Abstract
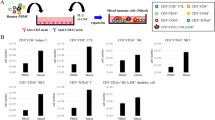
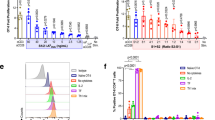
We have developed a culture method for the foreign serum-free generation of highly immunostimulatory, CD83+ human dendritic cells (DC). In this study, we evaluated the feasibility and consequences of endogenously expressing antigens in mature DC using adenoviral vectors. Transduction of DC with Ad-EGFP demonstrated endogenous fluorescence in 50–85% of CD83+ DC. Ad-transduced DC stimulated the proliferation of allogeneic CD8+ and CD4+ T cells at low DC: T cell ratios. However, at high DC: T cell ratios the stimulatory capacity of Ad-transduced DC was suppressed. This immunosuppressive effect was confirmed by demonstrating that the stimulatory function of untreated DC could be suppressed in a dose-dependent manner by addition of Ad-transduced DC. Furthermore, transwell experiments suggested that direct cell contact was required. Taken together, our results demonstrate the feasibility of efficiently expressing antigens in CD83+ DC using adenoviruses. However, immunosuppressive effects must be considered and carefully studied before Ad-transduced DC are employed for clinical trials.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banchereau J, Steinman RM . Dendritic cells and the control of immunity Nature 1998 392: 245–252
Romani N et al. Generation of mature dendritic cells from human blood. An improved method with special regard to clinical applicability J Immunol Meth 1996 196: 137–151
Jonuleit H et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and prostaglandins induce maturation of potent immunostimulatory dendritic cells under fetal calf serum-free conditions Eur J Immunol 1997 27: 3135–3142
Schuler G, Steinman RM . Dendritic cells as adjuvants for immune-mediated resistance to tumors J Exp Med 1997 186: 1183–1187
van Elsas A et al. Peptide-pulsed dendritic cells induce tumoricidal cytotoxic T lymphocytes from healthy donors against stably HLA-A*0201-binding peptides from the Melan-A/MART-1 self antigen Eur J Immunol 1996 26: 1683–1689
Nestle FO et al. Vaccination of melanoma patients with peptide- or tumor lysate-pulsed dendritic cells Nature Med 1998 4: 328–332
Tüting T, DeLeo AB, Lotze MT, Storkus WJ . Genetically modified bone marrow-derived dendritic cells expressing tumor-associated viral or ‘self’ antigens induce antitumor immunity in vivo Eur J Immunol 1997 27: 2702–2707
Specht JM et al. Dendritic cells retrovirally transduced with a model antigen gene are therapeutically effective against established pulmonary metastases J Exp Med 1997 186: 1213–1221
Song W et al. Dendritic cells genetically modified with an adenovirus vector encoding the cDNA for a model antigen induce protective and therapeutic antitumor immunity J Exp Med 1997 186: 1247–1256
Wan Y et al. Dendritic cells transduced with an adenoviral vector encoding a model tumor-associated antigen for tumor vaccination Hum Gene Ther 1997 8: 1355–1363
Gong J et al. Induction of antigen-specific antitumor immunity with adenovirus-transduced dendritic cells Gene Therapy 1997 4: 1023–1028
Perez-Diez A et al. Generation of CD8+ and CD4+ T-cell response to dendritic cells genetically engineered to express the MART-1/Melan-A gene Cancer Res 1998 58: 5305–5309
De Veerman M et al. Retrovirally transduced bone marrow-derived dendritic cells require CD4+ T cell help to elicit protective and therapeutic antitumor immunity J Immunol 1999 162: 144–151
Arthur JF et al. A comparison of gene transfer methods in human dendritic cells Cancer Gene Ther 1997 4: 17–25
Labeur MS et al. Generation of tumor immunity by bone marrow-derived dendritic cells correlates with dendritic cell maturation stage J Immunol 1999 162: 168–175
Mackey MF et al. Dendritic cells require maturation via CD40 to generate protective antitumor immunity J Immunol 1998 161: 2094–2098
Brossart P et al. Generation of functional human dendritic cells from adherent peripheral blood monocytes by CD40 ligation in the absence of granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor Blood 1998 92: 4238–4247
Tillman BW et al. Maturation of dendritic cells accompanies high-efficiency gene transfer by a CD40-targeted adenoviral vector J Immunol 1999 162: 6378–6383
Diao J et al. Human PBMC-derived dendritic cells transduced with adenovirus vector induce cytotoxic T-lymphocyte responses against vector-encoded antigen in vitro Gene Therapy 1999 6: 845–849
Hardy S et al. Construction of adenovirus vectors through Cre–lox recombination J Virol 1997 71: 1842–1849
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by grants No. SFB-432 (to AE) and Tu90/2-1 (to TT) from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jonuleit, H., Tüting, T., Steitz, J. et al. Efficient transduction of mature CD83+ dendritic cells using recombinant adenovirus suppressed T cell stimulatory capacity. Gene Ther 7, 249–254 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301077
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3301077
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Comparative Analysis of Transduced Primary Human Dendritic Cells Generated by the Use of Three Different Lentiviral Vector Systems
Molecular Biotechnology (2011)
-
Dendritic Cell Function After Gene Transfer with Adenovirus-calcium Phosphate Co-precipitates
Molecular Therapy (2007)
-
Construction of HA-1-DC nucleic-acid vaccine and induction of specific cytotoxic T lymphocytes
Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (2007)
-
Efficient transfer of PSA and PSMA cDNAs into DCs generates antibody and T cell antitumor responses in vivo
Cancer Gene Therapy (2005)
-
Priming of T cells with aAd-transduced DC followed by expansion with peptide-pulsed DC significantly enhances the induction of tumor-specific CD8+ T cells: implications for an efficient vaccination strategy
Gene Therapy (2003)