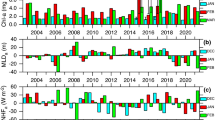
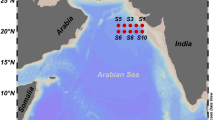
Abstract
THE Arabian Sea is one of the most biologically productive ocean regions1, mainly due to the upwelling of nutrients during the summer (southwest) monsoon. But the northern Arabian Sea continues to sustain fairly high biological production after the upwelling season and during much of the winter (northeast) monsoon2–4. The processes that enable this high winter productivity have hitherto been poorly understood, being variously attributed to surface cooling effects2,3 or wind-driven changes in ocean circulation4. Here we present physical, chemical and biological data that indicate that sea surface cooling drives convection processes that lead to the injection of nutrients up into the surface waters of the northeastern Arabian Sea during winter, and that this mechanism of nutrient supply is a dominant control on winter productivity. Observed seasonal changes in bacterial and microzooplankton populations may provide an explanation for the Arabian Sea 'paradox'5–8 that mesozooplank-ton biomass remains more or less invariable throughout the year.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ryther, J. H. & Menzel, D. W. Deep-Sea Res. 12, 199–209 (1965).
Banse, K. & McClain, C. R. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 34, 201–211 (1986).
Banse, K. & English, D. C. Mar. Res. 2, 83–103 (1993).
Yentsch, C. S. & Phinney, D. A. in Oceanography of the Indian Ocean (ed. Desai, B. N.) 57–66 (Oxford & IBH, New Delhi, 1992).
Smith, S. L. et al. Arabian Sea Process Study (Planning Rep. No. 13, US JGOFS, Woods Hole, Massachusetts, 1991).
Madhupratap, M., Haridas, P., Ramaiah, N. & Achuthankutty, C. T. in Oceanography of the Indian Ocean (ed. Desai, B. N.) 99–112 (Oxford & IBH, New Delhi, 1992).
Baars, M. A. et al., in Monsoons and Pelagic Systems (ed. Baars, M. A.) 13–34 (Natl Museum Nat. Hist., Leiden, 1994).
van Couwelaar, M. & Schalk, P. H. in Arabian Sea Workshop (abstr.) (Netherlands Inst. for Sea Res.,Texel, 1995).
Sen Gupta, R. & Naqvi, S. W. A. Deep-Sea Res. 31, 671–706 (1984).
Hastenrath, S. & Lamb, P. Climatic Atlas of the Indian Ocean. Part I, Surface Climate and Atmospheric Circulation (Univ. Wilconsin Press, 1979).
Radhakrisna, K., Devassy, V. P., Bhattathiri, P. M. A. & Bhargava, R. M. S. Indian J. Mar. Sci. 7, 137–139 (1978).
Radhakrisna, K., Devassy, V. P., Bhargava, R. M. S. & Bhattathiri, P. M. A. Indian J, Mar. Sci. 7, 271–275 (1978).
Owens, N. J. P. et al. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 697–709 (1993).
Chapman, D. W., Marra, J. & Takahashi, T. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 151–169 (1993).
Harrison, W. J. et al. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 279–305 (1993).
Ducklow, H. W., Kirchman, D. L., Quinby, H. L., Carlson, C. A. & Dam, H. G. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 245–263 (1993).
Lochte, K., Ducklow, H. W., Fasham, M. J. R. & Stienen, C. Deep-Sea Res. II 40, 91–114 (1993).
Azam, F. et al. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 10, 257–263 (1983).
Christoffersen, K., Riemann, B., Hansen, L. R., Klysner, A. & Sorensen, H. B. Microb. Ecol. 20, 253–272 (1990).
Painting, S. J., Moloney, C. L. & Lucas, M. I. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 100, 55–69 (1993).
Bunker, A. F. Mon. Weath. Rev. 104, 1122–1140 (1970).
Ramesh Kumar, M. R. & Prasad, T. G. J. Geophys. Res. (in the press).
Woodruff, S. D., Sultz, R. J., Jenne, R. L. & Steuer, P. M. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 68, 1239–1250 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Madhupratap, M., Kumar, S., Bhattathiri, P. et al. Mechanism of the biological response to winter cooling in the northeastern Arabian Sea. Nature 384, 549–552 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/384549a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/384549a0
This article is cited by
-
Enhanced phytoplankton bloom triggered by atmospheric high-pressure systems over the Northern Arabian Sea
Scientific Reports (2023)
-
Interlinking diatom frustule diversity from the abyss of the central Arabian Sea to surface processes: physical forcing and oxygen minimum zone
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2023)
-
A study on microzooplankton community from the coastal waters of eastern Arabian Sea: emphasis on the dominance of heterotrophic dinoflagellates
Environmental Monitoring and Assessment (2023)
-
Significance of Physico-Chemical and Biological Parameters on Spatio-Temporal PCO2 Distribution in the Northeastern Indian Ocean
Journal of the Indian Society of Remote Sensing (2023)
-
Phytoplankton community shift in response to experimental Cu addition at the elevated CO2 levels (Arabian Sea, winter monsoon)
Environmental Science and Pollution Research (2023)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.