, NSO and Sp2/0. In both systems, transfected α and κ chains were assembled into IgA monomers or into dimers covalently linked by the endogenous murine J chains. We propose that recombinant IgA monoclonal antibodies specific for airborne allergens may be applied to the mucosal surface of the nasal linings or of the lower airway of sensitized individuals to inhibit the entry of allergenic molecules across the mucosal epithelium and, therefore, to prevent the development of allergic responses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Metzger, H., Alcaraz, G., Hohman, R., Kinet, J.P., Pribluda, V. and Quarto, R. 1986. The receptor with high affinity for immunoglobulin E. Ann. Rev. Immunol. 4: 419–470.
Siraganian, R.P. 1993. Mechanism of IgE-mediated hypersensitivity, p. 105–134. In: Allergy Principles and Practice. Middleton Jr.,E., Reed, C. E., Ellis, E.F., Adkinson Jr., N.R., Yunginger, J.W., and Busse, W.W. (Eds). Mosby, NewYoric.
Bush, R.K. 1989. Aerobiology of pollen and fungal allergens. J. Allergy Clin Immunol. 84: 1120–1124.
Naclerio, R.M. 1991. Drug therapy: allergic rhinitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 325: 860–869.
Larrick, J.W., Danielsson, L., Brenner, C.A., Wallace, E.E., Abrahamson, M., Fry, K.E. and Borrebaeck, C.A.K. 1989. Polymerase chain reaction using mixed antibody variable region genes from single hybridoma cells. Bio/Technology 7: 934–938.
Lamson, G. and Koshland, M.E. 1984. Changes in J chain and μ chain expression as a function of B cell differentiation. J. Exp. Med. 160: 877–892.
Beatty, J.D., Beaty, B.G. and Vlahos, W.G. 1987. Measurement of monoclonal antibody affinity by non-competitive enzyme immunoassay. J. Immunol. Meth. 100: 173–179.
Riechmann, L., Clark, M., Waldmann, H. and Winter, G. 1988. Reshaping human antibodies for therapy. Nature 333: 323–327.
Owens, R.J. and Young, R.J. 1994. The genetic engineering of monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. Methods 168: 149–165.
Jolliffe, L.K. 1993. Humanized antibodies: enhancing therapeutic utility through antibody engineering. Int. Rev. Immunol. 10: 241–250.
Mountain, A. and Adair, J.R. 1992. Engineering antibodies for therapy. Biotechnol. Genet. Eng. Rev. 10: 1–142.
Mestecky, J. 1988. Immunobiology of IgA. Am J. Kidney Dis. 12: 378–383.
Childers, N.K., Bruce, M.G. and McGhee, J.R. 1989. Molecular mechanisms of immunoglobulin A defense. Ann. Rev. Microbiol. 43: 503–536.
Mazanec, M.B., Nedrud, J.G. and Lamm, M.E. 1987. Immunoglobulin A monoclonal antibodies protect against Sendai virus. J. Virol. 61: 2624–2626.
Martin, S., Casasnovas, J.M., Staunton, D.E. and Springer, T.A. 1993. Efficient neutralization and disruption of rhinovirus by chimeric ICAM-I/immunoglobulin molecules. J. Virol. 67: 3561–3568.
Strober, W. and Sneller, M.C. 1991. IgA deficiency. Ann. Allergy 66: 363–375.
Abu-Ghazaleh, R.I., Fujisawa, T., Mestecky, J., Kyle, R.A. and Gleich, G.J. 1989. IgA-induced eosinophil degranulation. J. Immunol. 142: 2393–2400.
King, T.P., Norman, P.S. and Connell, J.T. 1964. Isolation and characterization of allergens from ragweed pollen. II. Biochemistry 3: 458–468.
Mestecky, J., Leu, C. and Russell, M.W. 1991. Selective transport of IgA. Cellular and molecular aspects. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 20: 441–471.
Davis, A.C., Roux, K.H. and Shulman, M.J. 1988. On the structure of polymeric IgM. Eur. J. Immunol. 18: 1001–1008.
Morton, H.C., Atkin, J.D., Owens, R.J. and Woof, J.M. 1993. Purification and characterization of chimeric human IgAl and IgA2 expressed in COS and Chinese hamster ovary cells. J. Immunol. 151: 4743–4752.
Bruggemann, M., Williams, G.T., Bindon, C.I., Clark, M.R., Walker, M.R., Jefferis, R., Waldmann, H. and Neuberger, M.S. 1987. Comparison of the effector functions of human immunoglobulins using a matched set of chimeric antibodies. J. Exp. Med. 166: 1351–1361.
Carayannopoulos, L., Max, E.E. and Capra, J.D. 1994. Recombinant human IgA expressed in insect cells. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91: 8348–8352.
Olson, J.R. and Klapper, D.G. 1986. Two major human allergenic sites on ragweed pollen allergen antigen E identified by using monoclonal antibodies. J. Immunol. 136: 2109–2115.
Chen, P.F. and Platsoucas, C.D. 1992. Development of the non-palindromic adaptor polymerase chain reaction (NPA-PCR) for the amplification of alpha-and beta-chain T-cell receptor cDNAs. Scand.J. Immunol. 35: 539–549.
Yu, L., Peng, C., Starnes, S.M., Liou, R.S. and Chang, T.W. 1990. Two iso-forms of human membrane-bound α Ig resulting from alternative mRNA splicing in the membrane segment. J. Immunol. 145: 3932–3936.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, L., Fung, M., Sun, W. et al. Human IgA Monoclonal Antibodies Specific for a Major Ragweed Pollen Antigen. Nat Biotechnol 13, 779–786 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0895-779
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0895-779