Abstract
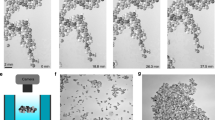
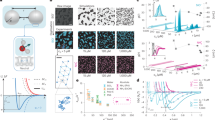
Suspensions of colloidal particles form a variety of ordered planar structures at an interface in response to an a.c. or d.c. electric field applied normal to the interface1–3. This field-induced pattern formation can be useful, for example, in the processing of materials. Here we explore the origin of the ordering phenomenon. We present evidence suggesting that the long-ranged attraction between particles which causes aggregation is mediated by electric-field-induced fluid flow. We have imaged an axially symmetric flow field around individual particles on a uniform electrode surface. The flow is induced by distortions in the applied electric field owing to inhomogeneities in the 'double layer' of ions and counterions at the electrode surface. The beads themselves can create these inhomogeneities, or alternatively, we can modify the electrode surfaces by lithographic patterning so as to introduce specified patterns into the aggregated structures.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Richetti, F., Prost, J. & Barois, P. J. Phys. Lett. 45, L1137–L1143 (1984).
Giersig, M. & Mulvaney, P. Langmuir 9, 3408–3413 (1993); J. Phys. Chem. 97, 6334–6336 (1993).
Trau, M., Saville, D. A. & Aksay, I. A. Science 272, 706–709 (1996).
Seul, M. & Murray, C. A. Science 262, 558–560 (1993).
Seul, M. & Chen, V. S. Phys. Rev. Lett. 70, 1658–1661 (1993).
Seul, M. & Andelman, D. Science 267, 476–484 (1995).
Hurley, M. M. & Singer, S. J. J. Phys. Chem. 96, 1951–1956 (1992).
Dukhin, S. S. & Derjaguin, B. V. Surface and Colloid Science Vol. 7 (ed. Matijević, E.) (Wiley, New York, 1974).
Russell, W. B., Saville, D. A. & Schowalter, W. R. Colloidal Dispersions (Cambridge Univ. Press, 1989).
Anderson, J. L. Annu. Rev. Fluid Mech. 21, 61–99 (1989).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, SR., Seul, M. & Shraiman, B. Assembly of ordered colloidal aggregrates by electric-field-induced fluid flow. Nature 386, 57–59 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/386057a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/386057a0
This article is cited by
-
Electrically controlled growths of 4-N,N-dimethylamino-4′-N′-methyl-stilbazolium tosylate (DAST) organic microcrystals
Applied Physics A (2020)
-
Effect of particles size on the characteristics of wet deposits during electrophoretic deposition
Journal of Electroceramics (2018)
-
Emergent vortices in populations of colloidal rollers
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Molecular Nanoshearing: An Innovative Approach to Shear off Molecules with AC-Induced Nanoscopic Fluid Flow
Scientific Reports (2014)
-
Electrophoretic deposition of titania nanoparticles: Wet density of deposits during EPD
Bulletin of Materials Science (2014)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.