Abstract
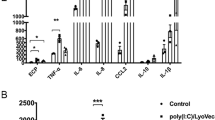
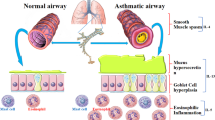
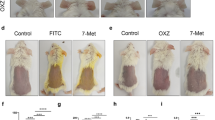
Asthmatic inflammation is mediated by a type 2 helper T cell (Th2) cytokine response, and blocking Th2 cytokine production is proven to have a potent therapeutic effect against asthmatic inflammation. Using IL-4-green fluorescent protein (GFP) reporter mice, we demonstrated that Bavachinin, a single compound isolated from a Chinese herb, significantly inhibited Th2 cytokine production, including IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13. Notably, this compound almost completely blocked inflammation in the ovalbumin (OVA)-sensitized animal asthma model. Furthermore, we demonstrated that this chemical selectively affects the level of GATA-3, most likely by affecting the stability of GATA-3 mRNA. Our results demonstrate, for the first time, the potential therapeutic value of this single compound derived from Chinese herbs.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 digital issues and online access to articles
$119.00 per year
only $9.92 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Iwata A, Nishio K, Winn RK, Chi EY, Henderson WR, Harlan JM . A broad-spectrum caspase inhibitor attenuates allergic airway inflammation in murine asthma model. J Immunol 2003; 170: 3386–3391.
Rodrigo GJ . Inhaled therapy for acute adult asthma. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol 2003; 3: 169–175.
Dhand R . Aerosol therapy for asthma. Curr Opin Pulm Med 2000; 6: 59–70.
Whittaker LA, Lauren C . Recent concepts in the pathogenesis and treatment of asthma [obstructive airways disease]. Clin Pulm Med 2002; 9: 135–144.
Reich DL, Silvay G . Ketamine: an update on the first twenty five years of clinical experience. Can J Anaesth 1989; 36: 186–197.
Youssef-Ahmed MZ, Silver P, Nimkoff L, Sagy M . Continuous infusion of ketamine in mechanically ventilated children with refractory bronchospasm. Intensive Care Med 1996; 22: 972–976.
Sarma VJ . Use of ketamine in acute severe asthma. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 1992; 36: 106–107.
Kung TT, Luo B, CrawIey Y, Garlisi CG, Devito K, Minnicozzi M et al. Effect of anti-mIL-9 antibody on the development of pulmonary inflammation and airway hyperresponsiveness in allergic mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 2001; 25: 600–605.
Gavett SH, Madison SL, Stevens MA, Costa DL . Residual oil fly ash amplifies allergic cytokines, airway responsiveness, and inflammation in mice. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999; 160: 1897–1904.
Morris MJ, Lane DJ . Tidal expiratory flow patterns in airflow obstruction. Thorax 1981; 36: 135–142.
McBride JT . Architecture of the tracheobronchial tree. In: Parent RA (ed.) Treatise on Pulmonary Toxicology: Comparative Biology of the Normal Lung. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press, 1992: 49–61.
Bates JH, Irvin CG . Time dependence of recruitment and derecruitment in the lung: a theoreticaI modeI. J Appl Physiol 2002; 93: 705–713.
Ouyang W, Ranganath SH, Weindel K, Bhattacharya D, Murphy TL, Sha WC et al. Inhibition of Th1 development mediated by GATA-3 through an IL-4-independent mechanism. Immunity 1998; 9: 745–755.
Nakamura Y, Ghaffar O, Olivenstein R, Taha RA, Soussi-Gounni A, Zhang DH et al. Gene expression of the GATA-3 transcription factor is increased in atopic asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 1999; 103: 215–222.
Zhang DH, Yang L, Cohn L, Parkyn L, Homer R, Ray P et al. Inhibition of allergic airway inflammation in a murine model of asthma by expression of a dominant negative mutant of GATA-3. Immunity 1999; 11: 473–482.
Ray A, Cohn L . Th2 cells and GATA-3 in asthma: new insights into the regulation of airway inflammation. J Clin Invest 1999; 104: 985–993.
