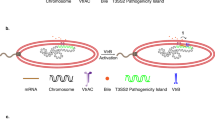
Abstract
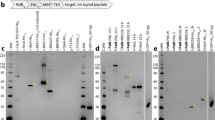
The export of Escherichia coli hemolysin across the cytoplasmic and the outer membranes requires the COOH-terminal signal sequence of HlyA, the two specific translocator proteins HlyB and HlyD, and the outer membrane protein TolC. We have developed an export cloning system that is composed of two vectors: one in which the fusion of the desired gene with the 3′-end of hlyA is generated, and a second in which the sequences containing the fusion are combined with the accessory genes hlyB and hlyD, thereby reconstructing the natural organization of the hly locus. In the second vector the fusion and the accessory genes are flanked by Not1 sites, allowing subcloning of the whole cluster into a variety of mini-transposons to achieve the stable integration of the constructs into the chromosome of Gram-negative bacteria. Since some applications may require the production of transcriptional fusions, an alternative version of the system provides the efficient translation initiation region of T7 phage gene 10 upstream of the fusion protein coding sequence. The usefulness of the system was assessed by constructing a fusion between the gene encoding the B subunit of Shiga-like toxin lie and the 3′-end of hlyA. An attenuated Salmonella typhimurium vaccine strain harboring the resulting construct, either in multicopy or mono-copy, efficiently expressed and exported the chimeric protein. We anticipate that this system will lead to a higher stability of the engineered function and permit a faithful monitoring of the export of the recombi-nant peptide under physiologic single-copy conditions.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$209.00 per year
only $17.42 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pugsley, A.P. 1993. The complete general secretion pathway in Gram-negative bacteria. Microbiol. Rev. 57: 50–108.
Holland, I.B., Wang, R., Seror, S.J., and Blight, M. Blight, M. 1990. Haemolysin secretion and other protein translocation mechanisms in gram-negative bacteria, pp. 219–254 in Microbial Products, New Approches. Baumberg, S., Hinster, I., and Rhodes, M. (eds.). Cambrige University Press, Cambridge, UK.
Wagner, W., Vogel, M., and Goebel, W. 1983. Transport of haemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherlchla coli requires two functions. J. Bacteriol. 154: 200–210.
Gray, L., Mackman, N., Nicaud, J.-M., and Holland, I.B. 1986. The carboxy-terminal region of haemolysin 2001 is required for secretion of the toxin from Escherichia coli . Mol. Gen. Genet. 205: 127–133.
Wandersman, C. and Delepelaire, P. 1990. TolC, an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein required for haemolysin secretion. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87: 4776–4780.
Koronakis, V., Stanley, P., Koronakis, E., and Hughes, C. 1992. The HlyB/HlyD-dependent secretion of toxins by Gram-negative bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Immunol. 105: 45–54.
Holland, I.B., Kenny, B., and Blight, M. 1990. Haemolysin secretion from E. coli . Biochimie 72: 131–141.
Mackman, N., Baker, K., Gray, L., Haigh, R., Nicaud, J.M., and Holland, I.B. 1987. Release of a chimeric protein into the medium from Escherichia coli using the C-terminal secretion signal of haemolysin. EMBO J. 6: 2835–2841.
Hess, J., Gentschev, I., Goebel, W., and Jarchau, T. 1990. Analysis of the haemolysin secretion system by PhoA-HlyA fusion proteins. Mol. Gen. Genet. 224: 201–208.
Gentschev, I., Hess, J., and Goebel, W. 1990. Change in the cellular localization of alcaline phosphatase by alteration of its carboxy terminal sequence. Mol. Gen. Genet. 222: 211–216.
Gentschev, I., Sokolovic, Z., Köhler, S., Krohne, G.F., Hof, H., Wagner, J., and Goebel, W. 1992. Identification of p60 antibodies in human sera and presentation of this listerial antigen on the surface of attenuated Salmonellae by the HlyB-HlyD secretion system. Infect. Immun. 60: 5091–5098.
Su, G.-F., Brahmbhatt, H.N., Wehland, J., and Timmis, K.N. 1992. Construction of LamB-Shiga toxin B subunit hybrids: analysis of expression in Salmonella typhimurium aroA strains and stimulation of B subunit-speciflc mucosal and serum antibody responses. Infect. Immun. 60: 3345–3359.
Su, G.-F., Brahmbhatt, H.N., de Lorenzo, V., Wehland, J., and Timmis, K.N. 1992. Extracellular export of Shiga toxin B-subunit/haemolysin A (C-terminus) fusion protein expressed in Salmonella typhimurium aro/A-mutant and stimulation of B-subunit specific antibody responses in mice. Microb. Pathogen. 13: 465–476.
