Abstract
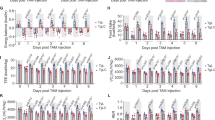
Cancer cachexia, characterized by anorexia, weight loss and progressive tissue wasting, has been postulated to be mediated by various cytokines. However, the precise mechanism of cachexia induction is not fully explained. We have developed synthetic double-stranded oligodeoxynucleotides (ODN) as ‘decoy’ cis-elements that block the binding of nuclear factors to promoter regions of targeted genes, resulting in the inhibition of gene transactivation in vivo as well as in vitro. This novel molecular strategy could be useful for treating a broad range of human diseases including cancer. In this study, we injected decoy ODN targeting the transcriptional factor, NF-kappaB (NFκB) binding cis-elements, which are essential for transactivation of gene expression of cytokines, directly into tumors of adenocarcinoma colon26 in mice, in order to examine whether or not cachexia is alleviated by inhibiting the action of cytokines. Tumor growth was not affected by transfection of NFκB decoy ODN as compared with scrambled decoy ODN. Nevertheless, transfection of NFκB decoy, but not scrambled decoy, ODN resulted in attenuation of the reductions in body weight, epididymal fat, gastrocnemius muscle mass and food intake, which were induced by the tumor presence. Interleukin 6 mRNA in the tumor was also markedly decreased by the transfection of NFκB decoy ODN. It is known that the transcriptional factor E2F plays a pivotal role in the coordinated transactivation of cell cycle regulatory genes. Therefore, we hypothesized that the introduction of synthetic double-stranded DNA with high affinity for E2F in vivo as ‘decoy’ cis-elements might inhibit the tumor growth of colon26, resulting in turn in inhibition of cachexia induction. However, injection of E2F decoy ODN failed to inhibit tumor growth and cachexia induction, as compared with mismatched decoy ODN. Overall, the present study demonstrated that cachexia induced by adenocarcinoma colon26 was inhibited by blocking of NFκB, using a novel molecular decoy strategy, without an effect on tumor growth, and also that tumor growth and cachexia induction in the colon26 model were not affected by E2F decoy ODN. These results suggest that cytokines regulated by NFκB may play a pivotal role in the induction of cachexia by colon26, providing a new therapeutic strategy for cancer cachexia.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 12 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $21.58 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout






Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeWys WD et al. Prognostic effect of weight loss proir to chemotherapy in cancer patients Am J Med 1980 69: 491–497
Curtis EB, Krech R, Walsh TDJ . Common symptoms in patients with advanced cancer Palliat Care 1991 7: 25–29
Kern KA, Norton JA . Cancer cachexia J Parenter Enter Nutr 1988 12: 286–298
Soda K, Kawakami M . Cancer cachexia: pathogenesis and possible role of cytokines Ann Cancer Res Ther 1994 3: 73–81
Espat NJ, Copeland EM, Moldawer LL . Tumour necrosis factor and cachexia: a current perspective Surg Oncol 1994 3: 255–262
Costelli P et al. Tumor necrosis factor-α mediates changes in tissue protein turnover in a rat cancer cachexia model J Clin Invest 1993 92: 2783–2789
Strassmann G, Fong M, Kenney JS, Jacob CO . Evidence for the involvement of interleukin 6 in experimental cancer cachexia J Clin Invest 1992 89: 1681–1684
Matthys P et al. Severe cachexia in mice inoculated with interferon-γ-producing tumor cells Int J Cancer 1991 49: 77–82
Darling G et al. Cachectic effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor in rats Cancer Res 1990 50: 4008–4013
Greenberg AS et al. Interleukin 6 reduces lipoprotein lipase activity in adipose tissue of mice in vivo and in 3T3-L1 adipocytes: a possible role for interleukin 6 in cancer cachexia Cancer Res 1992 52: 4113–4116
Bielinska A, Shivdasani RA, Zhang L, Nabel GJ . Regulation of gene expression with double-stranded phosphorothioate oligonucleotides Science 1990 250: 997–1000
Sullenger BA, Gallardo HF, Ungers GE, Giboa E . Overexpression of TAR sequence renders cells resistant to human immunodeficiency virus replication Cell 1990 63: 601–608
Yamada T et al. In vivo identification of a negative regulatory element in the mouse renin gene using direct gene transfer J Clin Invest 1995 96: 1230–1237
Morishita R et al. A novel molecular strategy using cis-element ‘decoy’ of E2F binding site inhibits smooth muscle proliferation in vivo Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1995 92: 5855–5859
