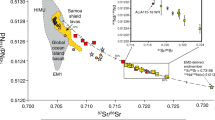
Abstract
AT convergent margins, the subducting oceanic slab is thought to dehydrate, producing fluids which metasomatize the overlying mantle wedge where island-arc magma forms. However, the nature and origin of the metasomatizing fluid, its source composition and its relation to the genesis of the chemical characteristics of arc magmas are largely controversial. Across-arc variation in the chemistry of arc lavas provides a useful key to this problem, because it may reflect the changes in the physical conditions of the subducting slab that control mass transfer from slab to mantle wedge as a function of depth. Here we report clear across-arc variations in the concentrations and isotopic compositions of boronand lead observed in lavas from the Izu arc (Japan). Our data suggest that a homogeneous slab fluid contributes to all Izu volcan-oes, but that the amount of this fluid decreases continuously with increasing depth of the subducting slab. Whereas the Izu slab fluid conies primarily from altered oceanic crust, our data for high-Mg andesites from the Setouchi volcanic belt (a nearby fore-arc) indicate a significant involvement of sediment in the fluid source.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Leeman, W. P. Eos 68, 462 (1987).
Morris, J. D., Leeman, W. P. & Tera, F. Nature 344, 31–36 (1990).
Spivack, A. J., Palmer, M. R. & Edmond, J. M. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 51, 1939–1949 (1987).
Palmer, M. R. Geology 19, 215–217 (1991).
Ishikawa, T. & Nakamura, E. Earth planet Sci. Lett. 117, 567–580 (1993).
Spivack, A. J. & Edmond, J. M. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 51, 1939–1649 (1987).
Ishikawa, T. & Nakamura, E. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 56, 1633–1639 (1992).
Ryan, J. G. & Langmuir, C. H. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 57, 1489–1498 (1993).
Sun, S.-s. & McDonough, W. F. in Magnetism in the Ocean Basins (eds Saunders, A. D. & Norry, M. J.) 313–345 (Geol. Soc. Lond. Spec. Publ. 42, London, 1989).
Leeman, W. P., Smith, D. R., Hildreth, W., Palacz, Z. & Rogers, N. J. geophys. Res. 95, 19561–19682 (1990).
Chaussidon, M. & Albarède, F. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 108, 229–241 (1992).
Green, T. H. J. Volcan. geotherm. Res. 10, 405–422 (1981).
Kelemen, P. B., Johnson, K. T. M., Kinzler, R. J. & Irving, A. J. Nature 345, 521–524 (1990).
Wyllie, P. J. & Sekine, T. Contr. Miner. Petrol. 79, 375–380 (1982).
Tatsumi, Y. J. geophys. Res. 94, 4697–4707 (1989).
Moran, A. E., Sisson, V. B. & Leeman, W. P. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 111, 331–349 (1992).
Bebout, G. E., Ryan, J. G. & Leeman, W. P. Geochim. cosmochim. Acta 57, 2227–2237 (1993).
Nakamura, E., Campbell, I. H. & Sun, S.-s. Nature 316, 55–58 (1985).
Nakamura, E., McCulloch, M. T. & Campbell, I. H. Tectonophysics 174, 207–233 (1990).
Harder, H. in Handbook of Geochemistry Vol. II, Ch. 5 (Springer, Berlin, 1974).
Woodhead, J. D. Chem. Geol. 76, 1–24 (1989).
Tatsumi, Y. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 60, 305–317 (1982).
Tatsumi, Y. & Maruyama, S. in Boninite and Related Rocks (ed. Crawford, A. J.) 50–71 (Unwin Hyman, London, 1989).
Ishizaka, K. & Carlson, R. W. Earth planet. Sci. Lett. 64, 327–340 (1983).
Bebout, G. E. Science 251, 413–416 (1991).
Taira, A., Katto, J., Tashiro, Y., Okamura, M. & Kodama, K. Mod. Geol. 12, 5–46 (1988).
Nakamura, E., Ishikawa, T., Birck, J.-L. & Ailègre, C. J. Chem. Geol. 94, 193–204 (1992).
Koide, Y. & Nakamura, E. Shitsuryobunseki 38, 241–252 (1990).
Goto, A. & Tatsumi, Y. Rigaku J. 22, 28–44 (1991).
Ando, A., Mita, N. & Terashima, S. Geostand. Newsl. 11, 159–166 (1987).
Kasahara, K. Rep. natn. Res. Cent. Disaster Prevention Japan 35, 33–137 (1985).
White, W. M., Hofmann, A. W. & Puchelt, H. J. geophys. Res. 92, 4881–4893 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ishikawa, T., Nakamura, E. Origin of the slab component in arc lavas from across-arc variation of B and Pb isotopes. Nature 370, 205–208 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/370205a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/370205a0
This article is cited by
-
Sources of dehydration fluids underneath the Kamchatka arc
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Boron isotopes in boninites document rapid changes in slab inputs during subduction initiation
Nature Communications (2022)
-
Cl, Br, B, Li, and noble gases isotopes to study the origin and evolution of deep groundwater in sedimentary basins: a review
Environmental Chemistry Letters (2022)
-
Molybdenum isotopes unmask slab dehydration and melting beneath the Mariana arc
Nature Communications (2021)
-
Peridotites, chromitites and diamonds in ophiolites
Nature Reviews Earth & Environment (2021)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.