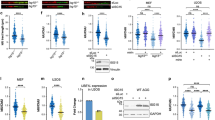
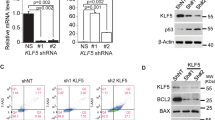
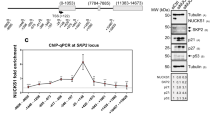
Abstract
NORMALLY growing cells promptly cease DNA synthesis when exposed to genotoxic stresses, such as radiation, and this cell-cycle arrest prevents the accumulation of mutations1,2. The transcription factor interferon regulatory factor (IRF)-1 is essential for the regulation of the interferon system3–5, inhibits cell growth, and manifests tumour-suppressor activities6,7. Here we show that mouse embryonic fibroblasts (EFs) lacking IRF-1 are deficient in their ability to undergo DNA-damage-induced cell-cycle arrest. A similar phenotype has been observed in EFs lacking the tumour suppressor p53 (refs 8, 9), although the expression of IRF-1 and p53 are independent of one another. Furthermore, we show that transcriptional induction of the gene encoding p21 (WAF1, CIP1)10–12 a cell-cycle inhibitor, by γ-irradiation is dependent on both p53 and IRF-1, and that the p21 promoter is activated, either directly or indirectly, by both in a transient cotransfection assay. These two tumour-suppressor transcription factors therefore converge functionally to regulate the cell cycle through the activation of a common target genes.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hartwell, L. Cell 71, 543–546 (1992).
Hunter, T. & Pines, J. Cell 79, 573–582 (1994).
Matsuyama, T. et al. Cell 75, 83–97 (1993).
Kamijo, R. et al. Science 263, 1612–1615 (1994).
Kimura, T. et al. Science 264, 1921–1924 (1994).
Tanaka, N. et al. Cell 77, 829–839 (1994).
Tamura, T. et al. Nature 376, 596–599 (1995).
Vogelstein, B. & Kinzler, K. W. Cell 70, 523–526 (1992).
Liebermann, D. A., Hoffman, B. & Steinman, R. A. Oncogene 11, 199–210 (1995).
El-Deiry, W. S. et al. Cell 75, 817–825 (1993).
Harper, J. W., Adami, G. R., Wei, N., Keyomarsi, K. & Elledge, S. J. Cell 75, 805–816 (1993).
Xiong, Y. et al. Nature 366, 701–704 (1993).
Lowe, S. W., Ruley, H. E., Jacks, T. & Housman, D. E. Cell 74, 957–967 (1993).
Sherr, C. J. & Roberts, J. M. Genes Dev. 9, 1149–1163 (1995).
Brugarolas, J. et al. Nature 377, 552–557 (1995).
Darnell Jr, J. E., Kerr, I. M. & Stark, G. R. Science 264, 1415–1421 (1994).
Chin, Y. E. et al. Science 272, 719–722 (1996).
Meraz, M. A. et al. Cell 84, 431–442 (1996).
Durbin, J. E., Hackenmiller, R., Simon, M. C. & Levy, D. E. Cell 84, 443–450 (1996).
Kastan, M. B., Onyekwere, O., Sidransky, D., Vogelstein, B. & Craig, R. W. Cancer Res. 51, 6304–6311 (1991).
El-Deiry, W. S. et al. Cancer Res. 54, 1169–1174 (1994).
El-Deiry, W. S. et al. Cancer Res. 55, 2910–2919 (1995).
Parker, S. B. et al. Science 267, 1024–1027 (1995).
Halevy, O. et al. Science 267, 1018–1021 (1995).
Cross, S. M. et al. Science 267, 1353–1356 (1995).
Willman, C. L. et al. Science 259, 968–971 (1993).
Matsushime, H. et al. Molec. Cell Biol. 14, 2066–2076 (1994).
Harada, H. et al. Science 259, 971–974 (1993).
Baker, S. J., Markowitz, S., Fearon, E. R., Willson, J. K. V. & Vogelstein, B. Science 249, 912–915 (1990).
Haupt, Y., Rowan, S., Shaulian, E., Vousden, K. H. & Oren, M. Genes Dev. 9, 2170–2183 (1995).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tanaka, N., Ishihara, M., Lamphier, M. et al. Cooperation of the tumour suppressors IRF-1 and p53 in response to DNA damage. Nature 382, 816–818 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/382816a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/382816a0
This article is cited by
-
Identification of loci associated with susceptibility to bovine paratuberculosis and with the dysregulation of the MECOM, eEF1A2, and U1 spliceosomal RNA expression
Scientific Reports (2021)
-
A rapid method for solubilization of chimeric human interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1) protein in Escherichia coli
Molecular Biology Reports (2021)
-
iNOS/NO is required for IRF1 activation in response to liver ischemia-reperfusion in mice
Molecular Medicine (2020)
-
The mechanism of cancer drug addiction in ALK-positive T-Cell lymphoma
Oncogene (2020)
-
Recombinant human interferon regulatory factor-1 (IRF-1) protein expression and solubilisation study in Escherichia coli
Molecular Biology Reports (2018)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.