Abstract
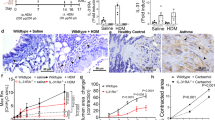
The pro-inflammation factor high-mobility group box protein 1 (HMGB1) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of asthma. In this study, we used a murine model of chronic asthma to evaluate the effects of HMGB1 on airway remodeling. Female BALB/c mice were randomly divided into four groups: control, ovalbumin (OVA) asthmatic, OVA+isotype antibody and OVA+anti-HMGB1 antibody. Anti-HMGB1 antibody therapy was started on day 21 and was administered three times per week for 6 weeks before intranasal challenge with OVA. In this mouse model, HMGB1 expression is significantly elevated. The anti-HMGB1 antibody group exhibited decreased levels of immunoglobulin E (IgE) and inflammatory mediators and reduced inflammatory cell accumulation, airway hyperresponsiveness (AHR), mucus synthesis, smooth muscle thickness and lung collagen content compared with the OVA groups. Treatment with HMGB1 increased proliferation, migration, collagen secretion and α-smooth muscle actin (SMA) expression in MRC-5 cells. Treatment with the HMGB1/IL-1β complex significantly increased the expression and secretion of transforming growth factor (TGF-β1), matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-9 and vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF). Altogether, these results suggest that blocking HMGB1 activity may reverse airway remodeling by suppressing airway inflammation and modulating lung fibroblast phenotype and activation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lotze MT, Tracey KJ . High-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1): nuclear weapon in the immune arsenal. Nat Rev Immunol 2005; 5: 331–342.
Karlsson S, Pettilä V, Tenhunen J, Laru-Sompa R, Hynninen M, Ruokonen E . HMGB1 as a predictor of organ dysfunction and outcome in patients with severe sepsis. Intensive Care Med 2008; 34: 1046–1053.
Taniguchi N, Kawahara K, Yone K, Hashiguchi T, Yamakuchi M, Goto M et al. High mobility group box chromosomal protein 1 plays a role in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis as a novel cytokine. Arthritis Rheum 2003; 48: 971–981.
Hou C, Zhao H, Liu L, Li W, Zhou X, Lv Y et al. High mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) in Asthma: comparison of patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease and healthy controls. Mol Med 2011; 17: 807–815.
Hou CC, Zhao HJ, Cai SX, Liu LY, Shen XB, Mo GW . Expression of high mobility group box-1 in the lung tissue and BALF of asthmatic mice and the influence of dexamethasone. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2010; 30: 2051–2054.
Shim EJ, Chun E, Lee HS, Bang BR, Kim TW, Cho SH et al. The role of high-mobility group box-1 (HMGB1) in the pathogenesis of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2012; 42: 958–965.
Hamada N, Maeyama T, Kawaguchi T, Yoshimi M, Fukumoto J, Yamada M et al. The role of high mobility group box1 in pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2008; 39: 440–447.
Biscetti F, Straface G, de Cristofaro R, Lancellotti S, Rizzo P, Arena V et al. High-mobility group box-1 protein promotes angiogenesis after peripheral ischemia in diabetic mice through a VEGF-dependent mechanism. Diabetes 2010; 59: 1496–1505.
Liu K, Mori S, Takahashi HK, Tomono Y, Wake H, Kanke T et al. Anti-high mobility group box 1 monoclonal antibody ameliorates brain infarction induced by transient ischemia in rat. FASEB J 2007; 21: 3904–3916.
Liang CC, Park AY, Guan JL . In vitro scratch assay: a convenient and inexpensive method for analysis of cell migration in vitro. Nat Protocols 2007; 2: 329–333.
Sugiura H, Liu X, Duan F, Kawasaki S, Togo S, Kamio K et al. Cultured lung fibroblasts from ovalbumin-challenged “asthmatic” mice differ functionally from normal. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2007; 37: 424–430.
Everitt JI, Boreiko CJ, Mangum JB, Martin JT, Iglehart JD, Hesterberg TW . Development of a tracheal implant xenograft model to expose human bronchial epithelial cells to to Xic gases. Toxicol Pathol 1989; 17: 465–473.
Sha Y, Zmijewski J, Xu Z, Abraham E . HMGB1 develops enhanced proinflammatory activity by binding to cytokines. J Immunol 2008; 180: 2531–2537.
Zimmermann N, Conkright JJ, Rothenberg ME . CC chemokine receptor-3 undergoes prolongedligand-induced internalization. J Biol Chem 1999; 274: 12611–12618.
Schleimer RP, Rutledge BK . Cultured human vascular endothelial cells acquire adhesiveness for neutrophils after stimulation with interleukin 1, endotoxin, and tumor-promoting phorbol diesters. J Immunol 1986; 136: 649–654.
Halwani R, Al-Muhsen S, Al-Jahdali H, Hamid Q . Role of transforming growth factor-β in airway remodeling in asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2011; 44: 127–33.
