Abstract
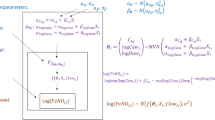
The measurement of exhaled nitric oxide and carbon monoxide concentrations is an emerging method of monitoring airway inflammation longitudinally in community-based studies. Inhaled concentrations of these monoxides influence exhaled concentrations. Little is known about the degree to which inhaled concentrations distort temporal trends in, or estimated effects of air pollutants on, exhaled monoxides. We sought to evaluate whether estimated effects of air pollutants on exhaled monoxides are distorted by trends in indoor and outdoor monoxides, and to characterize determinants of exhaled monoxide concentrations among residents of public housing. In a panel study, 42 residents of public housing provided over 1000 exhaled breath samples. Samples from all subjects were analyzed for nitric oxide; samples from 27 of these subjects were also analyzed for carbon monoxide. The effects of indoor and outdoor monoxide concentrations on exhaled concentrations were quantified. Confounding of associations between particulate matter concentrations and exhaled nitric oxide concentrations was explored. Determinants of exhaled monoxide concentrations among public housing residents are similar to those of other populations. Exhaled monoxide concentrations are more strongly associated with indoor than with outdoor monoxide concentrations. Approximately half of the variability in exhaled monoxide concentrations over time can be explained by changes in indoor monoxide concentrations. Indoor monoxide concentrations can markedly distort both temporal trends in exhaled concentrations as well as estimated effects of particulate matter on exhaled monoxides. Prior estimated effects of particulate matter on exhaled nitric oxide concentrations may have been confounded by nitric concentrations indoors at the time of exhaled air collection. To prevent distortions of longitudinal trends in airway inflammation and estimated health effects of air pollutants, inspiratory scrubber use is necessary but not sufficient to remove the confounding effect of indoor monoxides, and analyses should adjust exhaled monoxide concentrations for concentrations indoors.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamkiewicz G., Ebelt S., Syring M., Slater J., Speizer F.E., Schwartz J., Suh H., and Gold D.R. Association between air pollution exposure and exhaled nitric oxide in an elderly population. Thorax Mar 2004: 59 (3): 204–209.
Anonymous. Recommendations for standardized procedures for the on-line and off-line measurement of exhaled lower respiratory nitric oxide and nasal nitric oxide in adults and children — 1999. This official statement of the American Thoracic Society was adopted by the ATS Board of Directors, July 1999. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1999: 160 (6): 2104–2117.
Anonymous. ATS/ERS Recommendations for Standardized Procedures for the Online and Offline Measurement of Exhaled Lower Respiratory Nitric Oxide and Nasal Nitric Oxide, 2005. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005: 171 (8): 912–930.
Baraldi E., Azzolin N.M., Zanconato S., Dario C., and Zacchello F. Corticosteroids decrease exhaled nitric oxide in children with acute asthma. J Pediatr Sep 1997: 131 (3): 381–385.
Buchvald F., Baraldi E., Carraro S., Gaston B., De Jongste J., Pijnenburg M.W., Silkoff P.E., and Bisgaard H. Measurements of exhaled nitric oxide in healthy subjects age 4 to 17 years. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005: 115 (6): 1130–1136.
Chan C.C., and Wu T.H. Effects of ambient ozone exposure on mail carriers' peak expiratory flow rates. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (6): 735–738.
Corradi M., Pelizzoni A., Majori M., Cuomo A., de' Munari E., and Pesci A. Influence of atmospheric nitric oxide concentration on the measurement of nitric oxide in exhaled air. Thorax 1998: 53 (8): 673–676.
Dennekamp M., Howarth S., Dick C.A., Cherrie J.W., Donaldson K., and Seaton A. Ultrafine particles and nitrogen oxides generated by gas and electric cooking. Occup Environ Med 2001: 58 (8): 511–516.
Deveci S.E., Deveci F., Acik Y., and Ozan A.T. The measurement of exhaled carbon monoxide in healthy smokers and non-smokers. Respir Med 2004: 98 (6): 551–556.
