Abstract
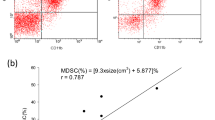
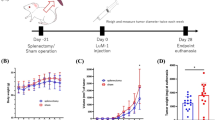
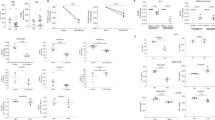
The i.v. injection of high doses (3 mg) of BCG into C3H mice bearing a transplantable 3-methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma caused the regression of a significant proportion. This effect was most evident when the BCG was injected on the day of the graft, or 7 days later. The injection of this agent either 14 days before the graft, or in low doses (0.1 or 0.5 mg), or directly into the tumour (i.t.) only prolonged the survival of the animals. Spleen cells from systemic high-dose BCG-treated mice were found to exert a strong nonspecific cytostatic effect in vitro that was not an artefact of the test conditions, and was not expressed by cells from low-dose animals. The cytostatic effect was shown to be caused by cells with the characteristics of macrophages, i.e. they were strongly adherent, unaffected by treatment with anti-Thy 1.2 + C', radioresistant but heat-sensitive, and were detected in BCG-treated "B" mice. The spleens of high-dose BCG-treated mice also contained suppressor cells that were capable of inhibiting the in vitro reactivity of normal T cells to PHA. Like the cytostatic effect, this suppressor activity was not detected in low-dose mice, and the cells responsible had the properties of macrophages, the effect was lost after the removal of adherent cells by sequential exposure to plastic and colloidal iron, but was conserved after treatment with anti-Thy 1.2 + C'. T-cell-deprived animals, such as "B" or nude mice, also developed suppressor-cell activity when treated with systemic high-dose BCG. Close parallels became evident between the in vivo anti-tumour activity of BCG, the in vitro cytostatic effect, and the suppressor-cell activity. We here discuss the possible role of suppressor cells in the mechanism of action of this agent.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castés, M., Lynch, N., Lespinats, G. et al. Possible role of macrophage-like suppressor cells in the anti-tumour activity of BCG. Br J Cancer 44, 828–837 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.281
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.281
This article is cited by
-
Role of immunotherapy in the prevention of recurrence and invasion of urothelial bladder tumors: a review
World Journal of Urology (1985)
-
The immunologic and immunotherapeutics equelae of intraperitoneal BCG
Irish Journal of Medical Science (1983)