Abstract
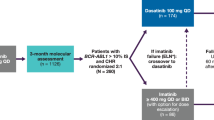
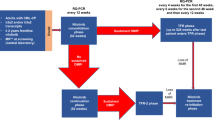
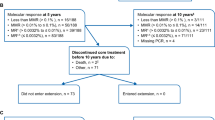
Dasatinib is a highly potent BCR–ABL inhibitor that has shown durable efficacy in patients with chronic phase (CP) chronic myeloid leukemia (CML) after resistance, suboptimal response, or intolerance to prior imatinib. In patients with CML, BCR–ABL transcript measurement is the most sensitive method for assessing minimal residual disease. Here, molecular responses were analyzed in 1067 patients with CML-CP treated with dasatinib during phase II/III trials. After 3, 6, 12, and 24 months of follow-up, a major molecular response (MMR) was achieved by 12, 22, 35, and 40% of patients, respectively. The 24-month MMR rate was 34% in patients with resistance or suboptimal response to imatinib (n=829) and 63% in imatinib-intolerant patients (n=238). Among patients who had achieved a complete cytogenetic response (CCyR), 72% also achieved MMR. Responses with dasatinib 100 mg once daily were similar to other doses. In landmark analyses, 24-month progression-free survival was higher in patients who had achieved MMR or CCyR at 12 months than in those without MMR or CCyR at 12 months. MMR at 12 months was associated with a longer duration of CCyR. Overall, this analysis shows that dasatinib treatment results in high MMR rates in patients with CML-CP after imatinib failure.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hehlmann R, Hochhaus A, Baccarani M . Chronic myeloid leukaemia. Lancet 2007; 370: 342–350.
Kavalerchik E, Goff D, Jamieson CH . Chronic myeloid leukemia stem cells. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 2911–2915.
Hughes T, Deininger M, Hochhaus A, Branford S, Radich J, Kaeda J et al. Monitoring CML patients responding to treatment with tyrosine kinase inhibitors: review and recommendations for harmonizing current methodology for detecting BCR-ABL transcripts and kinase domain mutations and for expressing results. Blood 2006; 108: 28–37.
O’Hare T, Walters DK, Stoffregen EP, Jia T, Manley PW, Mestan J et al. In vitro activity of Bcr-Abl inhibitors AMN107 and BMS-354825 against clinically relevant imatinib-resistant Abl kinase domain mutants. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 4500–4505.
Hochhaus A, Baccarani M, Deininger M, Apperley JF, Lipton JH, Goldberg SL et al. Dasatinib induces durable cytogenetic responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase with resistance or intolerance to imatinib. Leukemia 2008; 22: 1200–1206.
Kantarjian H, Pasquini R, Hamerschlak N, Rousselot P, Holowiecki J, Jootar S et al. Dasatinib or high-dose imatinib for chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of first-line imatinib: a randomized phase 2 trial. Blood 2007; 109: 5143–5150.
Shah NP, Kantarjian HM, Kim DW, Rea D, Dorlhiac-Llacer PE, Milone JH et al. Intermittent target inhibition with dasatinib 100 mg once daily preserves efficacy and improves tolerability in imatinib-resistant and -intolerant chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncol 2008; 26: 3204–3212.
Guilhot F, Apperley J, Kim DW, Bullorsky EO, Baccarani M, Roboz GJ et al. Dasatinib induces significant hematologic and cytogenetic responses in patients with imatinib-resistant or -intolerant chronic myeloid leukemia in accelerated phase. Blood 2007; 109: 4143–4150.
Cortes J, Kim DW, Raffoux E, Martinelli G, Ritchie E, Roy L et al. Efficacy and safety of dasatinib in imatinib-resistant or -intolerant patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in blast phase. Leukemia 2008; 22: 2176–2183.
Mauro MJ, Baccarani M, Cervantes F, Lipton JH, Matloub R, Sinha R, et al. Dasatinib 2-year efficacy in patients with chronic-phase chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML-CP) with resistance or intolerance to imatinib (START-C). J Clin Oncol 2008; 26 (Suppl.): 374s (abstract 7009).
Rousselot P, Facon T, Paquette R, Bleickardt E, Dejardin D, Kantarjian H . Dasatinib or high-dose imatinib for patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia chronic-phase (CML-CP) resistant to standard-dose imatinib: 2-year follow-up data from START-R. J Clin Oncol (ASCO Meeting Abstracts) 2008; 26 (Suppl.): 375s (abstract 7012).
Druker BJ, Guilhot F, O’Brien SG, Gathmann I, Kantarjian H, Gattermann N et al. Five-year follow-up of patients receiving imatinib for chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2006; 355: 2408–2417.
Hughes TP, Kaeda J, Branford S, Rudzki Z, Hochhaus A, Hensley ML et al. Frequency of major molecular responses to imatinib or interferon alfa plus cytarabine in newly diagnosed chronic myeloid leukemia. N Engl J Med 2003; 349: 1423–1432.
