Abstract
Objective:
To describe growth of prematurely born infants and create a growth chart adequate to assess growth of infants with less than 29 completed weeks of gestation.
Study design:
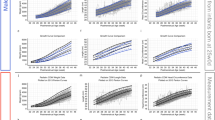
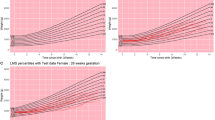
Birth weight, head circumference and length measurements of 7425 liveborn preterm infants from 1985 to 1997 were retrieved from a longitudinal database maintained by the neonatology division. The 3rd, 5th, 10th, 15th, 25th, 50th, 75th, 85th, 90th, 95th and 97th percentiles of each measurement were determined and used for mathematical modeling.
Results:
Birth weight was described with an exponential function while head circumference and length were described with linear functions. A preterm growth chart for the 10th, 50th and 90th percentiles for birth weight, weight growth, head circumference and length was generated.
Conclusion:
The mathematical models of growth provide smooth representations of the percentiles across gestational ages.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- A:
-
constant for birth weight equation
- AGA:
-
appropriate for gestational age
- B:
-
growth velocity for birth weight equation
- BW:
-
birth weight
- C:
-
growth velocity for head circumference equation
- D:
-
growth velocity for length equation
- GA:
-
gestational age
- HC:
-
head circumference
- LEN:
-
length
- LGA:
-
large for gestational age
- NICU:
-
Neonatal Intensive Care Unit
- SGA:
-
small for gestational age
- VUMC:
-
Vanderbilt University Medical Center
- WHO:
-
World Health Organization
References
World Health Organization. A Growth Chart for International Use in Maternal and Child Health Care: Guidelines for Primary Health Care Personnel. World Health Organization: Geneva, 1978.
World Health Organization. Physical Status: The Use and Interpretation of Anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee, Technical Report Series No. 854. World Health Organization: Geneva, 1995; 121–160.
Williams RL, Creasy RK, Cunningham GC, Hawes WE, Norris FD, Tashiro M . Fetal growth and perinatal viability in California. Obstet Gynecol 1982; 59 (5): 624–632.
Lubchenco LO, Hansman C, Dressler M, Boyd E . Intrauterine growth as estimated from liveborn birth-weight data at 24–42 weeks of gestation. Pediatrics 1963; 32: 793–800.
Lubchenco LO, Hansman C, Boyd E . Intrauterine growth in length and head circumference as estimated from live births at gestational ages from 26 to 42 weeks. Pediatrics 1966; 37 (3): 403–408.
Usher R, McLean F . Intrauterine growth of live-born Caucasian infants at sea level: standards obtained from measurements in 7 dimensions of infants born between 25 and 44 weeks of gestation. J Pediatr 1969; 74 (6): 901–910.
Babson SG, Benda GI . Growth graphs for the clinical assessment of infants of varying gestational age. J Pediatr 1976; 89 (5): 814–820.
Engle WA . Age terminology during the perinatal period. Pediatrics 2004; 114 (5): 1362–1364.
Niklasson A, Ericson A, Fryer JG, Karlberg J, Lawrence C, Karlberg P . An update of the Swedish reference standards for weight, length and head circumference at birth for given gestational age (1977–1981). Acta Paediatr Scand 1991; 80 (8–9): 756–762.
Polin RA, Fox WW . Fetal and Neonatal Physiology, Volume 1, WB Sanders: Philadelphia, 1992, p 182.
Akaike H . A new look at the statistical model identification. IEEE Trans Automat Control 1974; 19 (6): 716–723.
Schwarz G . Estimating the dimension of a model. Ann Statist 1978; 6 (2): 461–464.
Hadlock FP, Deter RL, Harrist RB, Park SK . Estimating fetal age: computer-assisted analysis of multiple fetal growth parameters. Radiology 1984; 152 (2): 497–501.
Ott WJ . Accurate gestational dating. Obstet Gynecol 1985; 66 (3): 311–315.
Persson PH, Weldner BM . Reliability of ultrasound fetometry in estimating gestational age in the second trimester. Acta Obstet Gynecol Scand 1986; 65 (5): 481–483.
Dubowitz L . Assessment of gestational age in newborn: a practical scoring system. Arch Dis Child 1969; 44 (238): 782.
Ballard JL, Novak KK, Driver M . A simplified score for assessment of fetal maturation of newly born infants. J Pediatr 1979; 95 (5 Part 1): 769–774.
Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R . New Ballard Score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. J Pediatr 1991; 119 (3): 417–423.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Riddle, W., DonLevy, S., LaFleur, B. et al. Equations describing percentiles for birth weight, head circumference, and length of preterm infants. J Perinatol 26, 556–561 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211572
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jp.7211572
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis to revise the Fenton growth chart for preterm infants
BMC Pediatrics (2013)
-
How Fast Should the Preterm Infant Grow?
Current Pediatrics Reports (2013)
-
Generating expected growth curves and Z-scores for premature infants
Journal of Perinatology (2010)
-
Simultaneous sudden unexpected death in infancy of twins: case report
International Journal of Legal Medicine (2010)