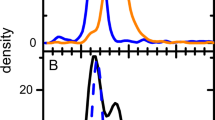
Abstract
Accurate adenovirus (Ad) quantification requires labor- and time-intensive viral stock purification. While crude viral lysates can be titered by plaque assay, this cell-based assay is neither rapid nor accurate. Consequently, a method for quantification of crude, unpurified viral culture lysates is needed. Given growing interest in alternative Ad serotypes (different from well-studied and characterized serotype Ad5) for basic research and for therapeutic applications, such a method should also apply to alternative serotypes. Using a Q Sepharose XL (QSXL) column-based method, we describe a robust quantification method resulting in efficient retention of viral particles of all serotypes, while non-viral components of crude infected cultures remain largely in the flow-through. The high-performance liquid chromatography-QSXL method allows rapid, accurate adenoviral quantification in crude lysates as well as identification of the various serotypes present in mixed-serotype crude lysates. We also report on conditions that efficiently strip and regenerate the column, extending its functional life.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ad:
-
adenovirus
- FBS:
-
fetal bovine serum
- HPLC:
-
high-performance liquid chromatography
- QSXL:
-
Q Sepharose XL
References
Shabram PW, Giroux DD, Goudreau AM, Gregory RJ, Horn MT, Huyghe BG et al. Analytical anion-exchange HPLC of recombinant type-5 adenoviral particles. Hum Gene Ther 1997; 8: 453–465.
Blanche F, Cameron B, Barbot A, Ferrero L, Guillemin T, Guyot S et al. An improved anion-exchange HPLC method for the detection and purification of adenoviral particles. Gene Therapy 2000; 7: 1055–1062.
Tollefson AE, Hermiston T, Wold WSM . Preparation and Titration of Cesium Chloride Banded Adenovirus Stock. Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 1999.
Lehmberg E, Traina JA, Chakel JA, Chang RJ, Parkman M, McCaman MT et al. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic assay for the adenovirus type 5 proteome. J Chromatogr B 1999; 732: 411–423.
Maizel Jr JV, White DO, Scharff MD . The polypeptides of adenovirus. II. Soluble proteins, cores, top components and the structure of the virion. Virology 1968; 36: 126–136.
Maizel Jr JV, White DO, Scharff MD . The polypeptides of adenovirus. I. Evidence for multiple protein components in the virion and a comparison of types 2, 7A, and 12. Virology 1968; 36: 115–125.
Acknowledgements
We thank Drs Richard Harkins and Elisabeth Lehmberg for helpful scientific discussions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuhn, I., Larsen, B., Gross, C. et al. High-performance liquid chromatography method for rapid assessment of viral particle number in crude adenoviral lysates of mixed serotype. Gene Ther 14, 180–184 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302851
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302851
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Identification and analysis of green corrosion inhibitors in pomegranate peel extracts: a theoretical and experimental study
Chemical Papers (2023)
-
Considerations for bioanalytical characterization and batch release of COVID-19 vaccines
npj Vaccines (2021)
-
In vitro analysis of cidofovir and genetically engineered TK expression as potential approaches for the intervention of ColoAd1-based treatment of cancer
Gene Therapy (2009)