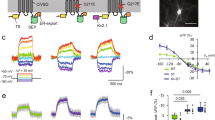
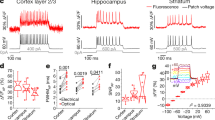
Abstract
THE primary function of the nerve cell is to process electrical signals. Over the past fifteen years1 there has been renewed interest in the detailed spatial analysis of signalling in individual neurons owing to experimental evidence that the regional electrical properties of neurons are complex. Thus the behaviour of many nerve cells cannot be understood on the basis of microelectrode measurements from the soma. Regional electrical properties of neurons have been studied using sharp microelectrode1 and patch-electrode2,3 recordings from neuronal processes, high-resolution multisite optical recordings of Ca2+ concentration changes4,5, and by using models to predict the distribution of membrane potential in the entire neuronal arborization6. Additional direct evidence about electrical signalling in neuronal processes in situ can now be obtained by recording membrane potential changes using voltage-sensitive dyes7,21. Here I demonstrate the existence of multiple action potential trigger zones in separate regions of the neuronal arborization of an identified molluscan neuron.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Llinas, R. & Sugimori, M. J. Physiol. 305, 197–213 (1980).
Stuart, G. J. & Sakmann, B. Nature 367, 69–72 (1994).
Stuart, G. J. & Häusser, M. Neuron 13, 703–712 (1994).
Ross, W. N. et al. Jap. J. Physiol. 43, S83–S89 (1993).
Eilers, J., Augustine, G. J. & Konnerth, A. Nature 373, 155–158 (1994).
Traub, R. D., Jefferys, J. G. R., Miles, R., Whittington, M. A. & Tóth, K. J. Physiol. 481, 79–95 (1994).
Antić, S. & Zečević, D. J. Neurosci. 15, 1392–1405 (1995).
Kandel, E. R. & Tauc, L. J. Physiol. 183, 269–286 (1965).
Tauc, L. J. gen. Physiol. 45, 1077–1097 (1962).
Tauc, L. & Hughes, G. H. J. gen. Physiol. 46, 533–549 (1963).
Korn, H. & Bennett, M. V. L. Brain Res. 27, 169–175 (1971).
Heitler, W. & Goodman, C. S. J. exp. Biol. 76, 63–84 (1978).
Combes, D., Simmers, J., Nonnotte, L. & Moulins, M. J. Physiol. 460, 581–602 (1993).
Huguenard, J. R., Joerges, J., Mainen, Z. F. & Sejnowski, T. J. Soc. Neurosci. abstr. 20, 1527 (1994).
Ross, W. N. & Krauthamer, V. J. Neurosci. 4, 659–672 (1984).
Midtgaard, J., Lasser-Ross, N. & Ross, W. N. J. Neurophysiol. 70, 2455–2469 (1993).
Regehr, W. G., Kehoe, J. S., Ascher, P. & Armstrong, C. Neuron 11, 145–151 (1993).
Cohen, L. B. & Salzberg, B. Rev. Physiol. biochem. Pharmac. 83, 35–88 (1978).
Wu, J. Y. & Cohen, L. B. in Fluorescent and Luminescent Probes for Biological Activity (ed. Mason, W. T.) 389–404 (Academic, New York, 1993).
Zečević, D. et al. J. Neurosci. 9, 3681–3689 (1989).
Grinvald, A., Salzberg, B. M., Lev-Ram, V. & Hildesheim, R. Biophys. J. 51, 643–651 (1987).
Grinvald, A., Lieke, E. E., Frostig, R. D. & Hildesheim, R. J. Neurosci. 14, 2545–2568 (1994).
Kogan, A., Ross, W., Zečević, D. & Lasser-Ross, N. Brain Res. 700, 235–239 (1995).
Gupta, R. K. et al. J. Membr. Biol. 58, 23–137 (1981).
Cohen, L. B. & Lesher, S. Soc. gen. Physiol. ser. 40, 71–99 (1986).
Salzberg, B. M., Obaid, A. L. & Bezanilla, F. Jap. J. Physiol. 43, S37–S41 (1993).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zec̆ević, D. Multiple spike-initiation zones in single neurons revealed by voltage-sensitive dyes. Nature 381, 322–325 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1038/381322a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/381322a0
This article is cited by
-
Spatio-temporal parameters for optical probing of neuronal activity
Biophysical Reviews (2021)
-
Dendritic sodium spikes endow neurons with inverse firing rate response to correlated synaptic activity
Journal of Computational Neuroscience (2018)
-
Electrical behaviour of dendritic spines as revealed by voltage imaging
Nature Communications (2015)
-
Evaluation of Voltage-Sensitive Fluorescence Dyes for Monitoring Neuronal Activity in the Embryonic Central Nervous System
The Journal of Membrane Biology (2013)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.