Abstract
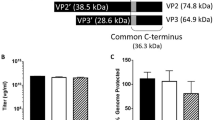
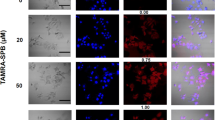
The capsid proteins of adenovirus serotype 5 (Ad5) are key to the virus’ highly efficient cell binding and entry mechanism. In particular, the penton base plays a significant role in both viral internalization and endosome penetration. We have produced an adenovirus penton fusion protein (HerPBK10) containing moieties for DNA transport and targeted delivery to breast cancer cells. HerPBK10 binds DNA through a polylysine appendage, while the EGF-like domain of the heregulin-α1 isoform is used as the targeting ligand. This ligand binds with high affinity to HER2/3 or HER2/4 heterodimers, which are overexpressed on certain aggressive breast cancers. In addition, this ligand is rapidly internalized after binding, thus adding to the utility of heregulin for targeting. HerPBK10 binds MDA-MB-453 breast cancer cells in a receptor-specific manner, and mediates the entry of a reporter plasmid in MDA-MB-453 cells in culture. Delivery can be competed by excess heregulin peptide, thus confirming receptor specificity. Importantly, the penton segment appears to contribute significantly to enhanced delivery. Complexes containing HerPBK10 and DNA have been optimized to provide targeted gene delivery to breast cancer cells in vitro. We demonstrate that delivery can be accomplished in the presence of serum, thus suggesting a potential use for in vivo delivery.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ilan Y et al. Oral tolerization to adenoviral antigens permits long-term gene expression using recombinant adenoviral vectors J Clin Invest 1997 99: 1098–1106
Yang Y, Ertl HC, Wilson JM . MHC class I-restricted cytotoxic T lymphocytes to viral antigens destroy hepatocytes in mice infected with E1-deleted recombinant adenoviruses Immunity 1994 1: 433–442
Kozarsky KF, Wilson JM . Gene therapy: adenovirus vectors Curr Opin Genet Dev 1993 3: 499–503
Greber UF, Willets M, Webster P, Helenius A . Stepwise dismantling of adenovirus 2 during entry into cells Cell 1993 75: 477–486
Bergelson JM et al. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5 Science 1997 275: 1320–1323
Wickham TJ, Mathias P, Cheresh DA, Nemerow GR . Integrins αvβ3 and αvβ5 promote adenovirus internalization but not virus attachment Cell 1993 73: 309–319
Seth P et al. Evidence that the penton base of adenovirus is involved in potentiation of toxicity of Pseudomonas exotoxin conjugated to epidermal growth factor Molec Cell Biol 1984 4: 1528–1533
Karayan L et al. Structural and functional determinants in adenovirus type 2 penton base recombinant protein J Virol 1997 71: 8678–8689
Fominaya J, Wels W . Target cell-specific DNA transfer mediated by a chimeric multidomain protein. Novel non-viral gene delivery system J Biol Chem 1996 271: 10560–10568
Gottschalk S et al. A novel DNA-peptide complex for efficient gene transfer and expression in mammalian cells Gene Therapy 1996 3: 48–57
Fisher KJ, Wilson JM . The transmembrane domain of diphtheria toxin improves molecular conjugate gene transfer Biochem J 1997 321: 49–58
Medina-Kauwe LK, Kasahara N, Kedes L . 3PO, a novel non-viral gene delivery system using engineered Ad5 penton proteins Gene Therapy 2001 8: 795–803
Bacus SS, Zelnick CR, Plowman G, Yarden Y . Expression of the erbB-2 family of growth factor receptors and their ligands in breast cancers. Implication for tumor biology and clinical behavior Am J Clin Pathol 1994 102: S13–S24
Bacus SS, Zelnick CR, Plowman G, Yarden Y . Expression of the erbB-2 family of growth factor receptors and their ligands in breast cancers. Implication for tumor biology and clinical behavior
Bacus SS, Zelnick CR, Plowman G, Yarden Y . Expression of the erbB-2 family of growth factor receptors and their ligands in breast cancers. Implication for tumor biology and clinical behavior
Bacus SS, Zelnick CR, Plowman G, Yarden Y . Expression of the erbB-2 family of growth factor receptors and their ligands in breast cancers. Implication for tumor biology and clinical behavior
Goldman R, Levy RB, Peles E, Yarden Y . Heterodimerization of the erbB-1 and erbB-2 receptors in human breast carcinoma cells: a mechanism for receptor transregulation Biochemistry 1990 29: 11024–11028
Hung MC et al. HER-2/neu-targeting gene therapy - a review Gene 1995 159: 65–71
Press MF et al. HER-2/neu oncogene amplification and expression in breast and ovarian cancers Prog Clin Biol Res 1990 354A: 209–221
