Abstract
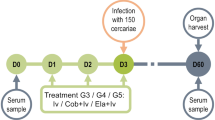
Experiments were conducted to determine whether bladder cancer would develop in primates (Papio sp.) infected with S. haematobium and concurrently exposed to low initiating doses of the bladder carcinogen N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine (BBN). To control for the systemic effects of schistosomiasis, 5 baboons were infected with S. mansoni, which does not lay its eggs in the bladder wall, to control for the effect of the carcinogen alone, 5 others were treated with BBN alone at the rate of 5 or 50 mg/kg per week for the duration of the experiment. Five animals were infected with S. haematobium and had no further treatment, and the main experimental group of 10 baboons was infected with S. haematobium and also treated weekly with 5 mg/kg BBN for up to 2½ years. Four of the 10 animals in the last group, but none in the three control groups developed neoplastic disease of the urothelium. Four animals with S. haematobium plus BBN treatment developed in situ carcinoma in the bladder (3 latent adenomatous lesions and 1 more advanced papillary tumour) and 2 of these animals plus 1 other had slightly dysplastic urothelial endophytic papillary growths of the ureter which penetrated the muscle layer. By contrast, none of the control animals developed urothelial carcinomas, though 4/5 of those with S. haematobium infection alone had inflamed bladders with polypoid lesions, and one individual had endophytic papillary hyperplasia of the ureter. The animals were killed after 2½ years while still relatively immature or adolescent, and it is possible that had they been allowed to survive longer some of the BBN-only group would have developed bladder cancer, and more of the latent lesions seen in the BBN + schistosomiasis group would have progressed to invasive carcinoma. It is postulated that, in this model for human bilharzial bladder cancer, schistosomiasis supplies the proliferative stimulus necessary to accelerate cancer growth from latent tumour foci produced by exposure to low doses of the bladder carcinogen. In areas of endemic schistosomiasis, carcinogenesis might be initiated, for example, by low doses of nitrosamines produced in the urinary tract during bouts of bacteriuria.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 24 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $10.79 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hicks, R., James, C. & Webbe, G. Effect of Schistosoma haematobium and N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine on the development of urothelial neoplasia in the baboon. Br J Cancer 42, 730–755 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.308
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.1980.308
This article is cited by
-
Some actual aspects of tumor induction and promotion
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (1984)