Abstract
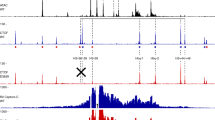
Immunoglobulin heavy-chain gene promoters contain two conserved upstream sequence elements, octamer and heptamer1–4, both of which are required for normal cell type-specific promoter function in vivo4–6. The octamer sequence motif 5′-ATGCAAAT-3′, and its precise inverse, are strongly conserved in heavy- and light-chain gene promoters1,2 and are important determinants for the lymphoid-specific function of these promoters7–9 and of the heavy-chain enhancer10,11. The heptameric sequence element with the consensus 5′-CTCATGA-3′ (refs 3 and 4) is also required in addition to the octamer for full lymphoid-specific activity of heavy-chain promoters4,6. Although these two elements have no sequence similarity, they are both recognized in vitro12 by the ubiquitous octamer transcription factor OTF-1 (reviewed in refs 13 and 14) and the lymphoid-specific OTF-2 (reviewed in refs 15 and 16). Here we show that purified OTF-2 binds cooperatively to the immunoglobulin heptamer and octamer elements so that interaction with the octamer element facilitates binding of OTF-2 to the heptamer motif. More important, cooperativity in OTF-2 binding is closely mirrored by functional cooperation between the heptamer and octamer elements in activating transcription from the heavy-chain promoter in vitro.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Falkner, F. G. & Zachau, H. G. Nature 310, 71–74 (1984).
Parslow, T. G., Blair, D. L., Murphy, W. J. & Granner, D. K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 2650–2654 (1984).
Siu, G., Springer, E. A., Huang, H. V., Hood, L. E. & Crews, S. T. J. Immun. 138, 4466–4471 (1987).
Eaton, S. & Calame, K. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 84, 7634–7638 (1987).
Mason, J. O., Williams, G. T. & Neuberger, M. S. Cell 41, 479–487 (1985).
Ballard, D. W. & Bothwell, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 9626–9630 (1986).
Mizushima-Sugano, J. & Roeder, R. G. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 8511–8515 (1986).
Dreyfus, M., Doyen, N. & Rougeon, F. EMBO J. 6, 1685–1690 (1987).
Wirth, T., Slaudt, L. & Baltimore, D. Nature 329, 174–178 (1987).
Gerster, T., Matthias, P., Thali, M., Jiricny, J. & Schaffner, W. EMBO J. 6, 1323–1330 (1987).
Lenardo, M., Pierce, J. W. & Baltimore, D. Science 236, 1573–1577 (1987).
Poellinger, L. & Roeder, R. G. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 747–756 (1989).
Fletcher, C., Heintz, N. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 51, 773–781 (1987).
O'Neill, E. A. et al. Science 241, 1210–1213 (1988).
Scheidereit, C., Heguy, A. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 51, 783–793 (1987).
Scheidereit, C. et al. Nature 336, 551–557 (1988).
Landolfi, N. F., Capra, D. J. & Tucker, P. W. Nature 323, 548–551 (1986).
Staudt, L. M. et al. Nature 323, 640–643 (1986).
Ko, H.-S., Fast, P., McBride, W. & Staudt, L. M. Cell 55, 135–144 (1988).
Weinberger, J., Baltimore, D. & Sharp, P. A. Nature 322, 846–848 (1986).
Westin, G., Gerster, T., Muller, M., Schaffner, G. & Schaffner, W. Nucleic Acids Res. 15, 6787–6798 (1987).
LeBowitz, J. H., Kobayashi, T., Staudt, L., Baltimore, D. & Sharp, P. A. Genes Dev. 2, 1227–1237 (1988).
Hochschild, A. & Ptashne, M. Cell 44, 681–687 (1986).
Robertson, M. Nature 327, 464–466 (1987).
Ptashne, M. Nature 335, 683–689 (1988).
Horikoshi, M., Carey, M. F., Kakidani, H. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 54, 665–669 (1988).
Van Dyke, M., Roeder, R. G. & Sawadogo, M. Science 241, 1335–1338 (1988).
Horikoshi, M., Hai, T., Lin, Y.-S., Green, M. & Roeder, R. G. Cell 54, 1033–1042 (1988).
Landschulz, W. H., Johnson, P. F. & McKnight, S. L. Science 240, 1759–1764 (1988).
Robertson, M. Nature 336, 522–524 (1988).
Dignam, J. D., Lebovitz, R. M. & Roeder, R. G. Nucleic Acids Res 11, 1475–1489 (1983).
Weaver, R. F. & Weissman, C. Nucleic Acids. Res. 7, 1175–1193 (1979).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 74, 560–564 (1977).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poellinger, L., Yoza, B. & Roeder, R. Functional cooperativity between protein molecules bound at two distinct sequence elements of the immunoglobulin heavy-chain promoter. Nature 337, 573–576 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/337573a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/337573a0
This article is cited by
-
Lorenz Poellinger MD, PhD (1957–2016)
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)
-
The immunoglobulin heavy chain VH6-1 promoter regulates Ig transcription in non-B cells
Cancer Cell International (2014)
-
Distinct regulatory mechanism of immunoglobulin gene transcription in epithelial cancer cells
Cellular & Molecular Immunology (2010)
-
Interdependence and nodule specificity of cis-acting regulatory elements in the soybean leghemoglobin lbc 3 and N23 gene promoters
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1990)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.