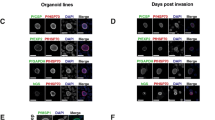
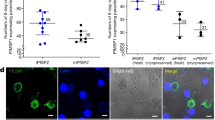
Abstract
The liver phase of development of malaria parasites has been studied only recently and remains poorly understood compared to the other stages such as sporozoïtes, merozoïtes and gametes1,2. Access to liver forms of Plasmodium falciparum has been improved by the development of in vivo3 and in vitro4 propagation methods, but the yield of mature schizonts remains limited and does not allow a detailed antigenic analysis. To date, only immunofluores-cence assays (IFA) have permitted a description of a species and liver-stage-specific antigen(s) (LSA; ref. 3). Monospecific antibodies to these antigens have not been obtained due either to difficulty in immunizing mice (against LSA), or to poor stability of human monoclonal antibodies. Therefore, as a means of characterizing the LSA, we used an alternative immunological approach to identify clones of the corresponding LSA genes. We describe here the isolation of a DNA sequence coding for a P. falciparum liver-stage-specific antigen composed of repeats of 17 amino-acids, which is immunogenic in man.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Miller, L. H., David, P. H. & Hadley, T. J. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B307, 99–115 (1984).
Nussenzweig, V. & Nussenzweig, R. S. Cell 42, 401–403 (1985).
Druilhe, P., Puebla, R. M., Miltgen, F. Perrin, L. & Gentilini, M. Am. J. trop. Med. Hyg. 33, 336–341 (1984).
Mazier, D. et al. Science 227, 440–442 (1985).
Rosario, V. Science 212, 137–138 (1981).
Young, R. A. & Davies, R. W. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1194–1198 (1983).
Ozaki, L. S. et al. J. Immun. Meth. 89, 213–219 (1986).
Messing, J., Crea, R. & Seeburg, P. H. Nucleic Acids Res. 9, 309–321.
Smith, G. E. & Summers, M. D. Analyt. Biochem. 109, 123–129 (1980).
Schwartz, D. C. & Cantor, C. R. Cell 37, 67–65 (1984).
Carle, G. F. & Olson, M. V. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 5647–5664 (1984).
Van der Ploeg, L. H. T. et al. Science 229, 658–661 (1985).
Kemp, D. J. et al. Nature 315, 347–350 (1985).
Sanger, F., Nicklen, S. & Coulson, A. R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A 74, 5463–5674 (1977).
Cowman, A. F. et al. Molec. biol. Med. 2, 207–221 (1984).
Stahl, H. D. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 543–547 (1985).
Kemp, D. J. et al. Parasitology 91, S83–S1O8 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guerin-Marchand, C., Druilhe, P., Galey, B. et al. A liver-stage-specific antigen of Plasmodium falciparum characterized by gene cloning. Nature 329, 164–167 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1038/329164a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/329164a0
This article is cited by
-
In vitro production of infectious Plasmodium falciparum sporozoites
Nature (2022)
-
Strains used in whole organism Plasmodium falciparum vaccine trials differ in genome structure, sequence, and immunogenic potential
Genome Medicine (2020)
-
Development of a high-throughput flexible quantitative suspension array assay for IgG against multiple Plasmodium falciparum antigens
Malaria Journal (2018)
-
Optimization of incubation conditions of Plasmodium falciparum antibody multiplex assays to measure IgG, IgG1–4, IgM and IgE using standard and customized reference pools for sero-epidemiological and vaccine studies
Malaria Journal (2018)
-
Sterile protection against human malaria by chemoattenuated PfSPZ vaccine
Nature (2017)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.