Abstract
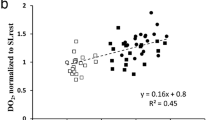
Tumour tissue oxygenation has been measured in man during carbogen breathing (95% O2, 5% CO2) using a commercially available polarographic electrode system (Eppendorf p02 histograph). At least 200 tumour measurements in each of 17 patients with accessible tumours were taken before, and subsequently continuously after the commencement of carbogen breathing for periods of 10 to 30 min. In 12 out of 17 patients studied there was a significant increase in median tumour p02 during the first 10 min of carbogen breathing (range 9 to 1800%). There was an initial rapid increase in tumour p02 which was maintained until 8 to 12 min, but then decreased throughout the subsequent treatment period. Although there was a reduction in the proportion of point measurements < or = 10 mmHg in 11 out of 13 patients, during carbogen breathing, measured points of < or = 2.5 mmHg were only eliminated in three out of 11 tumours. The time course has implications for the planning of clinical trials utilising radiotherapy with carbogen breathing.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Falk, S., Ward, R. & Bleehen, N. The influence of carbogen breathing on tumour tissue oxygenation in man evaluated by computerised p02 histography. Br J Cancer 66, 919–924 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1992.386
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1992.386
This article is cited by
-
Biophysics in tumor growth and progression: from single mechano-sensitive molecules to mechanomedicine
Oncogene (2023)
-
Oxygenation Status of Malignant Tumors vs. Normal Tissues: Critical Evaluation and Updated Data Source Based on Direct Measurements with pO2 Microsensors
Applied Magnetic Resonance (2021)
-
A role for dynamic contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging in predicting tumour radiation response
British Journal of Cancer (2016)
-
Carbogen breathing increases prostate cancer oxygenation: a translational MRI study in murine xenografts and humans
British Journal of Cancer (2009)
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha in high-risk breast cancer: an independent prognostic parameter?
Breast Cancer Research (2004)