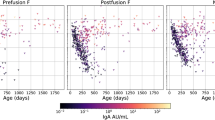
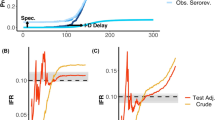
Abstract
A recent seroprevalence study of newborns indicates that one in 62 children born in New York City has antibodies to the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)1. The distribution of incubation periods for paediatric patients is needed to estimate future AIDS case loads from these seroprevalence data. Current estimates of incubation periods for paediatric patients are based on limited data2–5. We use parametric5,6 and non-parametric7,8 methods to analyse incubation periods for 215 paediatric patients with AIDS whose only known route of infection is maternal. We conclude that incubation periods are longer than previously reported9; that there is a distinct knee in the incubation period distribution at seven months which suggests two risk populations; and that there is an increase in incidence which is consistent with exponential growth.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aids in New York State (New York State Department of Health, 1988).
Medley, G. F., Anderson, R. M., Cox, D. R. & Billard, L. Nature 328, 719–721 (1987).
Medley, G. F., Billard, L., Cox, D. R. & Anderson, R. M. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. B 233, 367–377 (1988).
Kalbfleisch, J. D. & Lawless, J. F. Nature 333, 504–505 (1988).
Lui, K., Peterman, T. A., Lawrence, D. N. & Allen, J. M. Statistics in Medicine 7, 395–401 (1988).
Lui, K. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 83, 3051–3055 (1986).
Lagakos, S., Barraj, L. M. & De Gruttola, V. Biometrika 75, 515–523 (1988).
Turnbull, B. W. J. R. Statist. Soc. B 83, 290–295 (1976).
Rogers, M. F. et al. Pediatrics 79, 1008–1014 (1987).
AIDS Reporting System, (Center for Disease Control).
Mortality and Morbitity Weekly Report (Center for Disease Control) 34, 373–375 (1985).
Thomas, P., O'Donnell, R., Williams, R. & Chiasson, M. A. New Engl. J. Med. 319, 374 (1988).
Mortality and Morbitity Weekly Report (Center for Disease Control) 36, (suppl S-6), 1–48 (1987).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Auger, I., Thomas, P., De Gruttola, V. et al. Incubation periods for paediatric AIDS patients. Nature 336, 575–577 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1038/336575a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/336575a0
This article is cited by
-
HIV-1 co-receptor usage:influence on mother-to-child transmission and pediatric infection
Journal of Translational Medicine (2011)
-
Characterization of HIV-1 subtype C envelope glycoproteins from perinatally infected children with different courses of disease
Retrovirology (2006)
-
The dynamics of CD4+ T-cell depletion in HIV disease
Nature (2001)
-
Breast-feeding and human immunodeficiency virus
The Indian Journal of Pediatrics (1997)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.