Abstract
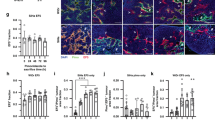
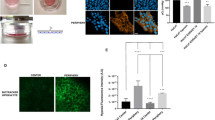
Chronically hypoxic cells were 5 times more resistant to Adriamycin (ADR) than exponentially growing oxic cells. On reoxygenation, resistance decreased slowly to reach the ADR sensitivity of oxic cells after 24 h. With increasing pH, ADR efficiency increased more in oxic than in chronically hypoxic cells. With increasing cell density, ADR efficiency decreased linearly. The differences in ADR efficiency under the various conditions were accompanied by differences in intracellular ADR uptake. Chronically hypoxic cells incorporated 1.6 times less than oxic cells, the incorporation rate at pH 6.5 was half that at pH 7.4; and at a cell density of 5 X 10(5)/bottle the intracellular uptake was 6 times that at 5 X 10(6)/bottle. The observed differences in uptake of ADR were not, however, sufficient to explain the differences in cytotoxicity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Born, R., Eichholtz-Wirth, H. Effect of different physiological conditions on the action of adriamycin on Chinese hamster cells in vitro. Br J Cancer 44, 241–246 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.175
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1981.175
This article is cited by
-
The pH partition theory predicts the accumulation and toxicity of doxorubicin in normal and low-pH-adapted cells
British Journal of Cancer (1999)
-
Effect of pH and moderate hyperthermia on doxorubicin, epirubicin and aclacinomycin A cytotoxicity for Chinese hamster ovary cells
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (1993)
-
Kinetic resistance to anticancer agents
Cytotechnology (1993)
-
Relationship between tumor cell density and drug concentration and the cytotoxic effects of doxorubicin or vincristine: mechanism of inoculum effects
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (1992)
-
The influence of tumor cell density on cellular accumulation of doxorubicin or cisplatin in vitro
Cancer Chemotherapy and Pharmacology (1991)