Abstract
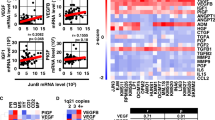
Alterations in the expression and signalling pathways of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) have been linked to the clinical features and pathogenesis of hematologic malignancies. In this study, we showed that VEGF protein expression was statistically significantly higher in the leukemic blasts than in the normal hematopoietic counterparts. A statistically significant correlation between expression of VEGF and p27Kip1 was observed in bone marrows from 42 patients with acute myeloid leukemia (P<0.001). We further demonstrated that forced VEGF overexpression or autocrine VEGF stimulation of VEGFR-2 triggers proliferation and migration/invasion of U-937 leukemic cells, thereby inducing a more invasive tumor phenotype. U-937 cells overexpressing VEGF were resistant to all-trans-retinoic acid-(ATRA) or camptothecin-induced apoptosis. Finally, we showed that increased p27Kip1 expression enhanced the ability of VEGF and VEGFR-2 to promote the migration of U-937 cells. Taken together, our results suggest that elevated level of VEGF may contribute to the adverse patient outcome by promoting cell growth, survival and migration of leukemic cells and by reducing the sensitivity of leukemic cells to therapeutic agents-induced apoptosis.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santos SC, Dias S . Internal and external autocrine VEGF/KDR loops regulate survival of subsets of acute leukemia through distinct signaling pathways. Blood 2004; 103: 3883–3889.
Neufeld G, Cohen T, Gengrinovitch S, Poltorak Z . Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and its receptors. FASEB J 1999; 13: 9–22.
Shibuya M . Role of VEGF-flt receptor system in normal and tumor angiogenesis. Adv Cancer Res 1995; 67: 281–316.
Gerber HP, Malik AK, Solar GP, Sherman D, Liang XH, Meng G et al. VEGF regulates haematopoietic stem cell survival by an internal autocrine loop mechanism. Nature 2002; 417: 954–958.
Broxmeyer HE, Cooper S, Li ZH, Lu L, Song HY, Kwon BS et al. Myeloid progenitor cell regulatory effects of vascular endothelial cell growth factor. Int J Hematol 1995; 62: 203–215.
Podar K, Anderson KC . The pathophysiologic role of VEGF in hematologic malignancies: therapeutic implications. Blood 2005; 105: 1383–1395.
de Jonge HJ, Weidenaar AC, Ter Elst A, Boezen HM, Scherpen FJ, Bouma-Ter Steege JC et al. Endogenous vascular endothelial growth factor-C expression is associated with decreased drug responsiveness in childhood acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer Res 2008; 14: 924–930.
Hicklin DJ, Ellis LM . Role of the vascular endothelial growth factor pathway in tumor growth and angiogenesis. J Clin Oncol 2005; 23: 1011–1027.
List AF . Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling pathway as an emerging target in hematologic malignancies. Oncologist 2001; 6 (Suppl 5): 24–31.
Fiedler W, Graeven U, Ergun S, Verago S, Kilic N, Stockschlader M et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor, a possible paracrine growth factor in human acute myeloid leukemia. Blood 1997; 89: 1870–1875.
Bellamy WT, Richter L, Frutiger Y, Grogan TM . Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptors in hematopoietic malignancies. Cancer Res 1999; 59: 728–733.
Mayerhofer M, Valent P, Sperr WR, Griffin JD, Sillaber C . BCR/ABL induces expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its transcriptional activator, hypoxia inducible factor-1alpha, through a pathway involving phosphoinositide 3-kinase and the mammalian target of rapamycin. Blood 2002; 100: 3767–3775.
Gabrilovich D, Ishida T, Oyama T, Ran S, Kravtsov V, Nadaf S et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibits the development of dendritic cells and dramatically affects the differentiation of multiple hematopoietic lineages in vivo. Blood 1998; 92: 4150–4166.
Podar K, Tai YT, Davies FE, Lentzsch S, Sattler M, Hideshima T et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor triggers signaling cascades mediating multiple myeloma cell growth and migration. Blood 2001; 98: 428–435.
Le Gouill S, Podar K, Amiot M, Hideshima T, Chauhan D, Ishitsuka K et al. VEGF induces Mcl-1 up-regulation and protects multiple myeloma cells against apoptosis. Blood 2004; 104: 2886–2892.
Dias S, Hattori K, Zhu Z, Heissig B, Choy M, Lane W et al. Autocrine stimulation of VEGFR-2 activates human leukemic cell growth and migration. J Clin Invest 2000; 106: 511–521.
Ellis LM, Hicklin DJ . VEGF-targeted therapy: mechanisms of anti-tumour activity. Nat rev 2008; 8: 579–591.
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM . CDK inhibitors: positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes dev 1999; 13: 1501–1512.
