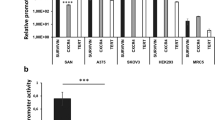
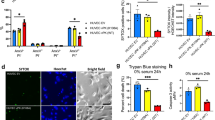
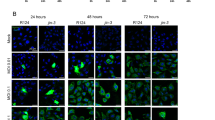
Abstract
The ability of viruses to selectively target, replicate within, and destroy tumour cells without deleterious effects in normal cells (oncolysis), makes the use of viruses as an attractive tool for cancer treatment. Pancreatic adenocarcinoma, being insensitive to traditional therapy and having a rather poor prognosis, represents a suitable target to evaluate viral oncolysis as a novel therapeutic approach. Herpes simplex virus (HSV) has been reported to produce an oncolytic effect in cells overexpressing Ras. As Ras signalling is frequently aberrant in pancreatic cancer, we compared four pancreatic cell lines (which differ in the presence of mutated or wild-type ras) for their ability to support growth of γ34.5-replication attenuated HSV-1 (R3616). Our data show that permissiveness to viral replication is neither associated with enhanced Ras signalling nor with defective PKR activity. By contrast, we provide evidence that disregulation of the PI 3-kinase signalling pathway allows conditionally replication-defective R3616 virus to overcome the cellular antiviral activity.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yoshida T, Ohnami S, Aoki K . Development of gene therapy to target pancreatic cancer. Cancer Sci 2004; 95: 283–289.
Hecht JR, Bedford R, Abbruzzese JL, Lahoti S, Reid TR, Soetikno RM et al. A phase I/II trial of intratumoral endoscopic ultrasound injection of ONYX-015 with intravenous gemcitabine in unresectable pancreatic carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res 2003; 9: 555–561.
Liu TC, Kirn D . Viruses with deletions in antiapoptotic genes as potential oncolytic agents. Oncogene 2005; 24: 6069–6079.
Clemens MJ, Elia A . The double-stranded RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR: structure and function. J Interferon Cytokine Res 1997; 17: 503–524.
Whitley RJ . Herpes simplex viruses. In: Knipe DM, Howley PM (eds). Fields Virology. Lippincott: Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia, 2001, pp 2461–2509.
He B, Gross M, Roizman B . The gamma(1)34.5 protein of herpes simplex virus 1 complexes with protein phosphatase 1 alpha to dephosphorylate the alpha subunit of the eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 and preclude the shutoff of protein synthesis by double-stranded RNA-activated protein kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1997; 94: 843–848.
Kirn DH . Replicating oncolytic viruses: an overview. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 1996; 5: 753–762.
Mundschau LJ, Faller DV . Endogenous inhibitors of the dsRNA-dependent eIF-2 alpha protein kinase PKR in normal and ras-transformed cells. Biochimie 1994; 76: 792–800.
Moore PS, Sipos B, Orlandini S, Sorio C, Real FX, Lemoine NR et al. Genetic profile of 22 pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Analysis of K-ras, p53, p16 and DPC4/Smad4. Virchows Arch 2001; 439: 798–802.
Coffey MC, Strong JE, Forsyth PA, Lee PW . Reovirus therapy of tumours with activated Ras pathway. Science 1998; 282: 1332–1334.
Farassati F, Yang AD, Lee PW . Oncogenes in Ras signalling pathway dictate host-cell permissiveness to herpes simplex virus 1. Nat Cell Biol 2001; 3: 745–750.
Almoguera C, Shibata D, Forrester K, Martin J, Arnheim N, Perucho M . Most human carcinomas of the exocrine pancreas contain mutant c-K-ras genes. Cell 1988; 53: 549–554.
Berrozpe G, Schaeffer J, Peinado MA, Real FX, Perucho M . Comparative analysis of mutations in p53 and K-ras genes in pancreatic cancer. Int J Cancer 1994; 58: 185–191.
Brtva TR, Drugan JK, Ghosh S, Terrell RS, Campbell-Burk S, Bell RM et al. Two distinct Raf domains mediate interaction with Ras. J Biol Chem 1995; 270: 9809–9812.
Singh LP, Arorr AR, Wahba AJ . Phosphorylation of the guanine nucleotide exchange factor and eukaryotic initiation factor 2 by casein kinase II regulates guanine nucleotide binding and GDP/GTP exchange. Biochemistry 1994; 33: 9152–9157.
Zhang X, Lin M, van Golen KL, Yoshioka K, Itoh K, Yee D . Multiple signaling pathways are activated during insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) stimulated breast cancer cell migration. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2005; 93: 159–168.
Kleijn M, Scheper GC, Voorma HO, Thomas AA . Regulation of translation initiation factors by signal transduction. Eur J Biochem 1998; 253: 531–544.
