Abstract
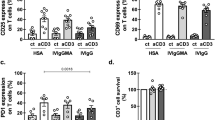
Seventeen patients with terminal malignancy have been entered into a sequential investigation of two doses of continuous infusion recombinant interleukin-2 (bioleukin) given in the setting of a general ward. After an initial experience of a dose of 300 micrograms m-2 in eight patients the remainder received 400 micrograms m-2. Temporary interruption of treatment at the first sign of any serious toxicity led to rapid resolution of side-effects. No patient needed intensive care support, although nine of 17 required temporary interruption of infusion, lasting on average 4 h. Median lymphocyte rebound on day 14 was 3.6 times the pre-treatment level. It remained above pre-treatment levels in four of five patients who had no shown disease progression at day 56 after more than 28 days off treatment. Minor responses occurred in five patients, lasting on average 4 months.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Oliver, R., Crosby, D., Nouri, A. et al. Evaluation of the effect of continuous infusion recombinant interleukin-2 (bioleukin) on peripheral blood leucocytes of patients with terminal malignancy. Br J Cancer 60, 934–937 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.393
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.393