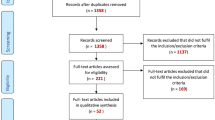
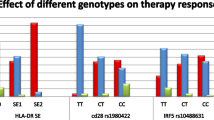
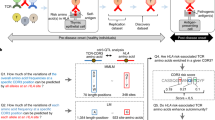
Abstract
Certain class II determinants of the human histocompatibility locus antigens (HLA) have been implicated in the aetiology of several autoimmune diseases, including rheumatoid arthritis (RA) and insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM). HLA-Dw4 was the first HLA determinant found to be significantly increased in RA patients compared with controls1, while Dw4 and Dw3 were found to be significantly increased in IDDM patients2,3. When the HLA-DR system was defined, RA patients were found to have an increased frequency of DR4 and IDDM patients an increased incidence of both DR4 and DR3 (ref. 4) compared with controls. As the HLA-Dw specificities are narrower than the serologically defined DR specificities, it was of specific interest to the present study that Dw4, Dw10, Dw13, Dw14, Dw15 and DKT2 are included in DR4 (ref. 5). We describe here new restriction fragment length polymorphisms (RFLPs) and, together with the newly described serologically defined DQ specificity TA10 (ref. 6), test their prevalence and associations in controls and diseased patients. We find that the newly characterized DNA bands are present at a much higher frequency in RA and IDDM patients than in controls. These findings may lead to a greater understanding of the pathogenesis of such diseases.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Stastny, P. Tissue Antigens 4, 571–579 (1974).
Thomsen, M. et al. Transplant Rev. 22, 120–147 (1985).
Sachs, J. A., Cudworth, A. G., Jaraquemada, D., Gorsuch, A. N. & Festenstein, H. Diabetologia 18, 41–43 (1980).
Batchelor, J. R. & Morris, P. J. in Histocompatibility Testing 1977 (eds Bodmer, W. F. et al.) 205–258 (Munksgaard, Copenhagen, 1977).
Jaraquemada, D. et al. in Histocompatibility Testing 1984 (eds Albert, E. D. et al.) 270–273 (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
Maeda, H. Tissue Antigens 23, 163–170 (1984).
Giles, R. C. & Capra, J. D. Tissue Antigens 25, 57–68 (1985).
Jaraquemada, D., Okoye, R. C., Oilier, W., Awad, J. & Festenstein, H. in Histocompatibility Testing 1984 (eds Albert, E. D. et al) 472–473 (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
Sachs, J. A., Jaraquemada, J. & Festenstein, H. Tissue Antigens 17, 43–56 (1981).
Auffray, C., Kuo, J., Demars, R. & Strominger, J. L. Nature 304, 174–177 (1983).
Trowsdale, J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 1972–1976 (1983).
Hui, K. M. et al. in Histocompatibility Testing 1984 (eds Albert, E. D. et al.) 590–594 (Springer, Berlin, 1984).
Spielman, R. S., Lee, J., Bodmer, W. F., Bodmer, J. G. & Trowsdale, J. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 3461–3465 (1984).
Nepom, B.S. et al. J. exp. Med. (in the press).
Jaraquemada, D. et al. Hum. Immun. (in the press).
Navarrete, C. thesis, Univ. London (1985).
Kim, S.J. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (in the press).
Cohen-Haguenauer, O. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 82, 3335–3339 (1985).
Svejgaard, A., Plaiz, P. & Ryder, L. P. Immun. Rev. 70, 193–218 (1983).
Ollier, W. et al. Tissue Antigens 24, 279–291 (1984).
Jaraquemada, D. et al. Ann. rheum. Dis. (in the press).
Tail, B. D. et al. Tissue Antigens 24, 228–233 (1984).
Grennan, D. M., Sanders, P. A., Dyer, P. A. & Harris, R. Ann. Rheum. (in the press).
Nichol, F. E. & Woodrow, J. C. Lancet i, 220–221 (1981).
Schiff, B., Mizrachi, Y., Orgad, S., Yaron, J. & Gazit, E. Ann. rheum. Dis. 41, 403 (1982).
Duquesnoy, R. J., Marrari, M., Hackbarth, S. & Zeevi, A. Hum. Immun. 10, 165–176 (1984).
Charron, D. J., Lotteau, V. & Turmel, P. Nature 312, 157–159 (1984).
Haldane, J. B. S. Ann. hum. Genet. 20, 309–311 (1955).
Woolf, B. Ann. hum. Genet. 19, 251–253 (1955).
Southern, E. M. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975).
Rigby, P. W. J., Diekmann, M., Rhodes, C. & Berg, P. J. molec. Biol. 113, 237–251 (1977).
Hitman, G.A. et al. Immunogenetics 23, 47–51 (1986).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Festenstein, H., Awad, J., Hitman, G. et al. New HLA DNA polymorphisms associated with autoimmune diseases. Nature 322, 64–67 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/322064a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/322064a0
This article is cited by
-
Identifying genetically driven clinical phenotypes using linear mixed models
Nature Communications (2016)
-
In Finland insulin gene region encoded susceptibility to IDDM exerts maximum effect when there is low HLA-DR associated risk
Diabetologia (1995)
-
Particular HLA-DQ molecules play a dominant role in determining susceptibility or resistance to Type 1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus
Diabetologia (1993)
-
HLA-DR4-DQw8, but not DR4-DQw7 haplotypes occur in Indian patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatology International (1992)
-
High risk of squamous cell carcinoma of the cervix for women with HLA-DQw3
Nature (1991)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.