Abstract
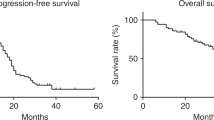
This phase II study evaluates the efficacy and toxicity of a prolonged schedule of oral etoposide in patients with measurable advanced ovarian cancer resistant to, or relapsed following, platinum-based chemotherapy. Forty-seven patients participated, 20 of whom had received more than one prior treatment. Seventy-seven per cent had evidence of disease progression during or within 6 months of the previous chemotherapy. Initially, oral etoposide, 50 mg b.d. (regardless of patient size), was given for 14 days on a 21-day cycle. However, after encountering toxicity, the schedule was modified to 7 days' treatment escalating to 10 then 14 days if well tolerated. Among 41 assessable patients there were two complete and eight partial objective responses (24% response rate; 95% confidence interval 12-41%). Nine further patients (22%) had stable disease, four with a sustained fall of > 50% in CA-125. Median duration of response or stable disease was 35 weeks (range 21-49). Overall median survival was 41 weeks from study entry (range 2 to 96+ weeks). Toxicity for most patients was mild, but sporadic severe myelotoxicity occurred, with two treatment-related deaths. Risk factors for severe toxicity were: performance status 3; hepatic impairment; renal impairment. We conclude that oral etoposide has activity in platinum-resistant ovarian cancer and that it is a useful palliative therapy. It has significant toxicity which may be avoided by appropriate patient selection and an escalating-duration schedule.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seymour, M., Mansi, J., Gallagher, C. et al. Protracted oral etoposide in epithelial ovarian cancer: a phase II study in patients with relapsed or platinum-resistant disease. Br J Cancer 69, 191–195 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.33
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1994.33
This article is cited by
-
Recurrent Ovarian Cancer: When and How to Treat
Current Oncology Reports (2011)
-
Feasibility study of oral cyclophosphamide salvage therapy for the treatment of heavily pretreated patients with recurrent epithelial ovarian cancer
International Journal of Clinical Oncology (2010)
-
Phase I/II study of oral etoposide plus GM-CSF as second-line chemotherapy in platinum-pretreated patients with advanced ovarian cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2005)
-
Pharmacokinetically guided phase I trial of topotecan and etoposide phosphate in recurrent ovarian cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2005)
-
Weekly platinum chemotherapy for recurrent ovarian cancer
British Journal of Cancer (2002)