Abstract
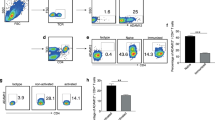
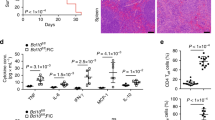
The role of B7-DC in T-cell responses remains controversial because both coinhibitory and costimulatory functions have been reported in various experimental systems in vitro and in vivo. In addition to interacting with the coinhibitory receptor PD-1, B7-DC has also been shown to bind repulsive guidance molecule b (RGMb). The functional consequences of the B7-DC/RGMb interaction, however, remain unclear. More than a decade ago, we reported that replacement of a murine B7-DC mutant lysine with serine (K113S) at positive 113 resulted in a loss of binding capacity to PD-1. Nevertheless, K113S remained costimulatory for T cells in vitro, implicating a dual functionality for B7-DC in T-cell responses. Here we show that recombinant K113S protein interacts with RGMb with a similar affinity to wild-type B7-DC. More importantly, K113S costimulates CD4+ T-cell responses via RGMb and promotes Th1 polarization. RGMb is expressed on the surface of naive mouse T cells, macrophages, neutrophils and dendritic cells. Finally, K113S/RGMb costimulation suppresses Th2-mediated asthma and ameliorates small airway inflammation and lung pathology in an experimental mouse model. Our findings indicate that RGMb is a costimulatory receptor for B7-DC. These findings from the K113S variant provide not only a possible explanation for the B7-DC-triggered contradictory effects on T-cell responses, but also a novel approach to investigate the B7-DC/PD-1/RGMb axis. Recombinant K113S or its derivatives could potentially be developed as an agonist for RGMb to costimulate the Th1 response without triggering PD-1-mediated T-cell inhibition.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Latchman Y, Wood CR, Chernova T, Chaudhary D, Borde M, Chernova I et al. PD-L2 is a second ligand for PD-I and inhibits T cell activation. Nat Immunol 2001; 2: 261–268.
Chen L, Flies DB. Molecular mechanisms of T cell co-stimulation and co-inhibition. Nat Rev Immunol 2013; 13: 227–242.
Tseng SY, Otsuji M, Gorski K, Huang X, Slansky JE, Pai SI et al. B7-DC, a new dendritic cell molecule with potent costimulatory properties for T cells. J Exp Med 2001; 193: 839–846.
Rodig N, Ryan T, Allen JA, Pang H, Grabie N, Chernova T et al. Endothelial expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2 down-regulates CD8(+) T cell activation and cytolysis. Eur J Immunol 2003; 33: 3117–3126.
Ghiotto M, Gauthier L, Serriari N, Pastor S, Truneh A, Nunes JA et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 differ in their molecular mechanisms of interaction with PD-1. Int Immunol 2010; 22: 651–660.
Ishida M, Iwai Y, Tanaka Y, Okazaki T, Freeman GJ, Minato N et al. Differential expression of PD-L1 and PD-L2, ligands for an inhibitory receptor PD-1, in the cells of lymphohematopoietic tissues. Immunol Lett 2002; 84: 57–62.
Shin T, Yoshimura K, Shin T, Crafton EB, Tsuchiya H, Housseau F et al. In vivo costimulatory role of B7-DC in tuning T helper cell 1 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med 2005; 201: 1531–1541.
Wang S, Bajorath J, Flies DB, Dong H, Honjo T, Chen L. Molecular modeling and functional mapping of B7-H1 and B7-DC uncouple costimulatory function from PD-1 interaction. J Exp Med 2003; 197: 1083–1091.
Shin T, Kennedy G, Gorski K, Tsuchiya H, Koseki H, Azuma M et al. Cooperative B7-1/2 (CD80/CD86) and B7-DC costimulation of CD4(+) T cells independent of the PD-1 receptor. J Exp Med 2003; 198: 31–38.
Xiao YP, Yu SH, Zhu BG, Bedoret D, Bu X, Francisco LM et al. RGMb is a novel binding partner for PD-L2 and its engagement with PD-L2 promotes respiratory tolerance. J Exp Med 2014; 211: 943–959.
Bell CH, Healey E, van Erp S, Bishop B, Tang C, Gilbert RJ et al. Structure of the repulsive guidance molecule (RGM)-neogenin signaling hub. Science 2013; 341: 77–80.
Severyn CJ, Shinde U, Rotwein P. Molecular biology, genetics and biochemistry of the repulsive guidance molecule family. Biochem J 2009; 422: 393–403.
Li J, Ye L, Sanders AJ, Jiang WG. Repulsive guidance molecule B (RGMB) plays negative roles in breast cancer by coordinating BMP signaling. J Cell Biochem 2012; 113: 2523–2531.
Kanomata K, Kokabu S, Nojima J, Fukuda T, Katagiri T. DRAGON, a GPI-anchored membrane protein, inhibits BMP signaling in C2C12 myoblasts. Genes Cells 2009; 14: 695–702.
Babitt JL, Huang FW, Wrighting DM, Xia Y, Sidis Y, Samad TA et al. Bone morphogenetic protein signaling by hemojuvelin regulates hepcidin expression. Nat Genet 2006; 38: 531–539.
Xia Y, Cortez-Retamozo V, Niederkofler V, Salie R, Chen S, Samad TA et al. Dragon (repulsive guidance molecule b) inhibits IL-6 expression in macrophages. J Immunol 2011; 186: 1369–1376.