Marin D, Milojkovic D, Olavarria E, Khorashad JS, de Lavallade H, Reid AG et al. European LeukemiaNet criteria for failure or suboptimal response reliably identify patients with CML in early chronic phase treated with imatinib whose eventual outcome is poor. Blood 2008; 112: 4437–4444.
Kantarjian H, O’Brien S, Shan J, Huang X, Garcia-Manero G, Faderl S et al. Cytogenetic and molecular responses and outcome in chronic myelogenous leukemia: Need for new response definitions? Cancer 2008; 112: 837–845.
Cortes J, Talpaz M, O’Brien S, Jones D, Luthra R, Shan J et al. Molecular responses in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia in chronic phase treated with imatinib mesylate. Clin Cancer Res 2005; 11: 3425–3432.
Iacobucci I, Saglio G, Rosti G, Testoni N, Pane F, Amabile M et al. Achieving a major molecular response at the time of a complete cytogenetic response (CCgR) predicts a better duration of CCgR in imatinib-treated chronic myeloid leukemia patients. Clin Cancer Res 2006; 12: 3037–3042.
Paschka P, Müller MC, Merx K, Kreil S, Schoch C, Lahaye T et al. Molecular monitoring of response to imatinib (Glivec) in CML patients pretreated with interferon alpha. Low levels of residual disease are associated with continuous remission. Leukemia 2003; 17: 1687–1694.
Press RD, Love Z, Tronnes AA, Yang R, Tran T, Mongoue-Tchokote S et al. BCR-ABL mRNA levels at and after the time of a complete cytogenetic response (CCR) predict the duration of CCR in imatinib mesylate-treated patients with CML. Blood 2006; 107: 4250–4256.
Qin Y, Jiang B, Jiang Q, Jiang H, Li J, Zhang Y et al. Molecular responses of late chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia patients after achieving complete cytogenetic responses with imatinib treatment: A 6-year follow-up. Ann Hematol 2009; 88: 37–41.
Hochhaus A, Kantarjian HM, Baccarani M, Lipton JH, Apperley JF, Druker BJ et al. Dasatinib induces notable hematologic and cytogenetic responses in chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia after failure of imatinib therapy. Blood 2007; 109: 2303–2309.
Emig M, Saussele S, Wittor H, Weisser A, Reiter A, Willer A et al. Accurate and rapid analysis of residual disease in patients with CML using specific fluorescent hybridization probes for real time quantitative RT-PCR. Leukemia 1999; 13: 1825–1832.
Branford S, Hughes TP, Rudzki Z . Monitoring chronic myeloid leukaemia therapy by real-time quantitative PCR in blood is a reliable alternative to bone marrow cytogenetics. Br J Haematol 1999; 107: 587–599.
Branford S, Hughes T . Diagnosis and monitoring of chronic myeloid leukemia by qualitative and quantitative RT-PCR. Methods Mol Med 2006; 125: 69–92.
Branford S, Fletcher L, Cross NC, Müller MC, Hochhaus A, Kim DW et al. Desirable performance characteristics for BCR-ABL measurement on an international reporting scale to allow consistent interpretation of individual patient response and comparison of response rates between clinical trials. Blood 2008; 112: 3330–3338.
Ernst T, Erben P, Muller MC, Paschka P, Schenk T, Hoffmann J et al. Dynamics of BCR-ABL mutated clones prior to hematologic or cytogenetic resistance to imatinib. Haematologica 2008; 93: 186–192.
Branford S, Hughes T . Detection of BCR-ABL mutations and resistance to imatinib mesylate. Methods Mol Med 2006; 125: 93–106.
Müller MC, Hanfstein B, Erben P, Schnittger S, Saussele S, Leitner A, et al. Early molecular response to first line imatinib therapy is predictive for long term PFS and EFS in CP-CML - an interim analysis of the randomized German CML Study IV. Haematologica 2009; 94 (Suppl 2): 442 (abstract 1094).
Acknowledgements
We thank the many investigators and centers who participated in the START-C, START-R, and CA180-034 studies. Funding for clinical trials, statistical analysis, and professional medical writing assistance was provided by Bristol-Myers Squibb. AH was supported by the German José-Carreras Foundation (DJCLS H 03/01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hochhaus, A., Müller, M., Radich, J. et al. Dasatinib-associated major molecular responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukemia in chronic phase following imatinib failure: response dynamics and predictive value. Leukemia 23, 1628–1633 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.156
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2009.156
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Quantitative prediction of long-term molecular response in TKI-treated CML – Lessons from an imatinib versus dasatinib comparison
Scientific Reports (2018)
-
Rapid initial decline in BCR-ABL1 is associated with superior responses to second-line nilotinib in patients with chronic-phase chronic myeloid leukemia
BMC Cancer (2013)
-
The development of dasatinib as a treatment for chronic myeloid leukemia (CML): from initial studies to application in newly diagnosed patients
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)
-
Improved tolerability by a modified intermittent treatment schedule of dasatinib for patients with chronic myeloid leukemia resistant or intolerant to imatinib
Annals of Hematology (2013)
-
Chronic Myelogenous Leukemia: Monitoring Response to Therapy
Current Hematologic Malignancy Reports (2011)