Hashimoto-Gotoh, T., Franklin, F.C.H., Nordheim, A., and Timmis, K.N. 1981. Specific purpose plasmid cloning vectors: I. Low copy number, temperature-sensitive, mobilization-defective pSC101-derived containment vectors. Gene 16: 227–235.
Karmali, M.A., Kausche, F.M., Dean, E.A., Arp, L.H., Samuel, J.E., and Moon, H.W. 1989. Infection by verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli . Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2: 15–38.
Wieler, L.H., Bauerfeind, R., and Baljer, G. 1992. Zur Bedeutung und Diagnostik von Infektionen landwirtschaftlicher Nutztiere mit Shiga Like Toxin produzieren-den E. coli (SLTEC). Tiërartzl. Umschau. 47: 524–533.
Weinstein, D.L., Jackson, M.P., Samuel, J.E., Holmes, R.K., and O'Brien, A.D. 1988. Cloning and sequencing of a single Shiga-Like Toxin typell variant from an Eschericha coli strain responsible for Edema disease of swine. J. Bacteriol. 170: 4223–4230.
Kristensen, C.S., Eberl, L., Sanchez-Romero, J.M., Givskov, M., Molin, S., and de Lorenzo, V. 1994. Site specific deletions of chromosomally located DNA segments with the multimer resolution system of broad-host range plasmid RP4. J. Bacteriol. 177: 52–58.
de Lorenzo, V. and Timmis, K.N. 1994. Analysis and construction of stable phe-notypes in Gram-negative bacteria with Tn5- and 7n10-derived minitransposons. Meth. Enzymol. 235: 386–405.
Herrero, M., de Lorenzo, V., and Timmis, K.N. 1990. Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in Gram-negative bacteria. J. Bacteriol. 172: 6557–6567.
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E.F., and Maniatis, T. 1982. Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, New York.
Takeshita, S., Sato, M., Toba, M., Masahashi, W., and Hashimoto-Gotoh, T. 1987. High-copy number and low-copy number plasmid vectors for lacZα-complementation and chloramphenicol- or kanamycin-resistance selection. Gene 61: 63–74.
Felmlee, T., Pellett, S., and Welch, R.A. 1985. Nucleotide sequence of an Escherichia coli chromosomal hemolysin. J. Bacteriol. 163: 94–105.
Olinsa, P.O., Devine, C.S., Rangwala, S.H., and Kavka, K.S. 1988. The T7 phage gene 10 leader RNA, a ribosome-binding site that dramatically enhances the expression of foreign genes in Escherichia coli . Gene 73: 227–235.
Hanahan, D. 1983. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J. Mol. Biol. 166: 577–580.
O'Callaghan, D. and Charbit, A. 1990. High efficiency transformation of Salmonella typhimurium and Salmonella typhi by electroporation. Mol. Gen. Genet. 223: 156–158.
Laemmli, U.K. 1970. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the heads of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227: 680–685.
Towbin, H., Staehlin, H., and Gordon, G. 1979. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 76: 4350–4354.
Richard, E. 1987. Preparation of genomic DNA from bacteria. Miniprep of bacterial chromosome DNA, pp. 1–2 in Current Protocols in Molecular Biology. Ausubel, F.M., Brent, R., Kingston, R.E., Moore, D.D., Seidman, J.G., Smith, J.A., and Struhl, K. (eds.). John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New York.
Yanisch-Perron, C., Viera, J., and Messing, J. 1985. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene 33: 103–119.
Mackman, N. and Holland, I.B. 1984. Functional characterisation of a cloned haemolysin determinant from E. coli of human origin, encoding information for the secretion of a 107K polypeptide. Mol. Gen. Genet 193: 129–134.
Nicaud, J.-M., Mackman, N., Gray, L., and Holland, I.B. 1986. The C-terminal, 23 kDa peptide of E. coli haemolysin 2001 contains all the information necessary for its secretion by the haemolysin (Hly) export machinery. FEBS Lett. 204: 331–335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tzschaschel, B., Guzmán, C., Timmis, K. et al. An Escherichia coli hemolysin transport system-based vector for the export of polypeptides: Export of shiga-like toxin IIeB subunit by Salmonella typhimurium aroA. Nat Biotechnol 14, 765–769 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0696-765
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt0696-765
This article is cited by
-
Screening and purification of nanobodies from E. coli culture supernatants using the hemolysin secretion system
Microbial Cell Factories (2019)
-
Genetic engineering of probiotic Escherichia coli Nissle 1917 for clinical application
Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology (2016)
-
A generalised module for the selective extracellular accumulation of recombinant proteins
Microbial Cell Factories (2012)
-
Enhancing functional expression of heterologous lipase B in Escherichia coli by extracellular secretion
Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology (2010)
-
In vivo gene regulation in Salmonella spp. by a salicylate-dependent control circuit
Nature Methods (2007)