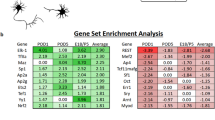
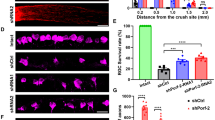
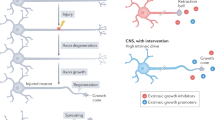
Abstract
Most neurons of the mammalian central nervous system (CNS) lose the ability to regenerate severed axons in vivo after a certain point in development1. At least part of this loss in regenerative potential is intrinsic to neurons2–4. Although embryonic retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) can grow axons into tectum of any age, most RGCs from older animals fail to extend axons into CNS tissue derived from donors of any age, including the embryonic tectum2. Here we report that the proto-oncogene bcl-2 plays a key role in this developmental change by promoting the growth and regeneration of retinal axons. This effect does not seem to be an indirect consequence of its well-known anti-apoptotic activity. Another anti-apoptotic drug, ZVAD, supported neuronal survival but did not promote axon regeneration in culture. This finding could lead to new strategies for the treatment of injuries to the CNS.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aubert, I., Ridet, J.-L. & Gage, F. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5, 625–635 (1995).
Chen, D. F., Jhaveri, S. & Schneider, G. E. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 92, 7287–7291 (1995).
Shewan, D., Berry, M. & Cohen, J. J. Neurosci. 15, 2057–2062 (1995).
Aigner, L. et al. Cell 83, 269–278 (1995).
Perry, V. H., Henderson, Z. & Linden, R. J. Comp. Neurol. 219, 3546–3568 (1983).
Veis, D. J., Sorenson, C. M., Shutter, J. R. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Cell 75, 229–240 (1993).
Martinou, J.-C. et al. Neuron 13, 1017–1030 (1994).
Dubois-Dauphin, M., Frankowski, H., Tsujimoto, Y., Huarte, J. & Martinou, J.-C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 3309–3313 (1994).
Schnell, L. & Schwab, M. E. Nature 343, 269–272 (1990).
Angelucci, A., Clascá, F. & Sur, M. J. Neurosci. Methods 65, 101–112 (1996).
Misantone, L. J., Gershenbaum, M. & Murray, M. J. Neurocytol. 13, 449–465 (1984).
Davies, A. M. Trends Neurosci. 18, 355–358 (1995).
Korsmeyer, S. J. Immunol. Today 13, 285–288 (1992).
Gagliardini, V. et al. Science 263, 826–828 (1994).
Miura, M., Zhu, H., Rotello, R., Hartwieg, E. A. & Yuan, J. Cell 75, 653–660 (1993).
Henkart, P. A. Immunity 4, 195–201 (1996).
Nicholson, D. W. et al. Nature 376, 37–43 (1995).
Fletcher, D. S. et al. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 15, 243–248 (1995).
Mansour-Robaey, S., Clarke, D. B., Wang, Y. C., Bray, G. M. & Aguayo, A. J. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 91, 1632–1636 (1994).
Sagot, Y., Tan, S. A., Hammang, J. P., Aebischer, P. & Kato, A. C. J. Neurosci. 16, 2335–2341 (1996).
Dusart, I. & Sotelo, C. J. Comp. Neurol. 347, 211–232 (1994).
Young, R. W. J. Comp. Neurol. 229, 362–373 (1984).
Merry, D. E., Veis, D. J., Hickey, W. F. & Korsmeyer, S. J. Development 120, 301–311 (1994).
Michaelidis, T. M. et al. Neuron 17, 75–89 (1996).
Zhang, K.-Z., Westberg, J. A., Hölttä, E. & Andersson, L. C. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. USA 93, 4504–4508 (1996).
Fernandez-Sarabia, M. J. & Bischoff, J. R. Nature 366, 274–275 (1993).
Wang, H.-G. et al. Oncogene 9, 2751–2756 (1994).
Greene, L. A. & Kaplan, D. R. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 5, 579–587 (1995).
Meyer-Franke, A., Kaplan, M. R., Pfrieger, F. W. & Barres, B. A. Neuron 15, 805–819 (1995).
Barres, B. A. et al. Cell 70, 31–46 (1992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, D., Schneider, G., Martinou, JC. et al. Bcl-2 promotes regeneration of severed axons in mammalian CNS. Nature 385, 434–439 (1997). https://doi.org/10.1038/385434a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/385434a0
This article is cited by
-
hBcl2 overexpression in BMSCs enhances resistance to myelin debris-induced apoptosis and facilitates neuroprotection after spinal cord injury in rats
Scientific Reports (2024)
-
Caspase dependent apoptosis is required for anterior regeneration in Aeolosoma viride and its related gene expressions are regulated by the Wnt signaling pathway
Scientific Reports (2020)
-
Bcl-2 Overexpression Induces Neurite Outgrowth via the Bmp4/Tbx3/NeuroD1 Cascade in H19-7 Cells
Cellular and Molecular Neurobiology (2020)
-
MTP18 is a Novel Regulator of Mitochondrial Fission in CNS Neuron Development, Axonal Growth, and Injury Responses
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
Associations of Bcl-2 rs956572 genotype groups in the structural covariance network in early-stage Alzheimer’s disease
Alzheimer's Research & Therapy (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.