Liu W, Li X, Zhao Y, Meng XM, Wan C, Yang B et al. Dragon (repulsive guidance molecule RGMb) inhibits E-cadherin expression and induces apoptosis in renal tubular epithelial cells. J Biol Chem 2013; 288: 31528–31539.
Busse WW, Lemanske RF Jr. Asthma. N Engl J Med 2001; 344: 350–362.
Baldacci S, Maio S, Cerrai S, Sarno G, Baiz N, Simoni M et al. Allergy and asthma: effects of the exposure to particulate matter and biological allergens. Respir Med 2015; 109: 1089–104.
Kanchongkittiphon W, Gaffin JM, Phipatanakul W. The indoor environment and inner-city childhood asthma. Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2014; 32: 103–110.
Holgate ST. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat Med 2012; 18: 673–683.
Mosmann TR, Moore KW. The role of IL-10 in crossregulation of TH1 and TH2 responses. Immunol Today 1991; 12: A49–A53.
Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Hamid Q. Airway remodelling in asthma. Curr Opin Pharmacol 2010; 10: 236–245.
Steinke JW, Borish L. Th2 cytokines and asthma. Interleukin-4: its role in the pathogenesis of asthma, and targeting it for asthma treatment with interleukin-4 receptor antagonists. Respir Res 2001; 2: 66–70.
Hamelmann E, Gelfand EW. IL-5-induced airway eosinophilia—the key to asthma? Immunol Rev 2001; 179: 182–191.
Hilvering B, Xue L, Pavord ID. Evidence for the efficacy and safety of anti-interleukin-5 treatment in the management of refractory eosinophilic asthma. Ther Adv Respir Dis 2015; 9: 135–145.
Kasaian MT, Miller DK. IL-13 as a therapeutic target for respiratory disease. Biochem Pharmacol 2008; 76: 147–155.
Wills-Karp M. Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Immunol Rev 2004; 202: 175–190.
Neurath MF, Finotto S, Glimcher LH. The role of Th1/Th2 polarization in mucosal immunity. Nat Med 2002; 8: 567–573.
Tang F, Wang F, An, Wang L. X. Upregulation of Tim-3 on CD4(+) T cells is associated with Th1/Th2 imbalance in patients with allergic asthma. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015; 8: 3809–3816.
Luo L, Zhu G, Xu H, Yao S, Zhou G, Zhu Y et al. B7-H3 promotes pathogenesis of autoimmune disease and inflammation by regulating the activity of different T cell subsets. PloS One 2015; 10: e0130126.
Gavett SH, O’Hearn DJ, Li X, Huang SK, Finkelman FD, Wills-Karp M. Interleukin 12 inhibits antigen-induced airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation, and Th2 cytokine expression in mice. J Exp Med 1995; 182: 1527–1536.
Samad TA, Srinivasan A, Karchewski LA, Jeong SJ, Campagna JA, Ji RR et al. DRAGON: a member of the repulsive guidance molecule-related family of neuronal- and muscle-expressed membrane proteins is regulated by DRG11 and has neuronal adhesive properties. J Neurosci 2004; 24: 2027–2036.
Wang SD, Zhu GF, Tamada K, Chen LP, Bajorath J. Ligand binding sites of inducible costimulator and high avidity mutants with improved function. J Exp Med 2002; 195: 1033–1041.
Azuma T, Zhu G, Xu H, Rietz AC, Drake CG, Matteson EL et al. Potential role of decoy B7-H4 in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis: a mouse model informed by clinical data. PLoS Med 2009; 6: e1000166.
McGee HS, Yagita H, Shao Z, Agrawal DK. Programmed death-1 antibody blocks therapeutic effects of T-regulatory cells in cockroach antigen-induced allergic asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2010; 43: 432–442.
Hamelmann E, Schwarze J, Takeda K, Oshiba A, Larsen GL, Irvin CG et al. Noninvasive measurement of airway responsiveness in allergic mice using barometric plethysmography. Am J Resp Crit Care 1997; 156: 766–775.
Kim HY, DeKruyff RH, Umetsu DT. The many paths to asthma: phenotype shaped by innate and adaptive immunity. Nat Immunol 2010; 11: 577–584.
Platts-Mills TA. The role of immunoglobulin E in allergy and asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2001; 164: S1–S5.
Zhang Y, Chung Y, Bishop C, Daugherty B, Chute H, Holst P et al. Regulation of T cell activation and tolerance by PDL2. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2006; 103: 11695–11700.
Acknowledgements
We thank Jingjing Song for support of the lung function assays and Beth Cadugan for editing the manuscript. This study is partially supported by grants from Guangdong Province Innovative Research Program Project (No. 2011Y035), 863 Project grants to Sun Yat-sen University and the United Technologies Corporation endowed chair from Yale University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
LC and XN developed the concept and designed the experiments. WC, YZ, BH, WY, ZW, SG, YZ, LL and SW performed and/or advised the experiments.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
LC is an advisor/board member for Pfizer, AstraZeneca, NextCure, GenomiCare and Vcanbio and received research support from Boehringer Ingelheim, Pfizer and NextCure. LC is also an uncompensated adjunct faculty member of Sun Yat-sen University. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
This article is cited by
-
RNA processing modification mediated subtypes illustrate the distinctive features of tumor microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
Genes & Immunity (2024)
-
Enhanced antitumor immune response in melanoma tumor model by anti-PD-1 small interference RNA encapsulated in nanoliposomes
Cancer Gene Therapy (2022)
-
PD‐L1 and PD‐L2 expression correlated genes in non‐small‐cell lung cancer
Cancer Communications (2019)