Abstract
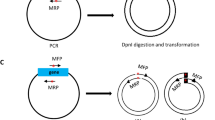
Conditions which gave a high yield of oligonucleotide-directed site specific mutagenesis were obtained with use of the lpp gene of Escherichia coli cloned in the versatile expression plasmid vector, pIN-II. This plasmid (5.6-kb) was digested by PstI followed by exonuclease (Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I) to remove a portion of the gene for β-lactamase. Another sample was digested by Xbal which cuts at a unique site in the pIN-II vector, and EcoRI to remove the portion of the lpp gene to be mutagenized. Both fragments were mixed with a synthetic oligonucleotide (the mutagen) and the mixture was denatured at 100°C for 3 min, followed by gradual cooling to reanneal. The mixture of renatured DNA was treated with the Klenow fragment of DNA polymerase I plus deoxynucleotide triphosphates in the presence of T4 ligase, and ampicillin-resistant transformants were isolated. In the case of a single base substitution, the yield of the desired mutant was as high as 13%. The present method can be applied to any gene cloned in a plasmid vector and is more convenient and simpler than the method using an M13 phage vector, since the mutated gene can be expressed directly from the plasmid vector used for the mutagenesis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smith, M. and Gillam, S. 1981. Constructed mutants using synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides as site-specific mutagens, p. 1–32. In: Genetic Engineering Vol. 3, Setlow, J., and Hollaender, A. (eds.) Plenum, New York.
Vlasuk, G.P. and Inouye, S. 1983. Site specific mutagenesis using synthetic oligodeoxyribonucleotides as mutagens, p. 292–303. In: Experimental Manipulation of Gene Expression, Inouye, M. (ed.), Academic Press, New York.
Wallace, R.B., Johnson, P.F., Tanaka, S., Schold, M., Itakura, K., and Abelson, J. 1980. Directed deletion of a yeast transfer RNA intervening sequence. Science, 209: 1396–1400.
Vlasuk, G.P., Inouye, S., Ito, H., Itakura, K., and Inouye, M. 1983. Effects of the complete removal of basic amino acid residues from the signal peptide on secretion of lipoprotein of Escherichia coli . J. Biol. Chem., 258: 7141–7148.
Zoller, M.J. and Smith, M. 1982. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis using M13-derived vectors: an efficient and general procedure for the production of point mutations in any fragment of DNA. Nuc. Acid. Res., 10: 6487–6500.
Zoller, M.J. and Smith, M. 1983. Oligonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of DNA fragments cloned into M13 vectors. Methods in Enzymology, 100: 468–500.
Nakamura, K., Masui, Y., and Inouye, M. 1982. Construction of versatile expression cloning vehicles using the lipoprotein gene of Escherichia coli . EMBO J. 1: 771–775.
Masui, Y., Coleman, J., and Inouye, M. 1983. Multipurpose expression cloning vehicles in Escherichia coli, p. 15–32. In: Experimental Manipulation of Gene Expression, Inouye, M., (cd.), Academic Press, New York.
Oostra, B.A., Harvey, R., Ely, B.K., Markham, A.F., and Smith, A.E. 1983. Transforming activity of polyoma virus middle-T antigen probed by site-directed mutagenesis. Nature, 304: 467–469.
Nakamura, K. and Inouye, M. 1979. DNA sequence of the gene for the outer membrane lipoprotein of E.coli: an extremely AT-rich promoter. Cell 18: 1109–1117.
Nakamura, K., Masui, Y., and Inouye, M. 1982. Use of a lac promoter, operator fragment of a transcriptional control switch for expression of the constitutive lpp gene in Escherichia coli . J. Appl. Mol. Genet., 1: 289–299.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morinaga, Y., Franceschini, T., Inouye, S. et al. Improvement Of Oligonucleotide-Directed Site-Specific Mutagenesis Using Double-Stranded Plasmid DNA. Nat Biotechnol 2, 636–639 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0784-636
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0784-636