Dorevitch S., Demirtas H., Persky V.W., Erdal S., Conroy L., Schoonover T.M., and Scheff P.A. Demolition of high-rise public housing increases particulate matter air pollution in communities of high-risk asthmatics. J Air Waste Manag Assoc 2006: 56 (7): 1022–1032.
Franklin P.J., Stick S.M., Le Souef P.N., Ayres J.G., and Turner S.W. Measuring exhaled nitric oxide levels in adults: the importance of atopy and airway responsiveness. Chest 2004: 126 (5): 1540–1545.
Horvath I., Donnelly L.E., Kiss A., Paredi P., Kharitonov S.A., and Barnes P.J. Raised levels of exhaled carbon monoxide are associated with an increased expression of heme oxygenase-1 in airway macrophages in asthma: a new marker of oxidative stress. Thorax 1998: 53 (8): 668–672.
Jansen K.L., Larson T.V., Koenig J.Q., Mar T.F., Fields C., Stewart J., and Lippmann M. Associations between health effects and particulate matter and black carbon in subjects with respiratory disease. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (12): 1741–1746.
Jobsis Q., Schellekens S.L., Kroesbergen A., Hop W.C., and de Jongste J.C. Off-line sampling of exhaled air for nitric oxide measurement in children: methodological aspects. Eur Respir J 2001: 17 (5): 898–903.
Jouaville L.F., Annesi-Maesano I., Nguyen L.T., Bocage A.S., Bedu M., and Caillaud D. Interrelationships among asthma, atopy, rhinitis and exhaled nitric oxide in a population-based sample of children. Clin Exp Allergy 2003: 33 (11): 1506–1511.
Kharitonov S.A., Donnelly L.E., Montuschi P., Corradi M., Collins J.V., and Barnes P.J. Dose-dependent onset and cessation of action of inhaled budesonide on exhaled nitric oxide and symptoms in mild asthma. Thorax 2002: 57 (10): 889–896.
Kharitonov S.A., Yates D.H., and Barnes P.J. Inhaled glucocorticoids decrease nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1996: 153 (1): 454–457.
Kharitonov S.A., Yates D., Robbins R.A., Logan-Sinclair R., Shinebourne E.A., and Barnes P.J. Increased nitric oxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Lancet 1994: 343 (8890): 133–135.
Koenig J.Q., Jansen K., and Mar T.F., et al. Measurement of offline exhaled nitric oxide in a study of community exposure to air pollution. Environ Health Perspect 2003: 111 (13): 1625–1629.
Koenig J.Q., Mar T.F., Allen R.W., Jansen K., Lumley T., Sullivan J.H., Trenga C.A., Larson T., and Liu L.J. Pulmonary effects of indoor- and outdoor-generated particles in children with asthma. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (4): 499–503.
Mar T.F., Jansen K., Shepherd K., Lumley T., Larson T.V., and Koenig J.Q. Exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma and short-term PM2.5 exposure in Seattle. Environ Health Perspect 2005: 113 (12): 1791–1794.
McSharry C.P., McKay I.C., Chaudhuri R., Livingston E., Fraser I., and Thomson N.C. Short and long-term effects of cigarette smoking independently influence exhaled nitric oxide concentration in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2005: 116 (1): 88–93.
Nightingale J.A., Maggs R., and Cullinan P., et al. Airway inflammation after controlled exposure to diesel exhaust particulates. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000: 162 (1): 161–166.
Pearson P., Lewis S., Britton J., and Fogarty A. Exhaled carbon monoxide levels in atopic asthma: a longitudinal study. Respir Med 2005: 99 (10): 1292–1296.
Pijnenburg M.W., Bakker E.M., Hop W.C., and De Jongste J.C. Titrating steroids on exhaled nitric oxide in children with asthma: a randomized controlled trial. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2005: 172 (7): 831–836.
Ramirez M., Garcia-Rio F., Vinas A., Prados C., Pino J.M., and Villamor J. Relationship between exhaled carbon monoxide and airway hyperresponsiveness in asthmatic patients. J Asthma 2004: 41 (1): 109–116.
Ricciardolo F.L., Di Maria G.U., Mistretta A., Sapienza M.A., and Geppetti P. Impairment of bronchoprotection by nitric oxide in severe asthma [letter]. Lancet 1997: 350 (9087): 1297–1298.
