Abstract
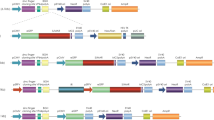
Avian myeloblastosis virus (AMV), like other acute transforming viruses, arose by recombination between its helper virus and host cellular sequences. The latter sequences, termed v-myb, are responsible for the oncogenic properties of the virus. AMY causes acute myeloblastic leukaemia in chickens and transforms a specific class of haematopoietic cells in vitro, but does not induce morphological transformation of cultured fibroblasts, suggesting that only a restricted target-cell population is responsive to its transforming gene product1,2. The normal cellular counterpart of v-myb, c-myb, is highly conserved and is present in all vertebrate and some invertebrate species examined3,4. DNA rearrangements and altered expression of the myb oncogene have been reported in mouse lymphoid tumours5–7 and human myeloid8 and colon tumours9. The mechanism of activation of the cellular proto-oncogenes is thought to involve the structural alteration of the coding regions that result in either the synthesis of an altered gene product or the enhanced expression of a proto-oncogene caused by alterations in its regulatory elements. To distinguish between these two mechanisms, we have cloned and sequenced the chicken c-myb complementary DNA and compared it with that of v-myb sequences. We demonstrate that during the transduction of the cellular sequences and/or viral passage a substantial portion of the coding region of the c-myb gene has been lost from both the 5′ and 3′ ends, resulting in the generation of a truncated gene product that mediates the transforming function of the virus.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baluda, M. A. & Goetz, I. E. J. Virol 15, 185–199 (1961).
Moscovici, C. Curr. Topics Microbiol. Immun. 71, 79–96 (1975).
Franchini, G., Wong-Staal, F., Baluda, M. A., Lengel, C. & Tronick, S. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 7385–7389 (1983).
Katzen, A. L., Kornberg, T. B. & Bishop, J. M. Cell 41, 449–456 (1985).
Mushinski, J. F., Potter, M., Bauer, S. & Reddy, E. P. Science 220, 795–798 (1983).
Shen-Ong, G. L. C., Potter, M., Mushinski, J. F., Lavu, S. & Reddy, E. P. Science 226, 1077–1080 (1984).
Lavu, S., Mushinski, J. F., Shen-Ong, G. L. C., Potter, M. & Reddy, E. P. Cancer Cells 3, 301–306 (1985).
Pelicci, P.-G., Lanfrancone, L., Brathwaite, M. D., Wolman, S. R. & Dalla-Favera, R. Science 224, 1117–1121 (1984).
Alitalo, K. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 4534–4538 (1984).
Kozak, M. Nucleic Acids Res. 12, 857–872 (1984).
Klempnauer, K. H. et al. Cell 33, 345–355 (1983).
Maizel, J. & Leuk, R. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 78, 7665–7669 (1981).
Klempnauer, K. H., Symonds, G., Evans, G. I. & Bishop, J. M. Cell 37, 537–547 (1984).
Boyle, W. J., Lampert, M. A., Lipsick, J. S. & Baluda, M. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 81, 4265–4267 (1984).
Moelling, K. et al. Cell 40, 983–990 (1985).
Gonda, T. J., Gough, N. M., Dunn, A. R. & de Blaquiere, J. EMBO J. 4, 2003–2008 (1985).
Rushlow, K. E. et al. Science 216, 1421–1423 (1982).
Klempnauer, K. H., Gonda, T. J. & Bishop, J. M. Cell 31, 453–463 (1982).
Nunn, M. F., Seeberg, P. H., Moscovici, C. & Duesberg, P. H. Nature 306, 391–395 (1983).
Boyle, W. J., Lipsik, J. S., Reddy, E. P. & Baluda, M. A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 80, 2834–2839 (1983).
Weinstein, Y., Ihle, J. N., Lavu, S. & Reddy, E. P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. (submitted).
Gubler, U. & Hoffmann, B. J. Gene 5, 263–269 (1983).
Maxam, A. M. & Gilbert, W. Meth. Enzym. 65, 499–560 (1980).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosson, D., Reddy, E. Nucleotide sequence of chicken c-myb complementary DNA and implications for myb oncogene activation. Nature 319, 604–606 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1038/319604a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/319604a0
This article is cited by
-
Transformation by v-Myb
Oncogene (1999)
-
Cloning and initial characterization of 14 myb-related cDNAs from tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum cv. Ailsa Craig)
Plant Molecular Biology (1996)
-
Regulation of hematopoietic cell proliferation and differentiation by themyb oncogene family of transcription factors
International Journal of Clinical and Laboratory Research (1996)
-
DNA-binding domain ancestry
Nature (1989)
-
Multiple genes are transcribed in Hordeum vulgare and Zea mays that carry the DNA binding domain of the myb oncoproteins
Molecular and General Genetics MGG (1989)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.