Slamon DJ et al. Human breast cancer: correlation of relapse and survival with amplification of the HER-2/neu oncogene Science 1987 235: 177–182
Slamon DJ, Clark GM . Amplification of c-erbB-2 and aggressive human breast tumors? Science 1988 240: 1795–1798
Yarden Y, Weinberg RA . Experimental approaches to hypothetical hormones: detection of a candidate ligand of the neu protooncogene Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 3179–3183
Holmes WE et al. Identification of heregulin, a specific activator of p185erbB2 Science 1992 256: 1205–1210
Lenferink AE et al. Differential endocytic routing of homo- and hetero-dimeric ErbB tyrosine kinases confers signaling superiority to receptor heterodimers EMBO J 1998 17: 3385–3397
Li W et al. Heregulin is rapidly translocated to the nucleus and its transport is correlated with c-myc induction in breast cancer cells Oncogene 1996 12: 2473–2477
Sliwkowski MX et al. Coexpression of erbB2 and erbB3 proteins reconstitutes a high affinity receptor for heregulin J Biol Chem 1994 269: 14661–14665
Tzahar E et al. ErbB-3 and ErbB-4 function as the respective low and high affinity receptors of all Neu differentiation factor/heregulin isoforms J Biol Chem 1994 269: 25226–25233
Waterman H, Sabanai I, Geiger B, Yarden Y . Alternative intracellular routing of ErbB receptors may determine signaling potency J Biol Chem 1998 273: 13819–13827
Medina-Kauwe LK, Leung V, Wu L, Kedes L . Assessing the binding and endocytosis activity of cellular receptors using GFP-ligand fusions BioTechniques 2000 29: 602–609
Harris CE et al. Receptor-mediated gene transfer to airway epithelial cells in primary culture Am J Resp Cell Molec Biol 1993 9: 441–447
Han X, Kasahara N, Kan YW . Ligand-directed retroviral targeting of human breast cancer cells Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 9747–9751
Gao X, Huang L . Potentiation of cationic liposome-mediated gene delivery by polycations Biochemistry 1996 35: 1027–1036
Fominaya J, Uherek C, Wels W . A chimeric fusion protein containing transforming growth factor-α mediates gene transfer via binding to the EGF receptor Gene Therapy 1998 5: 521–530
Uherek C, Fominaya J, Wels W . A modular DNA carrier protein based on the structure of diphtheria toxin mediates target cell-specific gene delivery J Biol Chem 1998 273: 8835–8841
Fender P et al. Adenovirus dodecahedron, a new vector for human gene transfer Nature Biotechnol 1997 15: 52–56
Prchla E et al. Virus-mediated release of endosomal content in vitro: different behavior of adenovirus and rhinovirus serotype 2 J Cell Biol 1995 131: 111–123
O'Keefe DO et al. pH-dependent insertion of proteins into membranes: B-chain mutation of diphtheria toxin that inhibits membrane translocation, Glu-349-Lys Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1992 89: 6202–6206
Wickham TJ, Filardo EJ, Cheresh DA, Nemerow GR . Integrin alpha v beta 5 selectively promotes adenovirus mediated cell membrane permeabilization J Cell Biol 1994 127: 257–264
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the following people for ongoing discussions and support: Xinhua Chen, Gene Chung, Yasuo Hamamori, John Hwang, Tatsuya Iso, Kimi Kong, Vivian Leung, Jochen Muller-Ehmsen, Alex Oxyzoglou, Coralie Poizat, Tsuyoshi Sakoda, Vittorio Sartorelli, Terry Saluna, David Tinsley and Hung-Yi Wu. Grants to LHK from the Susan G Komen Breast Cancer foundation, the Department of Defense, and the National Institutes of Health (CA59318-07) and a fellowship to LKM-K from the National Institutes of Health (HL09638-02) supported this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Medina-Kauwe, L., Maguire, M., Kasahara, N. et al. Nonviral gene delivery to human breast cancer cells by targeted Ad5 penton proteins. Gene Ther 8, 1753–1761 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301583
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301583
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Structure prediction and validation of an affibody engineered for cell-specific nucleic acid targeting
Systems and Synthetic Biology (2010)
-
Intelligent Biosynthetic Nanobiomaterials (IBNs) for Hyperthermic Gene Delivery
Pharmaceutical Research (2008)
-
Specific Delivery of Corroles to Cells via Noncovalent Conjugates with Viral Proteins
Pharmaceutical Research (2006)
-
Intracellular trafficking of nonviral vectors
Gene Therapy (2005)
-
The Ad5 fiber mediates nonviral gene transfer in the absence of the whole virus, utilizing a novel cell entry pathway
Gene Therapy (2005)