Abstract
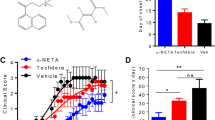
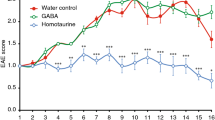
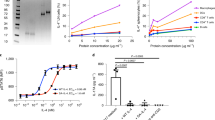
EXPERIMENTAL allergic encephalomyelitis (EAE) is an acute inflammatory autoimmune disease of the central nervous system that can be elicited in rodents and is the major animal model for the study of multiple sclerosis (MS)1,2. The pathogenesis of both EAE and MS directly involves the CD4+ helper T-cell subset3–5. Anti-CD4 monoclonal antibodies inhibit the development of EAE in rodents6–9, and are currently being used in human clinical trials for MS. We report here that similar therapeutic effects can be achieved in mice using a small (rationally designed) synthetic analogue of the CD4 protein surface. It greatly inhibits both clinical incidence and severity of EAE with a single injection, but does so without depletion of the CD4+ subset and without the inherent immunogenicity of an antibody. Furthermore, this analogue is capable of exerting its effects on disease even after the onset of symptoms.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martin, R., McFarland, H. F. & McFarlin, D. A. Rev. Immun. 10, 153–187 (1992).
Hafler, D. A. & Weiner, H. L. Immun. Today 10, 104–107 (1989).
Bernard, C. C. A., Leydon, J. & Mackay, I. R. Eur. J. Immun. 6, 655–660 (1976).
Traugott, U., Reinhertz, E. L. & Raine, C. S. Science 219, 308–310 (1982).
Ben-Nun, A., Wekerle, H. & Cohen, I. R. Eur. J. Immun. 11, 195–199 (1981).
Brostoff, S. W. & Mason, D. W. J. Immun. 133, 1938–1942 (1984).
Waldor, M. K. et al. Science 227, 415–417 (1985).
Sriram, S. & Roberts, C. A. J. Immun. 136, 4464–4469 (1986).
O'Neill, J. K. et al. Neuroimmunology 45, 1–14 (1993).
McDonnell, J. M., Blank, K. J., Rao, E. & Jameson, B. A. J. Immun. 149, 1626–1630 (1992).
McDonnell, J. M., Varnum, J. M., Mayo, K. H. & Jameson, B. A. Immunomethods 1, 33–39 (1992).
DeGrado, W. F. Adv. Prot. Chem. 39, 51–124 (1988).
Pietrzkowski, Z., Wernicke, D., Porcu, P., Jameson, B. A. & Baserga, R. Cancer Res. 52, 6447–6451 (1992).
Su, C. M. et al. Horm. Metab. Res. 23, 15–21 (1991).
Lasdun, A., Resnik, S., Molineaux, C. J. & Orlowski, M. J. Pharm. exp. Therapeutics 251, 439–447 (1989).
Dintzis, H. M., Symer, D. E., Dintzis, R. Z., Zawadzke, L. E. & Berg, J. M. Proteins 16, 306–308 (1993).
Waldman, H. A. Rev. Immun. 7, 407–444 (1989).
Herzog, C. et al. Lancet II, 1461–1462 (1987).
Hafler, D. A., Ritz, J., Schlossman, S. F. & Weiner, H. L. J. Immun. 141, 131–138 (1989).
Chan, E. K. L. & Boyd, N. D. J. immun. Meth. 33, 55–61 (1980).
Jameson, B. A. et al. Science 240, 1335–1339 (1988).
Baglia, F. A., Jameson, B. A. & Walsh, P. N. J. biol. Chem. 268, 3838–3844 (1993).
Korngold, R., Feldman, A., Rorke, L. B., Lublin, F. D. & Doherty, P. C. Immunogenetics 24, 309–315 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jameson, B., McDonnell, J., Marini, J. et al. A rationally designed CD4 analogue inhibits experimental allergic encephalomyelitis. Nature 368, 744–746 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/368744a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/368744a0
This article is cited by
-
Modeling multiple sclerosis in laboratory animals
Seminars in Immunopathology (2009)
-
Treatment of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in rat by 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 leads to early effects within the central nervous system
Acta Neuropathologica (2003)
-
Rational design of cytotoxic T-cell inhibitors
Nature Biotechnology (2000)
-
A structure-based approach to designing synthetic CD8α peptides that can inhibit cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses
Nature Medicine (1998)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.