Abstract
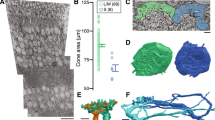
VISUAL acuity depends on the fine-grained neural image set by the foveal cone mosaic1–3. To preserve this spatial detail, cones transmit through non-divergent pathways: cone → midget bipolar cell → midget ganglion cell. Adequate gain must be established along each pathway; crosstalk and sources of variation between pathways must be minimized. These requirements raise fundamental questions regarding the synaptic connections: (1) how many synapses from bipolar to ganglion cell transmit a cone signal and with what degree of crosstalk between adjacent pathways; (2) how accurately these connections are reproduced across the mosaic; and (3) whether the midget circuits for middle (M) and long (L) wavelength sensitive cones are the same. We report here that the midget ganglion cell collects without crosstalk either 28 ±4 or 47 ± 3 midget bipolar synapses. Two cone types are defined by this difference; being about equal in number and distributing randomly in small clusters of like type, they are probably M and L.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Williams, D. R. Trends Neurosci. 9, 193–198 (1986).
DeValois, R. L., Morgan, H. & Snodderly, D. M. Vis. Res. 14, 75–81 (1974).
Merigan, W. H. & Katz, L. M. Vis. Res. 30, 985–991 (1990).
Kolb, H. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 258, 261–283 (1970).
Nelson, R., Famiglietti, E. V. & Kolb, H. J. Neurophysiol. 41, 472–483 (1978).
Dacey, D. & Lee, B. B. Nature 367, 731–735 (1994).
Polyak, S. L. The Retina (Univ. Chicago Press, Chicago, 1941).
Boycott, B. B. & Dowling, J. E. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B 255, 109–184 (1969).
Kolb, H. & Dekorver, L. J. comp. Neurol. 303, 617–636 (1991).
Dowling, J. E. & Boycott, B. B. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 166, 80–111 (1966).
Mendenhall, W., Wackerly, D. D. & Scheaffer, R. L. Mathematical Statistics with Applications 4th edn 708–715 (Duxbury, Belmont, CA, 1990).
Giacomelli, F., Wiener, J., Kruskal, J. B., Pomeranz, J. V. & Loud, A. V. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 19, 426–433 (1971).
Dacey, D. M. & Petersen, M. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 89, 9666–9670 (1992).
McGuire, B. A., Stevens, J. K. & Sterling, P. J. Neurosci. 4, 2920–2938 (1984).
Cohen, E. & Sterling, P. Eur. J. Neurosci. 4, 506–520 (1992).
Anhelt, P., Keri, C. & Kolb, H. J. comp. Neurol. 293, 39–53 (1990).
Wässle, H., Boycott, B. B. & Röhrenbeck, J. Eur. J. Neurosci. 1, 421–435 (1989).
Mollon, J. D. & Bowmaker, J. K. Nature 360, 677–679 (1992).
Klug, K., Tsukamoto, Y., Sterling, P. & Schein, S. J. Soc. for Neurosci. Abstr. 352.5 (Anaheim, CA, 1992).
Klug, K., Tsukamoto, Y., Sterling, P. & Schein, S. J. ARVO Abstr. 1398 (Association for Research in Vision and Ophthalmology, Sarasota, FL, 1993).
Mariani, A. P. Nature 308, 184–186 (1984).
Kouyama, N. & Marshak, D. W. J. Neurosci. 12, 1233–1252 (1992).
Tsukamoto, Y., Masarachia, P., Schein, S. J. & Sterling, P. Vis. Res. 32, 1809–1815 (1992).
Smith, R. G. J. Neurosci. Meth. 21, 55–69 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Calkins, D., Schein, S., Tsukamoto, Y. et al. M and L cones in macaque fovea connect to midget ganglion cells by different numbers of excitatory synapses. Nature 371, 70–72 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/371070a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/371070a0
This article is cited by
-
Primate vision: a single layer perception
Neural Computing and Applications (2021)
-
An S-cone circuit for edge detection in the primate retina
Scientific Reports (2019)
-
The diverse roles of ribbon synapses in sensory neurotransmission
Nature Reviews Neuroscience (2010)
-
Functional connectivity in the retina at the resolution of photoreceptors
Nature (2010)
-
Developmental patterning of glutamatergic synapses onto retinal ganglion cells
Neural Development (2008)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.