Abstract
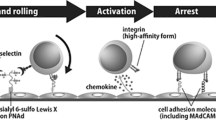
Tissue position-dependent or address-dependent expression of cell adhesion molecules has been proposed to play a part in cellular positioning in a variety of systems, for example during neural development, the metastasis of neoplasms, and the tissue-specific homing of lymphocytes. The extravasation of blood-borne lymphocytes is regulated by interactions with the endothelium of specialised venules, such as the high endothelial venules (HEY) in organized lymph nodes and mucosal lymphoid tissues1–4. At least three separate lymphocyte-HEV recognition systems have been described, one mediating tissue-selective lymphocyte interac-tions with HEV in peripheral lymph nodes, another in mucosal lymphoid organs, and a third in inflamed synovium4–8. We have previously identified a tissue-specific "vascular addressin’ in the mouse which is selectively expressed by venules mediating lym-phocyte-homing into mucosal tissues9. To determine whether this addressin is a specific adhesion molecule for lymphocytes, we have isolated it by monoclonal antibody-affinity chromatography and inserted it into supported phospholipid planar membranes10,11. Lymphocytes bind to membranes containing the addressin, but not to phospholipid bilayers or to control glycophorin-reconstituted membranes. Only those lymphocytes and lymphoma cell lines capable of binding to mucosal HEV adhere well to the isolated addressin; peripheral lymph node HEV-specific or HEV-non-binding cell lines do not bind. Binding is blocked by anti-addressin antibody MECA-367. We conclude that the mucosal vascular addressin is a tissue-specific endothelial cell-adhesion molecule for lymphocytes, and suggest that it could regulate lymphocyte traffic into mucosal tissues by mediating attachment of blood-borne cells to endothelium.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gowans, J. L. & Knight, E. J. Proc. R. Soc. B 159, 257–282 (1964).
Stamper, H. B. Jr & Woodruff, J. J. J. exp. Med. 144, 828–833 (1976).
Butcher, E. C. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immun. 133, 2961–2965 (1986).
Woodruff, J. J., Clarke, L. M. & Chin, Y. H., A. Rev. Immun. 5, 201–222 (1987).
Jalkanen, S. T. et al. Immunol. Rev. 91, 39–60 (1986).
Butcher, E. C., Scollay, R. G. & Weissman, I. L. Eur. J. Immun. 10, 556–561 (1980).
Jalkanen, S. T., Bargatze, R. F., de los Toyos, J. & Butcher, E. C. J. Cell Biol. 105, 983–990 (1987).
Jalkanen, S. T., Steere, A. C., Fox, R. I. & Butcher, E. C. Science 233, 556–558 (1986).
Streeter, P. R., Berg, E. L., Rouse, B. N., Bargatze, R. F. & Butcher, E. C. Nature 331, 41–46 (1988).
McConnell, H. M., Watts, T. H., Weis, R. M. & Brian, A. A. Biochim. biophys. Acta 864, 95–105 (1986).
Brian, A. A. & McConnell, H. M. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 6159–6163 (1984).
Bargatze, R. F., Wu, N. W., Weissman, I. L. & Butcher, E. C. J. exp. Med. 166, 1125–1131 (1987).
Chin, Y. H., Rasmussen, R. A., Woodruff, J. J. & Easton, T. G. J. Immun. 136, 2556–2561 (1986).
Holzman, B., McIntyre, B. U. & Weissman, I. L. Cell (in the press).
Streeter, P. R., Rouse, B. N. & Butcher, E. C. J. Cell. Biol. 107, 1853–1862 (1988).
Bergman, Y., Haimovich, J. & Melchers, F. Eur. J. Immun. 7, 574–579 (1977).
Duijvestijn, A. M., Kerkhove, M., Bargatze, R. F. & Butcher, E. C. J. Immun. 138, 713–719 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakache, M., Lakey Berg, E., Streeter, P. et al. The mucosal vascular addressin is a tissue-specific endothelial cell adhesion molecule for circulating lymphocytes. Nature 337, 179–181 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1038/337179a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/337179a0
This article is cited by
-
Response of swine spleen to Streptococcus suis infection revealed by transcription analysis
BMC Genomics (2010)
-
Differentiation and homing of IgA-secreting cells
Mucosal Immunology (2008)
-
Inflammatory cytokines induce MAdCAM-1 in murine hepatic endothelial cells and mediate alpha-4 beta-7 integrin dependent lymphocyte endothelial adhesion In Vitro
BMC Physiology (2007)
-
Homing of human autoreactive T cells into pancreatic tissue of NOD-scid mice
Diabetologia (2005)
-
Lymphocyte trafficking across high endothelial venules: dogmas and enigmas
Nature Reviews Immunology (2004)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.