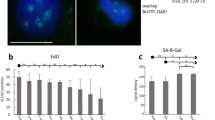
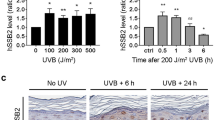
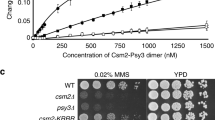
Abstract
WR 1065, 2-[(minopropyl) amino] ethanethiol is an effective scavenger of free radicals. When present during irradiation it reduces cellular DNA damage as analysed by alkaline elution from filters. The same technique indicates that without irradiation, WR 1065 has no effect of DNA integrity. Using nucleoid analysis, where DNA damage is detected at the level of replicon clusters, WR 1065 distorts replicon supercoiling without breaking the DNA molecule. This confirmational change in nucleoid structure occurs with no detectable change in nucleoid protein content. It is proposed that perturbation of replicon supercoiling affects the process of normal DNA synthesis and strand break rejoining, allowing a longer time for the accurate repair of DNA damage.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vaughan, A., Grdina, D., Meechan, P. et al. Conformational changes in chromatin structure induced by the radioprotective aminothiol, WR 1065. Br J Cancer 60, 893–896 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.386
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1989.386
This article is cited by
-
Comments on the mechanisms of action of radiation protective agents: basis components and their polyvalence
SpringerPlus (2014)
-
Amifostine reduces the seminiferous epithelium damage in doxorubicin-treated prepubertal rats without improving the fertility status
Reproductive Biology and Endocrinology (2010)
-
The cytoprotective aminothiol WR1065 activates p21waf-1 and down regulates cell cycle progression through a p53-dependent pathway
Oncogene (2000)
-
Amino acids and their derivatives as radioprotective agents
Amino Acids (1992)