Smith A.D., Cowan J.O., Brassett K.P., Herbison G.P., and Taylor D.R. Use of exhaled nitric oxide measurements to guide treatment in chronic asthma. N Engl J Med 2005: 352 (21): 2163–2173.
Steerenberg P.A., Nierkens S., van Loveren H., and van Amsterdam J.G. A simple method to sample exhaled NO not contaminated by ambient NO from children and adults in epidemiological studies. Nitric Oxide 2000: 4 (2): 168–174.
Steerenberg P.A., Snelder J.B., Fischer P.H., Vos J.G., van Loveren H., and van Amsterdam J.G. Increased exhaled nitric oxide on days with high outdoor air pollution is of endogenous origin. Eur Respir J 1999: 13 (2): 334–337.
Therminarias A., Flore P., Favre-Juvin A., Oddou M.F., Delaire M., and Grimbert F. Air contamination with nitric oxide: effect on exhaled nitric oxide response. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1998: 157 (3 Part 1): 791–795.
Uasuf C.G., Jatakanon A., James A., Kharitonov S.A., Wilson N.M., and Barnes P.J. Exhaled carbon monoxide in childhood asthma. J Pediatr 1999: 135 (5): 569–574.
Verbeke G., and Molenberghs G. Linear Mixed Models for Longitudinal Data. Springer, New York, 2000.
Wang X.K., and Lu W.Z. Seasonal variation of air pollution index: Hong Kong case study. Chemosphere 2006: 63 (8): 1261–1272.
Yamaya M., Sekizawa K., Ishizuka S., Monma M., Sasaki H., and Yamara M. Exhaled carbon monoxide levels during treatment of acute asthma. Eur Respir J 1999: 13 (4): 757–760.
Yamaya M., Hosoda M., Ishizuka S., Monma M., Matsui T., Suzuki T., Sekizawa K., and Sasaki H. Relation between exhaled carbon monoxide levels and clinical severity of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 2001: 31 (3): 417–422.
Zanconato S., Scollo M., Zaramella C., Landi L., Zacchello F., and Baraldi E. Exhaled carbon monoxide levels after a course of oral prednisone in children with asthma exacerbation. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2002: 109 (3): 440–445.
Zayasu K., Sekizawa K., Okinaga S., Yamaya M., Ohrui T., and Sasaki H. Increased carbon monoxide in exhaled air of asthmatic patients. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 1997: 156 (4 Part 1): 1140–1143.
Zetterquist W., Marteus H., Johannesson M., Nordval S.L., Ihre E., Lundberg J.O., and Alving K. Exhaled carbon monoxide is not elevated in patients with asthma or cystic fibrosis. Eur Respir J 2002: 20 (1): 92–99.
Zipprich J.L., Harris S.A., Fox J.C., and Borzelleca J.F. An analysis of factors that influence personal exposure to nitrogen oxides in residents of Richmond, Virginia. J Expo Anal Environ Epidemiol 2002: 12 (4): 273–285.
Zota A., Adamkiewicz G., Levy J.I., and Spengler J.D. Ventilation in public housing: implications for indoor nitrogen dioxide concentrations. Indoor Air 2005: 15 (6): 393–401.
Acknowledgements
The project described was supported by grant number K-08 ES011302 from the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences, NIH. Its contents are solely those of the author and do not necessarily reflect the official views of the NIEHS, NIH. Many thanks to Greg Washington and Geraldine Penny Walton of the Grand Boulevard Federation, and asthma educators Rev. Otis Prince, Janice Patton, Tamara Williams, Connie Jones, Lawanda Gilmore, Beverly Bishop, and Tammie Slugg; many thanks to Mr. Bob Swinford of the Illinois EPA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dorevitch, S., Demirtas, H., Scheff, P. et al. Bias and confounding in longitudinal measures of exhaled monoxides. J Expo Sci Environ Epidemiol 17, 583–590 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jes.7500545
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jes.7500545
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Noninvasive effects measurements for air pollution human studies: methods, analysis, and implications
Journal of Exposure Science & Environmental Epidemiology (2015)