Abstract
Objective:
It is now well recognized that obesity is a major public health concern, and its prevalence has tremendously increased worldwide over the last decades, including Tunisia. As obesity is associated with cardiovascular diseases, the purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of obesity on forearm skin blood flow (FSBF) response to acetylcholine (Ach), an endothelium-dependent vasodilator, in Tunisian women over a wide range of body mass indices (BMIs).
Subjects:
One hundred and eighty healthy women with an average age of 34±6 years, an average height of 162±7 cm and an average weight of 78±19 kg participated in this investigation. The mean BMIs of the 60 lean, 50 overweight and 70 obese subjects were 22.1±0.3, 27.7±0.2 and 38.4±0.7 kg m−2, respectively.
Measurements:
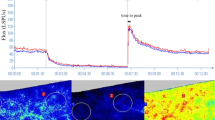
The FSBF was measured non-invasively using a laser Doppler flowmeter in response to local infusion of a cumulative dose of Ach.
Results:
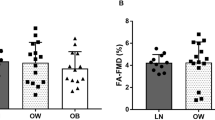
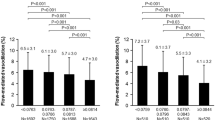
After adjusting for age, the mean response of FSBF to Ach was significantly greater in lean (1168%±78) than in overweight (643%±38) and obese subjects (323%±18) (P=0.002; P<0.0001, respectively), suggesting a reduction of the endothelium-dependent nitric oxide (NO) release by obesity. Our regression analysis also revealed that the maximum FSBF response to Ach (that is, its efficacy) was inversely correlated with BMI, waist and hip circumferences (r=−0.994, P=0.002; r=−0.2, P<0.0001, and r=−0.321, P=0.001, respectively).
Conclusion:
Our data demonstrate a reduction of skin vasodilatory reserve in obese patients and suggest a defect of both endothelial-dependent relaxation and wall compliance associated with obesity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bergeron C, Boulet LP, Hamid Q . Obesity, allergy and immunology. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005; 115: 1102–1104.
World Health Organization. WHO Global InfoBase Online: Quick Compare 2005. World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2005. pp 1–11.
Hedley AA, Ogden CL, Johnson CL, Carroll MD, Curtin LR, Flegal KM . Prevalence of overweight and obesity among US children, adolescents, and adults, 1999–2002. JAMA 2004; 291: 2847–2850.
Weiss ST, Shore S . NHLBI Workshop on obesity and asthma, directions for research. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2004; 169: 963–968.
Mokhtar N, Elati J, Chabir R, Bour A, Elkari K, Schlossman NP et al. Diet culture and obesity in Northern Africa. J Nutr 2001; 131: 887S–892S.
Khtib O . Noncommunicable diseases: risk factors and regional strategies for prevention and care. East Medit Health J 2004; 10: 778–788.
Bray GA . Medical consequence of obesity. J Clin End Metab 2004; 89: 2583–2589.
Joannidès R, Bellien J . Les méthodes cliniques d'exploration de la fonction endothéliale. Sang Thrombose Vaisseaux 2003; 15: 387–396.
Wilding J . Science, medicine, and the future: obesity treatment. BMJ 1997; 315: 997–1000.
Westerman RA, Widdop RE, Hannaford J, Low A, Roberts RG, Kent P et al. Laser Doppler velocimetry in the measurement of neurovascular function. Australas Phys Eng Sci Med 1988; 11: 53–66.
Morris SJ, Shore AC, Tooke JE . Responses of the skin microcirculation to acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside in patients with NIDDM. Diabetologia 1995; 38: 1337–1344.
Higashi Y, Sasaki S, Nakagawa K, Matsuura H, Chayama K, Oshima T . Effect of obesity on endothelium-dependent, nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in normotensive individuals and patients with essential hypertension. AmJ Hypertens 2001; 14: 1038–1045.
Higashi Y, Sasaki S, Nakagawa K, Matsuura H, Chayama K, Oshima T . Effect of obesity on endothelium-dependent, nitric oxide-mediated vasodilation in normotensive individuals and patients with essential hypertension. Am J Hypertens 2001; 14: 1038–1045.
Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS . Estimation of the concentration of low density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem 1972; 18: 499–502.
Carr RW, Delaney CA, Westerman RA, Roberts RG . Denervation impairs cutaneous microcircular function and blister healing in the rat hindlimb. Neuroreport 1993; 4: 467–470.
Nilsson GE, Tenland T, Oberg PA . Evaluation of a laser Doppler flowmeter for measurement of tissue blood flow. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng 1980; 27: 597–604.
Leahy MJ, de Mul FFM, Nilsson GE, Maniewski R . Principles and practice of the laser–Doppler perfusion technique. Technol Health Care 1999; 7: 143–162.
Morris SJ, Shore AC . Skin blood flow responses to the iontophoresis of acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside in man: possible mechanisms. J Physiol 1996; 496: 531–542.
Call-Smith K, Gangarosa Sr LP . Iontophoresis: a new approach to some old problems. New Dent 1979; 10: 20–22.
Noon JP, Walker BR, Hand MF, Webb DJ . Studies with iontophoretic administration of drugs to human dermal vessels in vivo: cholinergic vasodilatation is mediated by dilator prostanoids rather than nitric oxide. Br J Clin Pharmacol 1998; 45: 545–550.
Turrell WJ . The therapeutic action of the constant current. Proc R Soc Med 1921; 14: 41–52.
Mourad JJ, Des Guetz G, Debbabi H, Levy BI . Blood pressure rise following angiogenesis inhibition by bevacizumab. A crucial role for microcirculation. Ann Oncol 2008; 19: 927–934.