Martin KA, Blenis J . Coordinate regulation of translation by the PI 3-kinase and mTOR pathways. Adv Cancer Res 2002; 86: 1–39.
Vlahos CJ, Matter WF, Hui KY, Brown RF . A specific inhibitor of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, 2-(4-morpholinyl)-8-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-4-one (LY294002). J Biol Chem 1994; 269: 5241–5248.
Beretta L, Gingras AC, Svitkin YV, Hall MN, Sonenberg N . Rapamycin blocks the phosphorylation of 4E-BP1 and inhibits cap-dependent initiation of translation. EMBO J 1996; 15: 658–664.
Dudley DT, Pang L, Decker SJ, Bridges AJ, Saltiel AR . A synthetic inhibitor of the mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995; 92: 7686–7689.
Coukos G, Rubin SC, Molnar-Kimber KL . Application of recombinant herpes simplex virus-1 (HSV-1) for the treatment of malignancies outside the central nervous system. Gene Ther Mol Biol 1999; 3: 78–89.
Martuza RL, Malick A, Markert JM, Ruffner KL, Coen DM . Experimental therapy of human glioma by means of a genetically engineered virus mutant. Science 1991; 252: 854–856.
Ellis CA, Clark G . The importance of being K-Ras. Cell Signal 2000; 12: 425–434.
Clemens MJ, Bommer UA . Translational control: the cancer connection. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1999; 31: 1–23.
Hinnebusch AG . Mechanism and regulation of initiator methionyl-tRNA binding to ribosomes. In: Sonenberg N, Hershey JWB, Mathews MB (eds). Translational Control of Gene Expression. Cold Spring Harbor Press: Cold Spring Harbor, New York, 2000, pp 185–243.
Webb BL, Proud CG . Eukaryotic initiation factor 2B (eIF2B). Int J Biochem Cell Biol 1997; 29: 1127–1131.
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N . eIF4 initiation factors: effectors of mRNA recruitment to ribosomes and regulators of translation. Annu Rev Biochem 1999; 68: 913–963.
Kimball SR, Fabian JR, Pavitt GD, Hinnebusch AG, Jefferson LS . Regulation of guanine nucleotide exchange through phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2alpha. Role of the alpha- and delta-subunits of eIF2B. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 12841–12845.
Pap M, Cooper GM . Role of glycogen synthase kinase-3 in the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt cell survival pathway. J Biol Chem 1998; 273: 19929–19932.
Welsh GI, Miller CM, Loughlin AJ, Price NT, Proud CG . Regulation of eukaryotic initiation factor eIF2B: glycogen synthase kinase-3 phosphorylates a conserved serine which undergoes dephosphorylation in response to insulin. FEBS Lett 1998; 421: 125–130.
Mineta T, Rabkin S, Yazaki T, Hunter W, Martuza R . Attenuated multi-mutated herpes simplex virus-1 for the treatment of malignant gliomas. Nat Med 1995; 1: 938–943.
Mineta T, Rabkin S, Martuza R . Treatment of malignant gliomas using ganciclovir-hypersensitive, ribonucleotide reductase-deficient herpes simplex viral mutant. Cancer Res 1994; 54: 3963–3966.
Harland J, Dunn P, Cameron E, Conner J, Brown SM . The herpes simplex virus (HSV) protein ICP34.5 is a virion component that forms a DNA-binding complex with proliferating cell nuclear antigen and HSV replication proteins. J Neurovirol 2003; 9: 477–488.
Chou J, Kern ER, Whitley RJ, Roizman B . Mapping of herpes simplex virus-1 neurovirulence to gamma 134.5, a gene nonessential for growth in culture. Science 1990; 250: 1262–1266.
Killington RA, Powell KL . Growth, assay and purification of herpes viruses. In: BWJ Mahy (ed). Virology: A Practical Approach. IRL Press: Oxford, Washington DC, 1985, pp 207–236.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by AIDS grants from the Istituto Superiore di Sanità (Rome-AIDS Projects no. 40F-57 to GP and 30F.39 to CP), the Fondazione Cassa di Risparmio di Padova e Rovigo, Regione Veneto, MIUR, FIRB and AIRC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarinella, F., Calistri, A., Sette, P. et al. Oncolysis of pancreatic tumour cells by a γ34.5-deleted HSV-1 does not rely upon Ras-activation, but on the PI 3-kinase pathway. Gene Ther 13, 1080–1087 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302770
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3302770
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
A novel fusogenic herpes simplex virus for oncolytic virotherapy of squamous cell carcinoma
Virology Journal (2011)