Szabo SJ, Sullivan BM, Stemmann C, Satoskar AR, Sleckman BP, Glimcher LH et al. Distinct effects of T-bet in Th1 lineage commitment and IFN- production in CD4 and CD8 T cells. Science 2002; 295: 338–342.
Mullen AC, High FA, Hutchins AS, Lee HW, Villarino AV, Livingston DW et al. Role of T-bet in commitment of Th1 cells before IL-12-dependent selection. Science 2001; 292: 1907–1910.
Afkarian M, Sedy JR, Yang J, Jacobson NG, Cereb N, Yang SY et al. T-bet is a STAT1-induced regulator of IL-12R expression in naive CD4+ T cells. Nat Immunol 2002; 3: 549–557.
Nepal M, Choi HJ, Choi BY, Anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activity of Bavachinin by targeting hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Eur J Pharmacol 2012; 691: 28–37.
Sarada DV, Sangeetha S . Psoralea corylifolia linn. (seeds): a phytochemical review. J Pharm Res 2012; 5: 1694.
Veldhoen M, Hirota K, Christensen J, O'Garra A, Stockinger B . Natural agonists for aryl hydrocarbon receptor in culture medium are essential for optimal differentiation of Th17 T cells. J Exp Med 2009; 206: 43–49.
Pan M, Kang I, Craft J, Yin Z . Resistance to development of collagen-induced arthritis in C57BL/6 mice is due to a defect in secondary, but not in primary, immune response. J Clin Immunol 2004; 24: 481–491.
Yin ZN, Chen CH, Szabo SJ, Glimcher LH, Ray A, Craft J . T-bet expression and failure of GATA-3 cross-regulation lead to default production of IFN-g by gd T cells. J Immunol 2002; 168: 1566–1571.
Hitti E, Iakovleva T, Brook M, Deppenmeier S, Gruber AD, Radzioch D et al. Mitogen-activated protein kinase-activated protein kinase 2 regulates tumor necrosis factor mRNA stability and translation mainly by altering tristetraprolin expression, stability, and binding to adenine/uridine-rich element. Mol Cell Biol 2006; 26: 2399–2407.
Wen T, Li Y, Wu M, Sun X, Bao X, Liu Y et al. Therapeutic effects of a novel tylophorine analog, NK-007, on collagen-induced arthritis through suppressing tumor necrosis factor α production and Th17 cell differentiation. Arthritis Rheum 2012; 64: 2896–2906.
Serre K, Mohr E, Gaspal F, Lane PJ, Bird R, Cunningham AF et al. IL-4 directs both CD4 and CD8 T cells to produce Th2 cytokines in vitro, but only CD4 T cells produce these cytokines in response to alum-precipitated protein in vivo. Mol Immunol 2010; 47: 1914–1922.
Ramadas RA, Roche MI, Moon JJ, Ludwig T, Xavier RJ, Medoff BD . CARMA1 is necessary for optimal T cell responses in a murine model of allergic asthma. J Immunol 2011; 187: 6197–6207.
Hong, Lee, Jennifer, Brandon, Richard . Expression patterns of IL-4 and IL-13 define unique functions in allergic immunity. Nature Publishing Group 2011; 13: 58–66.
Kim SH, Kim, Lee . Antiasthmatic Effects of Hesperidin, a Potential Th2 Cytokine Antagonist, in a Mouse Model of Allergic Asthma. MEDIAT INFLAMM 2011; 2011: 1–12.
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (30890143), the Key Program for International S&T Cooperation Projects of China (2010DFB34000) and the National Basic Research Grant of China (2010CB529104) to ZY.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, X., Wen, T., Wei, J. et al. Treatment of allergic inflammation and hyperresponsiveness by a simple compound, Bavachinin, isolated from Chinese herbs. Cell Mol Immunol 10, 497–505 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.27
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/cmi.2013.27
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Bavachinin Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis Inflammation via PPARG/PI3K/AKT Signaling Pathway
Inflammation (2023)
-
Improvement of cytotoxicity of mitoxantrone and daunorubicin by candidone, tephrosin, and bavachinin
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)