ABSTRACT
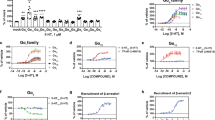
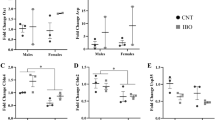
Serotonin is involved in disorders of the central nervous system; thus, specific 5-HT6 receptor antagonists have therapeutic potential. Nevertheless, preclinical tests showed that Ro 65-7199 caused hepatic steatosis. Here, we investigated the hepatic effects of Ro 65-7199 and Ro 66-0074 using toxicogenomics. The profiles obtained after exposure of rats to both compounds clearly show that two pharmacologically closely related compounds with different toxicological profiles can be distinguished based on gene expression profiles. Moreover, side effects can be detected earlier with toxicogenomics than with conventional end points. A possible link between the sterol metabolic pathway, the induction of CYP2B, and the hepatic fat accumulation was also established. Summarizing, gene expression profiles allow both compounds to be distinguished according to their toxicity and provide mechanistic insights. The results clearly show the power of toxicogenomics as a tool for obtaining characteristic fingerprints at early time-points and for generating mechanistic hypotheses.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 6 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $43.17 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ALT:
-
alanine aminotransferase
- AST:
-
aspartate aminotransferase
- γ-GT:
-
γ-glutathione transferase
- 5-HT:
-
serotonin
- LDH:
-
lactate dehydrogenase
- 5-ND:
-
5′-nucleotidase
References
Mossner R, Schmitt A, Syagailo Y, Gerlach M, Riederer P, Lesch KP . The serotonin transporter in Alzheimer's and Parkinson's disease. J Neural Transm Suppl 2000; 60: 345–350.
Saudou F, Hen R . 5-Hydroxytryptamine receptor subtypes in vertebrates and invertebrates. Neurochem Int 1994; 25: 503–532.
Ruat M, Traiffort E, Arrang JM, Tardivel-Lacombe J, Diaz J, Leurs R et al. A novel rat serotonin (5-HT6) receptor: molecular cloning, localization and stimulation of cAMP accumulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 1993; 193: 268–276.
Yoshioka M, Matsumoto M, Togashi H, Mori K, Saito H . Central distribution and function of 5-HT6 receptor subtype in the rat brain. Life Sci 1998; 62: 1473–1477.
Sleight AJ, Monsma Jr FJ, Borroni E, Austin RH, Bourson A . Effects of altered 5-ht6 expression in the rat: functional studies using antisense oligonucleotides. Behav Brain Res 1996; 73: 245–248.
Bourson A, Borroni E, Austin RH, Monsma Jr FJ, Sleight AJ . Determination of the role of the 5-ht6 receptor in the rat brain: a study using antisense oligonucleotides. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 1995; 274: 173–180.
Woolley ML, Bentley JC, Sleight AJ, Marsden CA, Fone KC . A role for 5-ht6 receptors in retention of spatial learning in the Morris water maze. Neuropharmacology 2001; 41: 210–219.
Pennie WD, Kimber I . Toxicogenomics; transcript profiling and potential application to chemical allergy. Toxicol In Vitro 2002; 16: 319–326.
Simmons PT, Portier CJ . Toxicogenomics: the new frontier in risk analysis. Carcinogenesis 2002; 23: 903–905.
Marchant GE . Toxicogenomics and toxic torts. Trends Biotechnol 2002; 20: 329–332.
Novatchkova M, Eisenhaber F . Can molecular mechanisms of biological processes be extracted from expression profiles? Case study: endothelial contribution to tumor-induced angiogenesis. BioEssays 2001; 23: 1159–1175.
de Longueville F, Surry D, Meneses-Lorente G, Bertholet V, Talbot V, Evrard S et al. Gene expression profiling of drug metabolism and toxicology markers using a low-density DNA microarray. Biochem Pharmacol 2002; 64: 137–149.
Waring JF, Ciurlionis R, Jolly RA, Heindel M, Ulrich RG . Microarray analysis of hepatotoxins in vitro reveals a correlation between gene expression profiles and mechanisms of toxicity. Toxicol Lett 2001; 120: 359–368.
Bulera SJ, Eddy SM, Ferguson E, Jatkoe TA, Reindel JF, Bleavins MR et al. RNA expression in the early characterization of hepatotoxicants in Wistar rats by high-density DNA microarrays. Hepatology 2001; 33: 1239–1258.
Hamadeh HK, Bushel PR, Jayadev S, DiSorbo O, Bennett L, Li L et al. Prediction of compound signature using high density gene expression profiling. Toxicol Sci 2002; 67: 232–240.
Fountoulakis M, de Vera M, Crameri F, Boess F, Gasser R, Albertini S et al. Modulation of gene and protein expression by carbon tetrachloride in the rat liver. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2002; 183: 71.
