Abstract
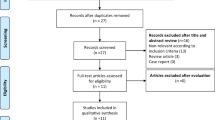
Performing a systematic review and meta-analysis to evaluate the diagnostic performance of the total prostate-specific antigen (tPSA) tests for diagnosis of prostate cancer among Chinese. Literatures related to diagnosis of prostate cancer by tPSA and the ratio of free to total PSA (f/tPSA) being retrieved in five electronic databases. Sensitivity, specificity, positive likelihood ratio, negative likelihood ratio and diagnostic odds ratio (DOR) were pooled using random effects models. Summary receiver operating characteristic curves (SROC) used to summarize overall test performance. In total 10 studies meting the inclusion criteria, 2256 patients were included. Among them 423 were patients of prostate cancer compared to 1833 were patients of benign prostate hyperplasia (BPH). The pooled sensitivity and specificity of tPSA>4.0 ng/ml, tPSA>10.0 ng/ml and f/tPSA<0.15 as threshold for the diagnosis of prostate cancer were heterogeneity. The areas under SROC (AUC) were 80, 85 and 87%, respectively (P<0.05). The pooled DOR were 8.44(95%CI: 4.45∼16.00), 9.94(95%CI: 4.15∼23.77) and 13.75(95%CI: 6.35∼29.76), respectively (P<0.05). χ2 test used for testing the heterogeneity. tPSA and f/tPSA made an important performance for diagnosis of prostate cancer in decade among Chinese. The use of f/tPSA<0.15 as threshold maintain a high prognostic accuracy for prostate cancer.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 4 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $64.75 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlay J, Bray F, Pisani P, Parkin DM . Globocan 2000: Cancer Incidence, Mortality and Prevalence Worldwide, Version 1.0. IARC Press: Lyon, 2001. http://www.iarc.fr/globocan/globocan.html (accessed June 2003).
Gao HW, Li YL, Wu SH, Wang SH, Zhang HF, Pan YZ et al. Mass screening of prostate cancer in a Chinese population: the relationship between pathological features of prostate cancer and serum prostate specific antigen. Asian J Androl 2005; 7: 159–163.
Nadler RB, Humphrey PA, Smith DS, Catalona WJ, Ratliff TL . Effect of inflammation and benign prostatic hyperplasia on elevated serum prostate-specific antigen levels. J Urol 1995; 154: 407–413.
Whiting P, Rutjes AW, Reitsma JB, Bossuyt PM, Kleijnen J . The development of QUADAS: a tool for the quality assessment of studies of diagnostic accuracy included in systematic reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol 2003; 3: 25.
Zamora J, Muriel A, Abraira V . Meta-Disc for Windows: A Software package for the Meta-analysis of Diagnostic Tests. XI Cochrane Colloquium Barcelona, 2003. http://www.hrc.es/investigacion/metadisc_en.html (accessed July 2005).
Zhang XC, Na YQ, Guo YL . Role of prostate specific antigen in the diagnosis of prostate carcinoma. Chin J Urol 2000; 21: 37–40 (in Chinese).
Ma LT, Wang YW, Li YP, Li Y, Wang XQ, Ni YY . The role of the ratio of free PSA and total PSA in diagnosing prostate carcinoma. J Xi'an Med Univ 2002; 23: 180–181 (in Chinese).
Zhou LQ, Chen WM, Na YQ, Huang YY, Feng T, Hao JR et al. Serum total PSA and the ratio of free to total PSA in patients of benign prostate hyperplasia and prostate cancer. Chin J Urol 2002; 23: 354–357 (in Chinese).
Huang X, Pan CK, Fu BQ, Qiu MX, Liao Y . Role of PSA, PSAD and fPSA/tPSA in diagnosis of prostate cancer. Med J West China 2003; 1: 13–15 (in Chinese).
Lin Y, Li LM, Qiang WM, Yu ST, Yan H, Hu ZD . The percentage of free to total prostate specific antigen used in detecting prostate cancer. Clin cancer China 2003; 30: 252–254 (in Chinese).
Zhu YK, Zhang Y, Yang GH, Quan TT, Qu L . The use and analysis of free to total prostate specific antigen for prostate diseases. Med J Practice 2003; 19: 866–867 (in Chinese).
Liu ZJ, Chen BH, Chen SA . The role of the ratio of free PSA and total PSA in diagnosis of prostate cancer. J Pract Med Tech 2004; 11: 569–571 (in Chinese).
Gao ZW, Liu G, Sheng BW . Changes of serum total PSA and free PSA in patients with prostate carcinoma and benign prostate hyperplasia. Chin J Cancer 2004; 23: 701–703 (in Chinese).
Guan LM, Li SJ . Detecting free to total prostate specific antigen for the diagnosis of prostate carcinoma. J Dalian Med Univ 2005; 27: 54–56 (in Chinese).
Chen GJ, Lu JH, Yang Y, Dong CL . Serum tPSA, f/t ratio in diagnosis of prostate cancer and its positive alarm value. Med J CPAPF 2005; 16: 174–176 (in Chinese).
Roddam AW, Duffy MJ, Hamdy FC, Ward AM, Patnick J, Price CP et al. Use of prostate-specific antigen (PSA) isoforms for the detection of prostate cancer in men with a PSA level of 2–10 ng/ml: systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur Urol 2005; 48: 386–399.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Y., Sun, G., Pan, J. et al. Performance of tPSA and f/tPSA for prostate cancer in Chinese. A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis 9, 374–378 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500906
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.pcan.4500906
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
An overview of prostate diseases and their characteristics specific to Asian men
Asian Journal of Andrology (2012)