Jiang Y, Zhao RC, Verfaillie CM . Abnormal integrin-mediated regulation of chronic myelogenous leukemia CD34+ cell proliferation: BCR/ABL up-regulates the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor, p27Kip, which is relocated to the cell cytoplasm and incapable of regulating cdk2 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2000; 97: 10538–10543.
Nagahara H, Vocero-Akbani AM, Snyder EL, Ho A, Latham DG, Lissy NA et al. Transduction of full-length TAT fusion proteins into mammalian cells: TAT-p27Kip1 induces cell migration. Nat med 1998; 4: 1449–1452.
McAllister SS, Becker-Hapak M, Pintucci G, Pagano M, Dowdy SF . Novel p27(kip1) C-terminal scatter domain mediates Rac-dependent cell migration independent of cell cycle arrest functions. Mol cell biol 2003; 23: 216–228.
Denicourt C, Dowdy SF . Cip/Kip proteins: more than just CDKs inhibitors. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 851–855.
Ekberg J, Holm C, Jalili S, Richter J, Anagnostaki L, Landberg G et al. Expression of cyclin A1 and cell cycle proteins in hematopoietic cells and acute myeloid leukemia and links to patient outcome. Eur J Haematol 2005; 75: 106–115.
Berglund P, Stighall M, Jirstrom K, Borgquist S, Sjolander A, Hedenfalk I et al. Cyclin E overexpression obstructs infiltrative behavior in breast cancer: a novel role reflected in the growth pattern of medullary breast cancers. Cancer Res 2005; 65: 9727–9734.
Ekberg J, Landberg G, Holm C, Richter J, Wolgemuth DJ, Persson JL . Regulation of the cyclin A1 protein is associated with its differential subcellular localization in hematopoietic and leukemic cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 9082–9089.
Besson A, Gurian-West M, Schmidt A, Hall A, Roberts JM . p27Kip1 modulates cell migration through the regulation of RhoA activation. Genes Dev 2004; 18: 862–876.
Jordan CT, Guzman ML . Mechanisms controlling pathogenesis and survival of leukemic stem cells. Oncogene 2004; 23: 7178–7187.
Folkman J . Role of angiogenesis in tumor growth and metastasis. Semin Oncol 2002; 29 (6 Suppl 16): 15–18.
Musolino C, Calabro L, Bellomo G, Martello F, Loteta B, Pezzano C et al. Soluble angiogenic factors: implications for chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Am J Hematol 2002; 69: 159–163.
Fielder W, Graeven U, Ergun S, Verago S, Kilic N, Stockschlader M et al. Expression of FLT4 and its ligand VEGF-C in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 1997; 11: 1234–1237.
Verstovsek S, Kantarjian H, Manshouri T, Cortes J, Giles FJ, Rogers A et al. Prognostic significance of cellular vascular endothelial growth factor expression in chronic phase chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood 2002; 99: 2265–2267.
Dias S, Shmelkov SV, Lam G, Rafii S . VEGF(165) promotes survival of leukemic cells by Hsp90-mediated induction of Bcl-2 expression and apoptosis inhibition. Blood 2002; 99: 2532–2540.
Dias S, Hattori K, Heissig B, Zhu Z, Wu Y, Witte L et al. Inhibition of both paracrine and autocrine VEGF/VEGFR-2 signaling pathways is essential to induce long-term remission of xenotransplanted human leukemias. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2001; 98: 10857–10862.
Zhu Z, Hattori K, Zhang H, Jimenez X, Ludwig DL, Dias S et al. Inhibition of human leukemia in an animal model with human antibodies directed against vascular endothelial growth factor receptor 2. Correlation between antibody affinity and biological activity. Leukemia 2003; 17: 604–611.
Acknowledgements
We thank Elise Nilsson for the excellent technical assistant. This work was supported by the Swedish National Research Council, the Swedish Cancer Society, the Swedish Children Cancer Foundation, Gunnar Nilsson Cancer Foundation, MAS Cancer Fondation, Kunlig Fysiografisk Sällskapet in Lund, Crafoordska stiftelsen, and Malmö Hospital Foundation, the Lund University Medical Faculty grant and Government Public Health Grant (ALF) to JLP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wegiel, B., Ekberg, J., Talasila, K. et al. The role of VEGF and a functional link between VEGF and p27Kip1 in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia 23, 251–261 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.300
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2008.300
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Leukemia stem cell-bone marrow microenvironment interplay in acute myeloid leukemia development
Experimental Hematology & Oncology (2021)
-
p27kip1 overexpression regulates VEGF expression, cell proliferation and apoptosis in cell culture from eutopic endometrium of women with endometriosis
Apoptosis (2015)
-
Endocan, a potential prognostic and diagnostic biomarker of acute leukemia
Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry (2014)
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor signaling in acute myeloid leukemia
Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences (2013)