Lian Z, Kluger Y, Greenbaum DS, Tuck D, Gerstein M, Berliner N et al. Genomic and proteomic analysis of the myeloid differentiation program: global analysis of gene expression during induced differentiation in the MPRO cell line. Blood 2002; 100: 3209–3220.
Whysner J, Ross PM, Williams GM . Phenobarbital mechanistic data and risk assessment: enzyme induction, enhanced cell proliferation, and tumor promotion. Pharmacol Ther 1996; 71: 153–191.
Omiecinski CJ, Hassett C, Costa P . Developmental expression and in situ localization of the phenobarbital-inducible rat hepatic mRNAs for cytochromes CYP2B1, CYP2B2, CYP2C6, and CYP3A1. Mol Pharmacol 1990; 38: 462–470.
Hoen PA, Bijsterbosch MK, van Berkel TJ, Vermeulen NP, Commandeur JN . Midazolam is a phenobarbital-like cytochrome P450 inducer in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 2001; 299: 921–927.
Waxman DJ, Walsh C . Cytochrome P-450 isozyme 1 from phenobarbital-induced rat liver: purification, characterization, and interactions with metyrapone and cytochrome b5. Biochemistry 1983; 22: 4846–4855.
Nakayama K, Suwa Y, Mizukami Y, Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y . Cloning and sequencing of a novel rat cytochrome P450 2B-encoding gene. Gene 1993; 136: 333–336.
Suwa Y, Mizukami Y, Sogawa K, Fujii-Kuriyama Y . Gene structure of a major form of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P- 450 in rat liver. J Biol Chem 1985; 260: 7980–7984.
Agrawal AK, Shapiro BH . Phenobarbital induction of hepatic CYP2B1 and CYP2B2: pretranscriptional and post-transcriptional effects of gender, adult age, and phenobarbital dose. Mol Pharmacol 1996; 49: 523–531.
Kawamoto T, Kakizaki S, Yoshinari K, Negishi M . Estrogen activation of the nuclear orphan receptor CAR (constitutive active receptor) in induction of the mouse Cyp2b10 gene. Mol Endocrinol 2000; 14: 1897–1905.
George DK, Crawford DH . Antibacterial-induced hepatotoxicity. Incidence, prevention and management. Drug Saf 1996; 15: 79–85.
Ourlin JC, Handschin C, Kaufmann M, Meyer UA . A link between cholesterol levels and phenobarbital induction of cytochromes P450. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2002; 291: 378–384.
Kocarek TA, Kraniak JM, Reddy AB . Regulation of rat hepatic cytochrome P450 expression by sterol biosynthesis inhibition: inhibitors of squalene synthase are potent inducers of CYP2B expression in primary cultured rat hepatocytes and rat liver. Mol Pharmacol 1998; 54: 474–484.
Yamada H, Matsuki Y, Yamaguchi T, Oguri K . Effect of a ligand selective for peripheral benzodiazepine receptors on the expression of rat hepatic P-450 cytochromes: assessment of the effect in vivo and in a hepatocyte culture system. Drug Metab Dispos 1999; 27: 1242–1247.
Guo GL, Lambert G, Negishi M, Ward JM, Brewer Jr HB, Kliewer SA et al. Complementary roles of Farnesoid X receptor, pregnane X receptor, and constitutive Androstane receptor in protection against bile acid toxicity. J Biol Chem 2003.
Honkakoski P, Negishi M . Regulation of cytochrome P450 (CYP) genes by nuclear receptors. Biochem J 2000; 347(Part 2): 321–337.
Leclercq I, Horsmans Y, Desager JP, Delzenne N, Geubel AP . Reduction in hepatic cytochrome P-450 is correlated to the degree of liver fat content in animal models of steatosis in the absence of inflammation. J Hepatol 1998; 28: 410–416.
Akiyama TE, Ward JM, Gonzalez FJ . Regulation of the liver fatty acid-binding protein gene by hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha (HNF1alpha). Alterations in fatty acid homeostasis in HNF1alpha-deficient mice. J Biol Chem 2000; 275: 27117–27122.
Freneaux E, Labbe G, Letteron P, The Le D, Degott C, Geneve J et al. Inhibition of the mitochondrial oxidation of fatty acids by tetracycline in mice and in man: possible role in microvesicular steatosis induced by this antibiotic. Hepatology 1988; 8: 1056–1062.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Ms Simona Romer for her excellent technical assistance. Special thanks go to Dr Rodolfo Gasser, Prof. Ulrich Certa, and Dr Franziska Boess for the many fruitful scientific discussions and their constant support, as well as for their critical reading of the manuscript. We are also deeply indebted to Dr Martin Neeb, Detlef Wolf, Clemens Broger, and the Bioinformatics group at F Hoffmann-La Roche AG for providing the tools and the assistance that made possible the data analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suter, L., Haiker, M., de Vera, M. et al. Effect of two 5-HT6 receptor antagonists on the rat liver: a molecular approach. Pharmacogenomics J 3, 320–334 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500207
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.tpj.6500207