Ohbayashi H, Shimokata K . Matrix metalloproteinase-9 and airway remodeling in asthma. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 2005; 4: 177–181.
Lee CG, Link H, Baluk P, Homer RJ, Chapoval S, Bhandari V et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induces remodeling and enhances TH2-mediated sensitization and inflammation in the lung. Nat Med 2004; 10: 1095–1103.
Lee CC, Lai YT, Chang HT, Liao JW, Shyu WC, Li CY et al. Inhibition of high-mobility group box 1 in lung reduced airway inflammation and remodeling in a mouse model of chronic asthma. Biochem Pharmacol 2013; 86: 940–949.
Hou C, Zhao H, Li W, Cai S . Hydrogen peroxide induces high mobility group box 1 release in human bronchial epithelial cells. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue Xue Bao 2012; 32: 1131–1134.
Ferhani N, Letuve S, Kozhich A, Thibaudeau O, Grandsaigne M, Maret M et al. Expression of high-mobility group box 1 and of receptor for advanced glycatio end products in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2010; 181: 917–927.
Orlova VV, Choi EY, Xie C, Chavakis E, Bierhaus A, Ihanus E et al. A novel pathway of HMGB1-mediated inflammatory cell recruitment that requires Mac-1-integrin. EMBO J 2007; 26: 1129–1139.
Cockcroft DW, Davis BE . Mechanisms of airway hyperresponsiveness. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2006; 118: 551–559.
Elias JA, Zhu Z, Chupp G, Homer RJ . Airway remodeling in asthma. J Clin Invest 1999; 104: 1001–1006.
Lappalainen U, Whitsett JA, Wert SE, Tichelaar JW, Bry K . Interleukin-1beta causes pulmonary inflammation, emphysema, and airway remodeling in the adult murine lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2005; 32: 311–318.
Cho JY, Pham A, Rosenthal P, Miller M, Doherty T, Broide DH . Chronic OVA allergen challenged TNF p55/p75 receptor deficient mice have reduced airway remodeling. Int Immunopharmacol 2011; 11: 1038–1044.
Degryse B, Bonaldi T, Scaffidi P, Müller S, Resnati M, Sanvito F et al. The high mobility group (HMG) boxes of the nuclear protein HMG1 induce chemotaxis and cytoskeleton reorganization in rat smooth muscle cells. J Cell Biol 2001; 152: 1197–1206.
Zhu Z, Homer RJ, Wang Z, Chen Q, Geba GP, Wang J et al. Pulmonary expression of interleukin-13 causes inflammation, mucus hypersecretion, subepithelial fibrosis, physiologic abnormalities, and eotaxin production. J Clin Invest 1999; 103: 779–788.
Tagaya E, Tamaoki J . Mechanisms of airway remodeling in asthma. Allergol Int 2007; 56: 331–340.
Lotfi R, Herzog GI, DeMarco RA, Beer-Stolz D, Lee JJ, Rubartelli A et al. Eosinophils oxidize damage-associated molecular pattern molecules derived from stressed cells. J Immunol 2009; 183: 5023–5031.
Andersson U, Wang H, Palmblad K, Aveberger AC, Bloom O, Erlandsson-Harris H et al. High mobility group 1 protein (HMG-1) stimulates proinflammatory cytokine synthesis in human monocytes. J Exp Med 2000; 192: 565–570.
Park JS, Arcaroli J, Yum HK, Yang H, Wang H, Yang KY et al. Activation of gene expression in human neutrophils by high mobility group box 1 protein. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 2003; 284: C870–C879.
Liu PL, Tsai JR, Hwang JJ, Chou SH, Cheng YJ, Lin FY et al. High-mobility group box 1-mediated matrix metalloproteinase-9 expression in non-small cell lung cancer contributes to tumor cell invasiveness. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2010; 43: 530–538.
Kawahara K, Hashiguchi T, Kikuchi K, Tancharoen S, Miura N, Ito T et al. Induction of high mobility group box 1 release from serotonin-stimulated human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Int J Mol Med 2008; 22: 639–644.
Ye YL, Chuang YH, Chiang BL . Strategies of mucosal immunotherapy for allergic diseases. Cell Mol Immunol 2011; 8: 453–461.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the Scientific Research and Technological Development Program Project of Guangxi Province (10124001A-32), the Young Science Foundation of Guangxi Medical University (GXMUSF201206) and the Innovation Project of Guangxi Graduate Education (YCBZ2013014).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies the paper on Cellular & Molecular Immunology's website (http://www.nature.com/cmi).
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hou, C., Kong, J., Liang, Y. et al. HMGB1 contributes to allergen-induced airway remodeling in a murine model of chronic asthma by modulating airway inflammation and activating lung fibroblasts. Cell Mol Immunol 12, 409–423 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.60
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2014.60