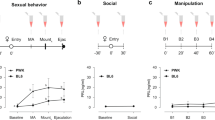
Abstract
It is well recognized that sexual stimulation leading to penile erection is controlled by different areas in the brain. Animal erection studies have shown that apomorphine (a D2>D1 dopamine receptors nonselective agonist) seems to act on neurons located within the paraventricular nucleus and the medial preoptic area of the hypothalamus. Yet, only recently, was a centrally acting agent, apomorphine sublingual, approved for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. The present functional magnetic resonance imaging placebo-controlled study presents the first in vivo demonstration of the apomorphine-induced modulation of cortical and subcortical brain structures in patients with psychogenic erectile dysfunction. Noteworthy, patients in comparison with potent controls, showed an increased activity in frontal limbic areas that was downregulated by apomorphine. This suggests that psychogenic impotence may be associated with previously unrecognized underlying functional abnormalities of the brain.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 8 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $32.38 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Melis MR, Argiolas A . Dopamine and sexual behavior. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 1999; 19: 19–38.
Drolet G, Adams M, Heaton JPW . Evidence for the central sites of action of apomorphine-induced erections. Int J Impot Res 1996; 8: 108.
Dominguez J, Riolo JV, Xu Z, Hull EM . Regulation by the medial amygdala of copulation and medial preoptic dopamine release. J Neurosci 2001; 21: 349–355.
Melis MR, Argiolas A, Gessa GL . Apomorphine-induced penile erection and yawning: site of action in brain. Brain Res 1987; 415: 98–104.
Melis MR, Stancampiano R, Argiolas A . Hippocampal oxytocin mediates apomorphine-induced penile erection and yawning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1992; 42: 61–66.
Argiolas A, Melis MR . Neuromodulation of penile erection: an overview of the role of neurotransmitters and neuropeptides. Prog Neurobiol 1995; 47: 235–255.
Chen KK, Chan SH, Chang LS . Dopaminergic neurotransmission at the paraventricular nucleus of hypothalamus in central regulation of penile erection in the rat. J Urol 1999; 162: 237–242.
Giuliano F, Rampin O . Central neural regulation of penile erection. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2000; 24: 517–533.
Heaton JPW . Central neuropharmacological agents and mechanisms in erectile dysfunction: the role of dopamine. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 2000; 24: 561–569.
Argiolas A, Hedlund H . The pharmacology and clinical pharmacokinetics of apomorphine SL. Br J Urol 2001; 88(Suppl 3): 18–21.
Rampin O, Giuliano F . Brain control of penile erection. World J Urol 2001; 19: 1–8.
Park K et al. Blood-oxygenation-level-dependent functional magnetic resonance imaging for evaluating cerebral regions of female sexual arousal response. Urology 2001; 57: 1189–1194.
Park K et al. A new potential of blood oxygenation level dependent (BOLD) functional MRI for evaluating cerebral centers of penile erection. Int J Impot Res 2001; 13: 73–81.
Friston KJ et al. Statistical parametric maps in functional imaging: a general approach. Hum Brain Mapp 1995; 2: 189–210.
Stoleru S et al. Neuroanatomical correlates of visually evoked sexual arousal in human males. Arch Sex Behav 1999; 28: 1–21.
Redoute J et al. Brain processing of visual sexual stimuli in human males. Hum Brain Mapp 2000; 11: 162–177.
Karama S et al. Areas of brain activation in males and females during viewing of erotic film excerpts. Hum Brain Mapp 2002; 16: 1–13.
Argiolas A, Melis MR, Mauri A, Gessa GL . Paraventricular nucleus lesion prevents yawning and penile erection induced by apomorphine and oxytocin but not by ACTH in rats. Brain Res 1987; 421: 349–352.
Rajfer J et al. Nitric oxide as a mediator of relaxation of the corpus cavernosum in response to nonadrenergic, noncholinergic neurotransmission. N Engl J Med 1992; 326: 90–94.
Melis MR et al. Role of nitric oxide in the control of penile erection and yawning. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 1997; 21: 899–922.
Andersson KE . Neurophysiology/pharmacology of erection. Int J Impot Res 2001; 13(Suppl 3): S8–S17.
Melis MR, Succu S, Iannucci U, Argiolas A . Oxytocin increases nitric oxide production in the paraventricular nucleus of the hypothalamus of male rats: correlation with penile erection and yawning. Regul Pept 1997; 69: 105–111.
Wagner G, Mulhall J . Pathophysiology and diagnosis of male erectile dysfunction. Br J Urol Int 2001; 88 (Suppl. 3): 3–10.
Bocher M et al. Cerebral activation associated with sexual arousal in response to a pornographic clip: a 15O-H2O PET study in heterosexual men. Neuroimage 2001; 14: 105–117.
Arnow BA et al. Brain activation and sexual arousal in healthy, heterosexual males. Brain 2002; 125: 1014–1023.
Tiihonen J et al. Increased in cerebral blood flow of right prefrontal cortex in man during orgasm. Neurosci Lett 1994; 170: 241–243.
Kapur S et al. Activation of specific cortical regions by apomorphine: an [15O]H2O PET study in humans. Neurosci Lett 1994; 176: 21–24.
Grasby P et al. The effect of the dopamine agonist, apomorphine, on regional cerebral blood flow in normal volunteers. Psychol Med 1993; 23: 605–612.
Gaspar P et al. Catecholamine innervation of the human cerebral cortex as revealed by comparative immunohistochemistry of tyrosine hydroxylase and dopamine-beta.hydroxylase. J Comput Neurol 1989; 279: 249–271.
Beck T et al. Alterations in regional energy metabolism in rat brain produced by small and by large doses of apomorphine: possible relations to autoreceptors. Eur J Pharmacol 1987; 139: 139–146.
Nguyen TV et al. Detection of the effects of dopamine receptor supersensitivity using pharmacological MRI and correlations with PET. Synapse 2000; 36: 57–65.
Schwarting RK, Huston JP . Behavioral concomitants of regional changes in the brain's biogenic amines after apomorphine and amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 1992; 41: 675–682.
Acknowledgements
We thank Ing. Massimo Danna for helping in data analysis. This study was supported by an unrestricted grant from Takeda Italia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Montorsi, F., Perani, D., Anchisi, D. et al. Apomorphine-induced brain modulation during sexual stimulation: a new look at central phenomena related to erectile dysfunction. Int J Impot Res 15, 203–209 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900999
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.ijir.3900999
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Aberrant baseline brain activity in psychogenic erectile dysfunction patients: a resting state fMRI study
Brain Imaging and Behavior (2018)
-
Inhibitory brainstem reflexes under external emotional-stimuli in bipolar I and II disorders
BMC Psychiatry (2017)
-
Sex for fun: a synthesis of human and animal neurobiology
Nature Reviews Urology (2012)
-
The effects of dopamine receptor agonists on BKCa channels and signal transduction mechanism in corpus cavernosal smooth muscle cells
International Journal of Impotence Research (2008)
-
Asexuality: Classification and Characterization
Archives of Sexual Behavior (2007)