Serné EH, IJzerman RG, Gans RO, Nijveldt R, de Vries G, Evertz R et al. Direct evidence for insulin-induced capillary recruitment in skin of healthy subjects during physiological hyperinsulinemia. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1515–1522.
Kubli S, Boëgli Y, Ave AD, Liaudet L, Revelly JP, Golay S et al. Endothelium-dependent vasodilation in the skin microcirculation of patients with septic shock. Shock 2003; 19: 274–280.
Kubli S, Waeber B, Dalle-Ave A, Feihl F . Reproducibility of laser Doppler imaging of skin blood flow as a tool to assess endothelial function. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 2000; 36: 640–648.
Furchgott RF, Zawadzki JV . The obligatory role of endothelial cells in the relaxation of arterial smooth muscle by acetylcholine. Nature 1980; 288: 373–376.
Brain SD, Grant AD . Vascular actions of calcitonin gene-related peptide and adrenomedullin. Physiol Rev 2004; 84: 903–934.
Harrison S, Geppetti P . Substance P. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2001; 33: 555–576.
Petrofsky J, Lee S, Cuneo M . Effects of aging and type 2 diabetes on resting and post occlusive hyperemia of the forearm; the impact of rosiglitazone. BMC Endocr Disord 2005; 5: 4.
World Health Organization. Obesity: Preventing and Managing the Global Epidemic. Report of a WHO consultation on obesity. WHO/NUT/NCD/981, WHO: Geneva, 1998.
Sciacqua A, Candigliota M, Ceravolo R, Scozzafava A, Sinopoli F, Corsonello A et al. Weight loss in combination with physical activity improves endothelial dysfunction in human obesity. Diabetes Care 2003; 26: 1673–1678.
Laine H, Yuki-Jarvinen H, Kirvela O, Tolvanen T, Raitakari M, Solin O et al. Insulin resistance of glucose uptake in skeletal muscle cannot be ameliorated by enhancing endothelium-dependent blood flow in obesity. J Clin Invest 1998; 101: 1156–1162.
Higashi Y, Oshima T, Ozono R, Matsuura H, Kajiyama G . Aging and severity of hypertension attenuate endothelium-dependent renal vascular relaxation in humans. Hypertension 1997; 30: 252–258.
Rubanyi GM . Endothelium-derived relaxing and contracting factors. J Cell Biochem 1991; 46: 27–36.
Ting HH, Timimi FK, Boles KS, Creager SJ, Ganz P, Creager MA . Vitamin C improves endothelium-dependent vasodilation in patients with non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. J Clin Invest 1996; 97: 22–28.
Chin JH, Azhar S, Hoffman BB . Inactivation of endothelial derived relaxing factor by oxidized lipoproteins. J Clin Invest 1992; 89: 10–18.
Lucas CP, Estigarribia JA, Darga LL, Reaven GM . Insulin and blood pressure in obesity. Hypertension 1985; 7: 702–706.
Hotamisligil GS, Arner P, Caro JF, Atkinson RL, Spiegelman BM . Increased adipose tissue expression of tumor necrosis-alpha in human obesity and insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 1995; 95: 2409–2415.
Steinberg HO, Paradisi G, Hook G, Crowder K, Cronin J, Baron AD . Free fatty acid elevation impairs insulin-mediated vasodilation and nitric oxide production. Diabetes 2000; 49: 1231–1238.
Clerk LH, Rattigan S, Clark MG . Lipid infusion impairs physiologic insulin-mediated capillary recruitment and muscle glucose uptake in vivo. Diabetes 2002; 51: 1138–1145.
Droog TE, Henricson J, Nilsson GE, Sjöberg F . A protocol for iontophoresis of acetylcholine and sodium nitroprusside that minimises nonspecific vasodilatory effects. Microvasc Res 2004; 67: 197–202.
Moncada S, Palmer RM, Higgs EA . Nitric oxide: physiology, pathophysiology, and pharmacology. Pharmacol Rev 1991; 43: 109–142.
Berghoff M, Kathpal M, Kilo S, Hilz MJ, Freeman R . Vascular and neural mechanisms of ACh-mediated vasodilation in the forearm cutaneous microcirculation. J Appl Physiol 2002; 92: 780–788.
Acknowledgements
Dr Abdellaziz Ben-Jebria was the recipient of the J William Fulbright Foreign Scholarship Award sponsored by the US Department of State to Lecturing/Research at the Medical School of Sousse in Tunisia, October 2007–July 2008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miâdi-Messaoud, H., Chouchane, A., Abderrazek, E. et al. Obesity-induced impairment of endothelium-dependent vasodilation in Tunisian women. Int J Obes 34, 273–279 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.231
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/ijo.2009.231
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Repository Describing the Anatomical, Physiological, and Biological Changes in an Obese Population to Inform Physiologically Based Pharmacokinetic Models
Clinical Pharmacokinetics (2022)
-
Prostaglandin Endoperoxide H Synthase-2 (PGHS-2) Variants and Risk of Obesity and Microvascular Dysfunction Among Tunisians: Relevance of rs5277 (306G/C) and rs5275 (8473T/C) Genetic Markers
Biochemical Genetics (2021)
-
Inflammation and impaired endothelium-dependant vasodilatation in non obese women with gestational diabetes mellitus: preliminary results
Lipids in Health and Disease (2013)
-
Six‐Minute Walk Test Improved Forearm Skin Blood Flow in Tunisian Obese Women
Obesity (2012)