Morishita R et al. Role of transcriptional cis-elements, angiotensinogen gene-activating element, of angiotensinogen gene in blood pressure regulation Hypertension 1996 27: 502–507
Lenardo MJ, Baltimore D . NF-kappa B: a pleitropic mediator of inducible and tissue-specific gene control Cell 1989 58: 227–229
Libermann TA, Baltimore D . Activation of interleukin-6 gene expression through the NF-kappa B transcription factor Mol Cell Biol 1990 10: 2327–2334
Siebenlist U, Franzoso G, Brown K . Structure, regulation and function of NF-κB Annu Rev Cell Biol 1994 10: 405–455
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T . Function and activation of NF-κB in the immune system Annu Rev Immunol 1994 12: 141–179
Neish AS et al. Functional analysis of the human vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 promoter J Exp Med 1992 176: 1583–1593
Brennan DC, Jevnikar AM, Takei F, Reubin-Kelley VE . Mesangial cell accessory functions: mediation by intracellular adhesion molecule-1 Kidney Int 1990 38: 1039–1046
Weinberg RA . E2F and cell proliferation: a world turned upside down Cell 1996 85: 457–459
Pardee AB . A restriction point for control of normal animal cell proliferation Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1994 71: 1286–1290
Jacks T, Weinberg RA . Cell-cycle control and its watchman Nature 1996 381: 713–716
Pearson BE, Nasheuer HP, Wang TSF . Human DNA polymerase α gene: sequences controlling expression in cycling and serum-stimulated cells Mol Cell Biol 1991 11: 2081–2095
Dalton S . Cell cycle regulation of the human cdc2 gene EMBO J 1992 11: 1797–1804
Kim YK, Lee AS . Identification of a 70-base-pair cell cycle regulatory unit within the promoter of the human thymidine kinase gene and its interaction with cellular factors Mol Cell Biol 1991 11: 2296–2302
Hiebert SW, Lipp M, Nevins JR . E1A-dependent trans-activation of the human myc promoter is mediated by the E2F factor Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 1989 86: 3594–3598
Nevins JR . E2F: a link between the Rb tumor suppressor protein and viral oncoproteins Science 1992 258: 424–429
Tanaka Y et al. Experimental cancer cachexia induced by transplantable colon26 adenocarcinoma in mice Cancer Res 1990 50: 2290–2295
Strassmann G, Masui Y, Chizzonite R, Fong MJ . Mechanisms of experimental cancer cachexia: local involvement of IL-1 in colon-26 tumor Immunology 1993 150: 2341–2345
Zhang Y, Lin JX, Vilcek J . Interleukin-6 induction by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin-1 in human fibroblasts involves activation of a nuclear factor binding to a κB-like sequence Mol Cell Biol 1990 10: 3818–3823
Soda K, Kawakami M, Kashii A, Miyata M . Manifestation of cancer cachexia induced by colon26 adenocarcinoma are not fully ascribable to interleukin-6 Int J Cancer 1995 62: 332–336
Yasumoto K et al. Molecular analysis of the cytokine network involved in cachexia in colon 26 adenocarcinoma-bearing mice Cancer Res 1995 55: 921–927
Tomita N et al. In vivo gene therapy of anti-Thy 1 nephritis using E2F decoy oligonucleotides J Am Soc Nephrol 1995 6: 887 (Abstr.)
Morishita R et al. In vivo transfection of cis-element ‘decoy’ against NFκB binding site prevented myocardial infarction as gene therapy Nature Med 1997 3: 894–899
Morishita R et al. Intimal hyperplasia after vascular injury is inhibited by antisense cdk 2 kinase oligonucleotides J Clin Invest 1994 93: 1458–1464
Morishita R et al. Pharmacokinetics of antisense oligonucleotides (cyclin B1 and cdc 2 kinase) in the vessel wall: enhanced therapeutic utility for restenosis by HVJ-liposome method Gene 1994 149: 13–19
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kawamura, I., Morishita, R., Tomita, N. et al. Intratumoral injection of oligonucleotides to the NFκB binding site inhibits cachexia in a mouse tumor model. Gene Ther 6, 91–97 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300819
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.gt.3300819
Keywords
This article is cited by
-
Molecular mechanism of sarcopenia and cachexia: recent research advances
Pflügers Archiv - European Journal of Physiology (2017)
-
Skeletal muscle atrophy: disease-induced mechanisms may mask disuse atrophy
Journal of Muscle Research and Cell Motility (2015)
-
MG132-mediated inhibition of the ubiquitin–proteasome pathway ameliorates cancer cachexia
Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology (2013)
-
Sarcopenia and cachexia: the adaptations of negative regulators of skeletal muscle mass
Journal of Cachexia, Sarcopenia and Muscle (2012)
-
The proteasome inhibitor MG132 reduces immobilization-induced skeletal muscle atrophy in mice
BMC Musculoskeletal Disorders (2011)